Korean J Neurotrauma.
2017 Apr;13(1):50-53. 10.13004/kjnt.2017.13.1.50.
Severe Retrolisthesis at the Adjacent Segment after Lumbar Fusion Combined with Dynamic Stabilization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. chosunns@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2378251
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2017.13.1.50
Abstract
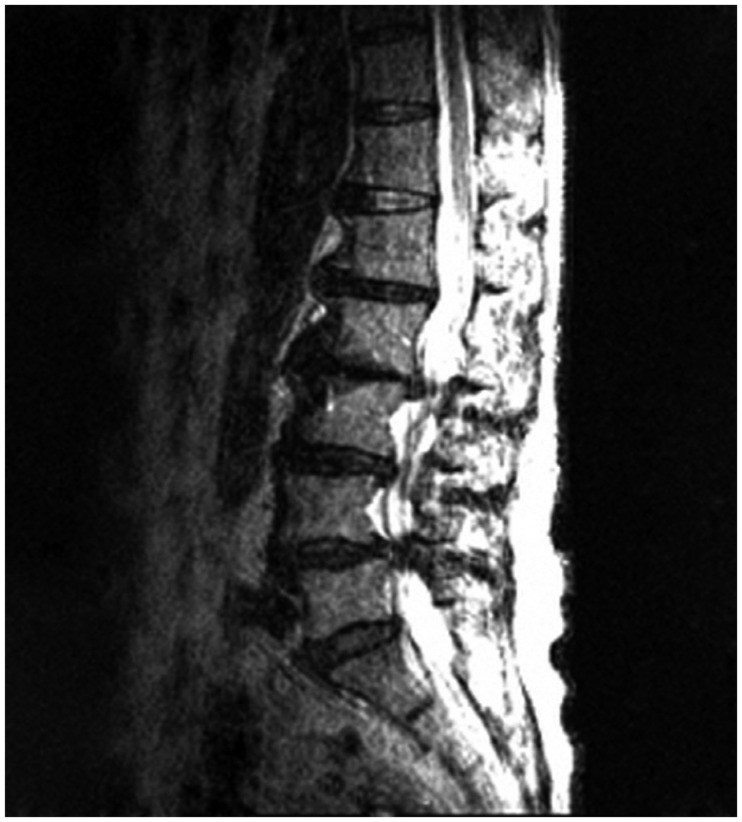
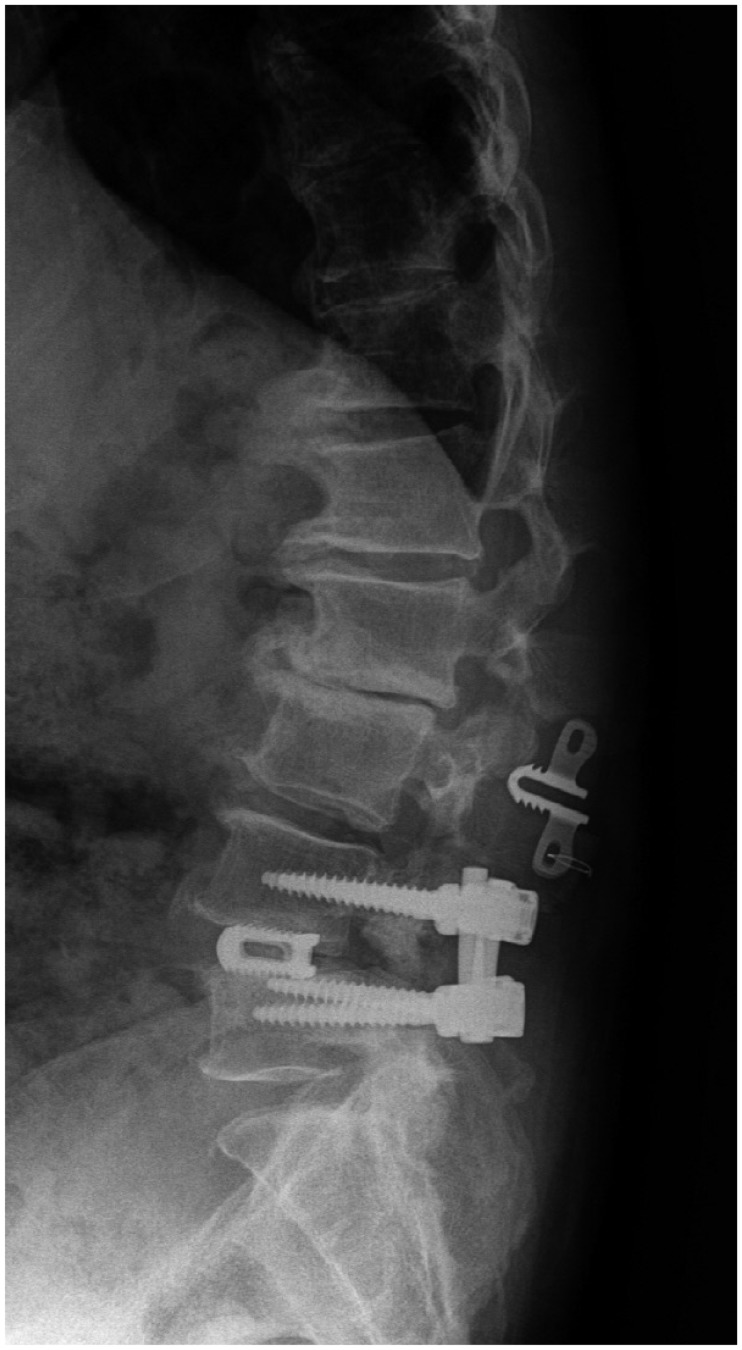
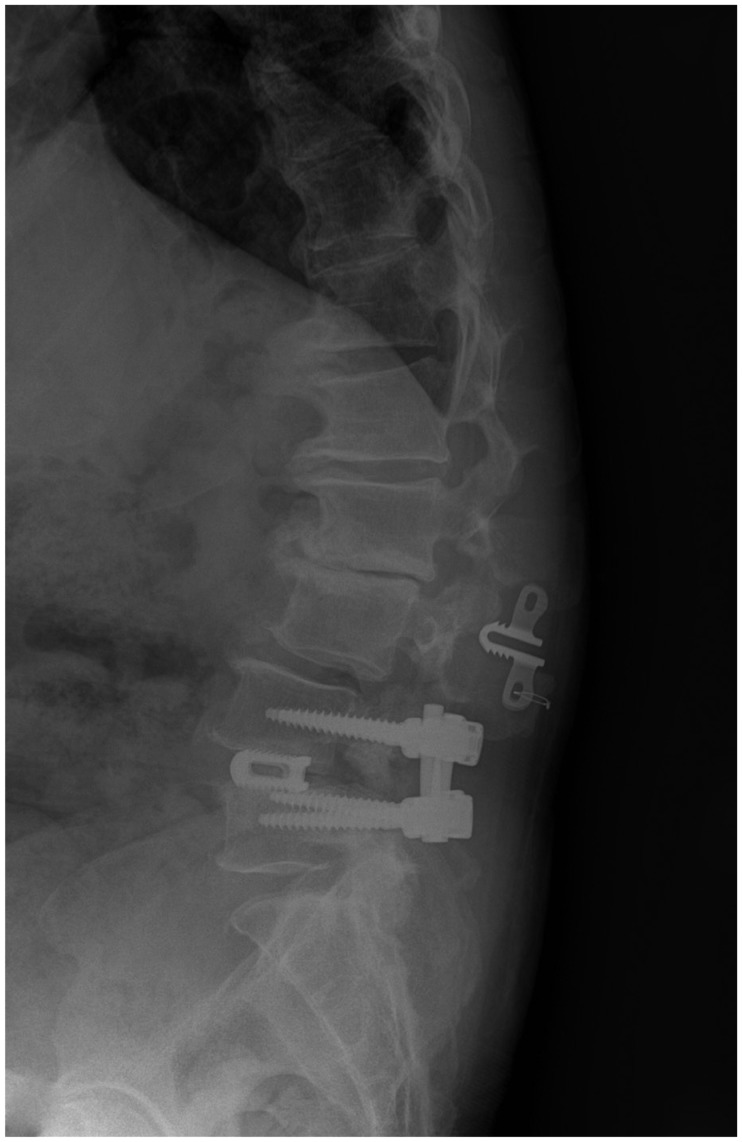
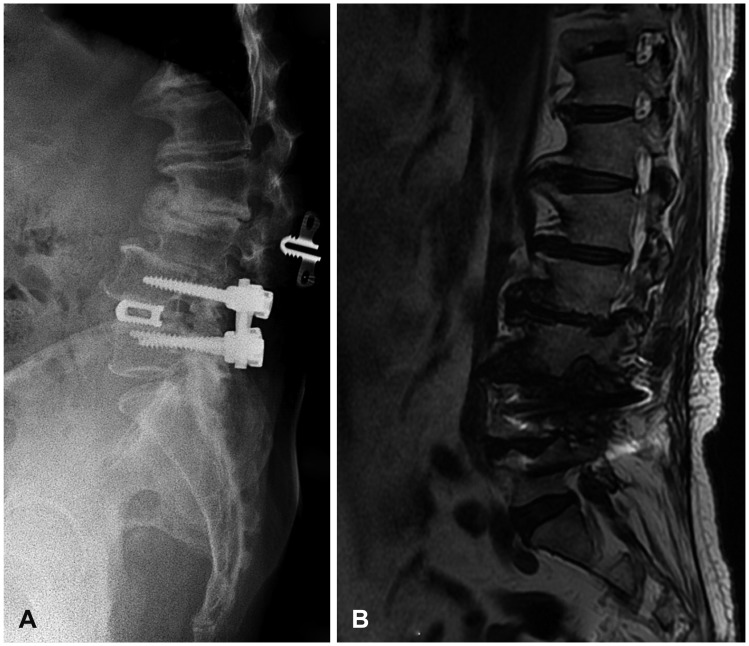
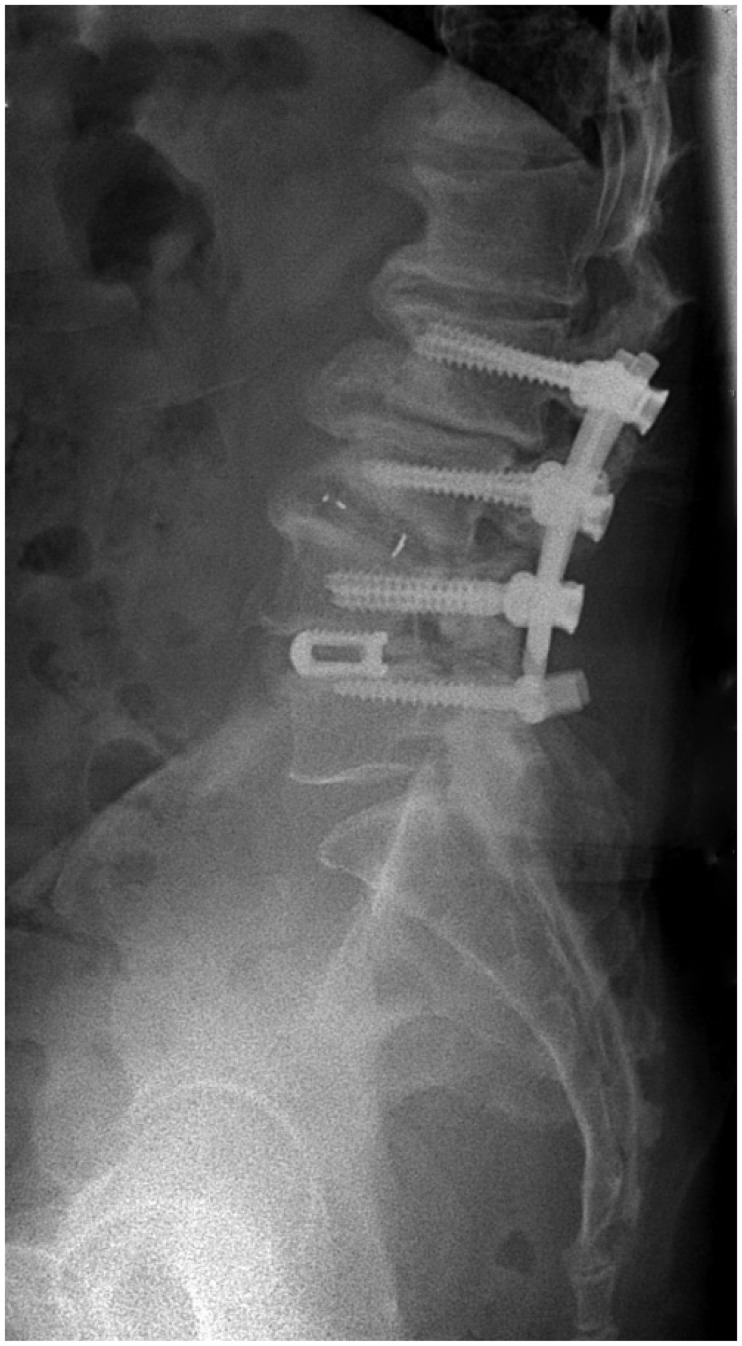
- Lumbar fusion using the pedicle screw system is a popular operative procedure, with favorable clinical results and high fusion rates. However, the risk of adjacent segment disease after lumbar fusion is problematic. We report a complicated case of severe retrolisthesis at L3-4 level following dynamic interspinous process stabilization at L2-3 level and a fusion at L4-5 level. The radiological and clinical findings of this complication are discussed, and a review of the literature is presented.