Ann Surg Treat Res.
2017 May;92(5):376-379. 10.4174/astr.2017.92.5.376.
Intramammary sentinel lymph node with capsular extravasation in breast cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Breast Surgery, AC Camargo Cancer Center, São Paulo, Brazil. paulo.alcantara@accamargo.org.br
- 2Department of Radiology, AC Camargo Cancer Center, São Paulo, Brazil.
- 3Department of Pathology, AC Camargo Cancer Center, São Paulo, Brazil.
- KMID: 2377710
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2017.92.5.376
Abstract
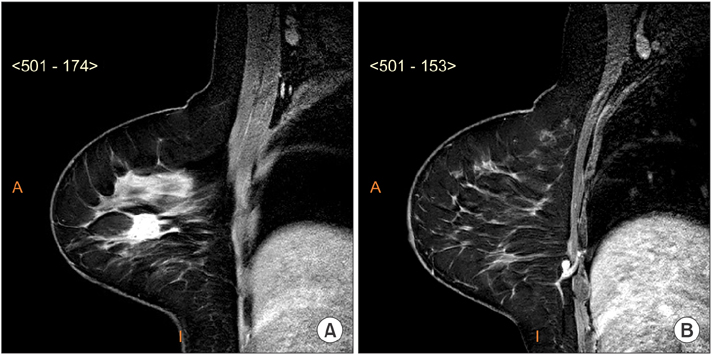
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy has been developed as the standard of treatment in breast cancer. Status of axillary sentinel lymph node is known to be a significant prognostic factor. Nevertheless, involvement of an intramammary lymph node with metastasis in breast cancer is a rare radiological and clinical presentation, and with extracapsular extravasation even more uncommon. Historically, reported series of patients with intramammary lymph node diagnosed by final histological examination are small in number and clinical significance of metastasis is still unclear. Here, we report a case of conservative breast cancer surgery with 3 intramammary sentinel lymph nodes containing metastasis and extracapsular extravasation. After multidisciplinary consensus, the patient was surgically reapproached with mastectomy. Even though the 3 intramammary sentinel lymph nodes were positive for metastases, pathology examination did not reveal any signs of malignancy in the mastectomy specimen.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pugliese MS, Stempel MM, Cody HS 3rd, Morrow M, Gemignani ML. Surgical management of the axilla: do intramammary nodes matter? Am J Surg. 2009; 198:532–537.2. Cho N, Moon WK, Han W, Park IA, Cho J, Noh DY. Preoperative sonographic classification of axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer: node-to-node correlation with surgical histology and sentinel node biopsy results. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:1731–1737.3. Mainiero MB. Regional lymph node staging in breast cancer: the increasing role of imaging and ultrasound-guided axillary lymph node fine needle aspiration. Radiol Clin North Am. 2010; 48:989–997.4. Mainiero MB, Cinelli CM, Koelliker SL, Graves TA, Chung MA. Axillary ultra sound and fine-needle aspiration in the preoperative evaluation of the breast cancer patient: an algorithm based on tumor size and lymph node appearance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:1261–1267.5. Alvarez S, Anorbe E, Alcorta P, Lopez F, Alonso I, Cortes J. Role of sonography in the diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: a systematic review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 186:1342–1348.6. Lee SK, Kim S, Choi MY, Kim J, Lee J, Jung SP, et al. The clinical meaning of intramammary lymph nodes. Oncology. 2013; 84:1–5.7. Abdullgaffar B, Gopal P, Abdulrahim M, Ghazi E, Mohamed E. The significance of intramammary lymph nodes in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg Pathol. 2012; 20:555–563.8. Vijan SS, Hamilton S, Chen B, Reynolds C, Boughey JC, Degnim AC. Intramammary lymph nodes: patterns of discovery and clinical significance. Surgery. 2009; 145:495–499.9. Diaz R, Degnim AC, Boughey JC, Nassar A, Jakub JW. A positive intramammary lymph node does not mandate a complete axillary node dissection. Am J Surg. 2012; 203:151–155.10. Koca B, Kuru B, Yuruker S, Gokgul B, Ozen N. Factors affecting surgical margin positivity in invasive ductal breast cancer patients who underwent breast-conserving surgery after preoperative core biopsy diagnosis. J Korean Surg Soc. 2013; 84:154–159.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Number of Removed Lymph Nodes for an Acceptable False Negative Rate in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer
- Validation and Controversy of Sentinel Node Biopsy for Breast Cancer
- Sentinel Lymph Node Imaging in Breast Cancer
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer: A Clinical Review and Update
- Optimized Criteria for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Patients with Clinically Node Negative Breast Cancer