J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2017 May;58(5):611-615. 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.5.611.
A Case of Acute Angle-closure Glaucoma Secondary to Spontaneous Suprachoroidal Hemorrhage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. proector97@gmail.com
- KMID: 2378635
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2017.58.5.611
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report a case of acute angle-closure glaucoma secondary to spontaneous suprachoroidal hemorrhage in a hemodialysis patient.
CASE SUMMARY
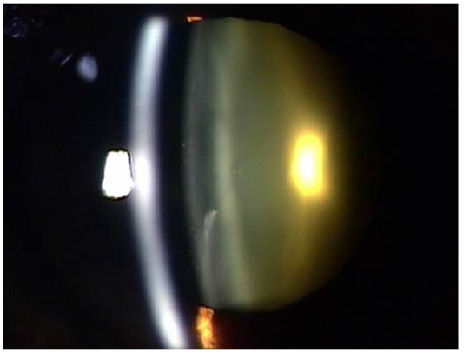
A 71-year-old man visited our clinic after 3 days of vision loss and ocular pain in the right eye. He had been treated with hemodialysis using heparin due to diabetic nephropathy. Visual acuity (VA) was hand motion in the right eye and 0.2 in the left eye. The intraocular pressure (IOP) was 58 mmHg in the right eye and 15 mmHg in the left eye. Gonioscopic examination revealed a closed angle in the right eye. Fundus examination of the right eye showed a massive hemorrhagic retinal detachment and ultrasound sonography revealed a dome-shaped retinal detachment with suprachoroidal hemorrhage in the right eye. The patient was treated with topical aqueous suppressants and cycloplegics. After two weeks of medical treatment, VA in the right eye was still hand motion and IOP was 8 mmHg. Gonioscopic examination showed a wide-open angle in the right eye. During the two-month observation period, VA in the right eye did not recover, however there was no sign of IOP elevation or symptoms of ocular pain.
CONCLUSIONS
Spontaneous suprachoroidal hemorrhage can occur in patients who receive hemodialysis with heparin. This spontaneous suprachoroidal hemorrhage can be subsequently accompanied by acute angle-closure glaucoma. Spontaneous decrease of suprachoroidal hemorrhage, loss of angle-closure, and decline of IOP can be expected by treating with topical aqueous suppressants and cycloplegics.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lakhanpal V. Experimental and clinical observations on massive suprachoroidal hemorrhage. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1993; 91:545–652.2. Ophir A, Pikkel J, Groisman G. Spontaneous expulsive suprachoroidal hemorrhage. Cornea. 2001; 20:893–896.3. Nguyen HN, Nork TM. Massive spontaneous suprachoroidal hemorrhage in a young woman with cystic fibrosis and diabetes mellitus on anticoagulants. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2012; 6:216–218.4. el Baba F, Jarrett WH 2nd, Harbin TS Jr, et al. Massive hemorrhage complicating age-related macular degeneration. Clinicopathologic correlation and role of anticoagulants. Ophthalmology. 1986; 93:1581–1592.5. Yang SS, Fu AD, McDonald HR, et al. Massive spontaneous choroidal hemorrhage. Retina. 2003; 23:139–144.6. Klein R, Myers CE, Lee KE, et al. Small drusen and age-related macular degeneration: The Beaver Dam Eye Study. J Clin Med. 2015; 4:424–440.7. Chak M, Williamson TH. Spontaneous suprachoroidal haemorrhage associated with high myopia and aspirin. Eye (Lond). 2003; 17:525–527.8. Hammam T, Madhavan C. Spontaneous suprachoroidal haemorrhage following a valsalva manoeuvre. Eye (Lond). 2003; 17:261–262.9. Fukuchi T, Suda K, Matsuda H, et al. Secondary acute angle closure with spontaneous suprachoroidal hemorrhage suspected by ultrasound biomicroscopic examination. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2009; 53:661–663.10. Pollack AL, McDonald HR, Ai E, et al. Massive suprachoroidal hemorrhage during pars plana vitrectomy associated with Valsalva maneuver. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 132:383–387.11. Maumenee AE, Schwartz MF. Acute intraoperative choroidal effusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 1985; 100:147–154.12. Beyer CF, Peyman GA, Hill JM. Expulsive choroidal hemorrhage in rabbits. A histopathologic study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1989; 107:1648–1653.13. Tovbin D, Belfair N, Shapira S, et al. High postdialysis urea rebound can predict intradialytic increase in intraocular pressure in dialysis patients with lowered intradialytic hemoconcentration. Nephron. 2002; 90:181–187.14. Tokuyama T, Ikeda T, Sato K. Effect of plasma colloid osmotic pressure on intraocular pressure during haemodialysis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1998; 82:751–753.15. Kang YS, Hwang YH, Kim JS, Lee JH. The effect of hemodialysis on intraocular pressure, retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and corneal thickness. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:1657–1662.16. Lohr JW, Schwab SJ. Minimizing hemorrhagic complications in dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991; 2:961–975.17. Slusher MM, Hamilton RW. Letter: Spontaneous hyphema during hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1975; 293:561.18. Alexandrakis G, Chaudhry NA, Liggett PE, Weitzman M. Spontaneous suprachoroidal hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration presenting as angle-closure glaucoma. Retina. 1998; 18:485–486.19. Chu TG, Green RL. Suprachoroidal hemorrhage. Surv Ophthalmol. 1999; 43:471–486.20. Knopp EA, Chynn KY. Spontaneous expulsive choroidal hemorrhage: CT findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1990; 11:1208–1209.21. Chen SN, Ho CL, Ho JD, et al. Acute angle-closure glaucoma resulting from spontaneous hemorrhagic retinal detachment in age-related macular degeneration: case reports and literature review. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2001; 45:270–275.22. Tilanus MA, Vaandrager W, Cuypers MH, et al. Relationship between anticoagulant medication and massive intraocular hemorrhage in age-related macular degeneration. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000; 238:482–485.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneous Eyeball Rupture in a 94-Year-Old Patient
- Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma from Spontaneous Massive Hemorrhagic Retinal Detachment
- Clinical Experiences of Iridocycloretraction Operation in Chronic Angle Closure Glaucoma
- Biometric Comparisons between Acute and Chronic Angle Closure Glaucoma
- Suprachoroidal Hemorrhage with Retinal Detachment During Trabeculectomy in Aphakic Glaucoma