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Axelsson P, Johnsson R, Strömqvist B. The spondylolytic vertebra and its adjacent segment. Mobility measured before and after posterolateral fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:414–417. PMID: 9055370.2. Barrey C, Roussouly P, Le Huec JC, D'Acunzi G, Perrin G. Compensatory mechanisms contributing to keep the sagittal balance of the spine. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22(Suppl 6):S834–S841. PMID: 24052406.
Article3. Chen CS, Cheng CK, Liu CL, Lo WH. Stress analysis of the disc adjacent to interbody fusion in lumbar spine. Med Eng Phys. 2001; 23:483–491. PMID: 11574255.
Article4. Dekutoski MB, Schendel MJ, Ogilvie JW, Olsewski JM, Wallace LJ, Lewis JL. Comparison of in vivo and in vitro adjacent segment motion after lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:1745–1751. PMID: 7973970.
Article5. Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Loeser JD, Bigos SJ, Ciol MA. Morbidity and mortality in association with operations on the lumbar spine. The influence of age, diagnosis, and procedure. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992; 74:536–543. PMID: 1583048.
Article6. Etebar S, Cahill DW. Risk factors for adjacent-segment failure following lumbar fixation with rigid instrumentation for degenerative instability. J Neurosurg. 1999; 90:163–169. PMID: 10199244.
Article7. Hartmann F, Dietz SO, Kuhn S, Hely H, Rommens PM, Gercek E. Biomechanical comparison of an interspinous device and a rigid stabilization on lumbar adjacent segment range of motion. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2011; 78:404–409. PMID: 22094153.8. Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC, Hoff JT, McGillicuddy JE. Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:1938–1944. PMID: 15534420.
Article9. Park SC, Yoon SH, Hong YP, Kim KJ, Chung SK, Kim HJ. Minimum 2-year follow-up result of degenerative spinal stenosis treated with interspinous u (coflex). J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46:292–299. PMID: 19893715.10. Refae HH. Nearby segment disease in the lumber spine. J Am Sci. 2013; 9:143–148.11. Webb H, van Woerden H. Interspinous devices for lumbar stenosis-a review of the literature. Internet J Surg. 2003; 5:3059.12. Yoon SM, Lee SG, Park CW, Yoo CJ, Kim DY, Kim WK. Late complications of the single level ‘interspinous U’ in lumbar spinal stenosis with mild segmental instability. Korean J Spine. 2008; 5:89–94.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Does the Addition of a Dynamic Pedicle Screw to a Fusion Segment Prevent Adjacent Segment Pathology in the Lumbar Spine?
- Preliminary Report on Usefulness of Adjacent Interspinous Stabilization using Interspinous Spacer Combined with Posterior Lumbosacral Spinal Fusion in Degenerative Lumbar Disease
- Pedicle Screw-based Dynamic Stabilization with a Hinged Screw Head System in the Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Disorders
- Change of Lumbar Motion after Multi-Level Posterior Dynamic Stabilization with Bioflex System : 1 Year Follow Up
- The Causes of Revision Arthrodesis for the Degenerative Changes at the Adjacent Segment after Lumbosacral Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Diseases