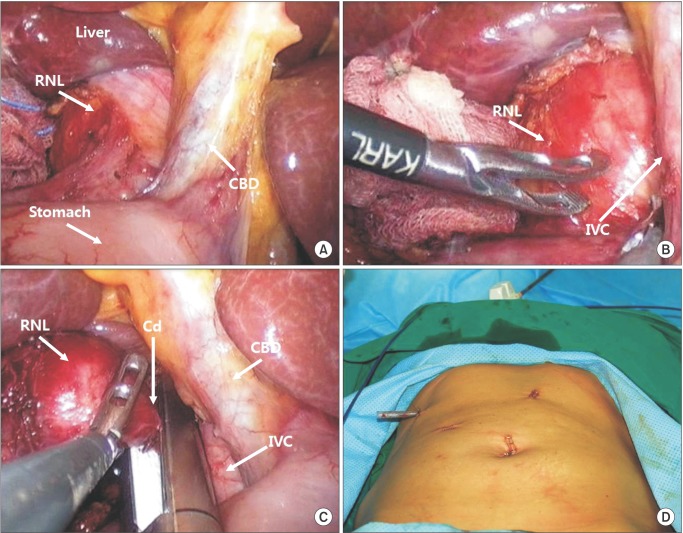
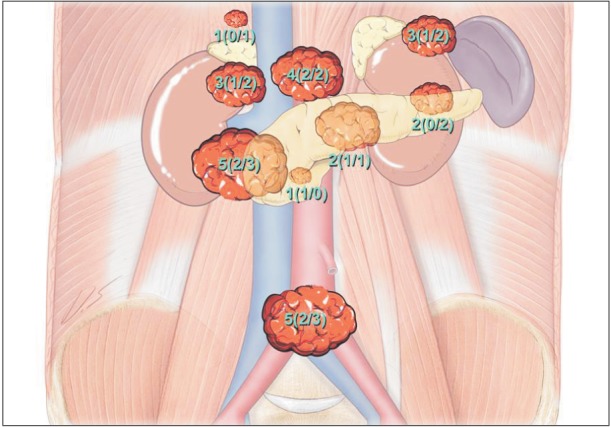
Ann Surg Treat Res.
2017 Mar;92(3):149-155. 10.4174/astr.2017.92.3.149.
Laparoscopic resection of retroperitoneal benign neurilemmoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shevchencko@yuhs.ac
- 2Gangnam Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Pancreaticobiliary Cancer Clinic, Yonsei Cancer Center, Institute of Gastroenterology Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2377557
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2017.92.3.149
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to verify that laparoscopic resection for treating retroperitoneal benign neurilemmoma (NL) is expected to be favorable for complete resection of tumor with technical feasibility and safety.
METHODS
We retrospectively analyzed 47 operations for retroperitoneal neurogenic tumor at Yonsei University College of Medicine, Severance Hospital and Gangnam Severance Hospital between January 2005 and September 2015. After excluding 21 patients, the remaining 26 were divided into 2 groups: those who underwent open surgery (OS) and those who underwent laparoscopic surgery (LS). We compared clinicopathological features between the 2 groups.
RESULTS
There was no significant difference in operation time, estimated blood loss, transfusion, complication, recurrence, or follow-up period between 2 groups. Postoperative hospital stay was significantly shorter in the LS group versus the OS group (OS vs. LS, 7.00 ± 3.43 days vs. 4.50 ± 2.16 days; P = 0.031).
CONCLUSION
We suggest that laparoscopic resection of retroperitoneal benign NL is feasible and safe by obtaining complete resection of the tumor. LS for treating retroperitoneal benign NL could be useful with appropriate laparoscopic technique and proper patient selection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. DasGupta TK, Brasfield RD, Strong EW, Hajdu SI. Benign solitary Schwannomas (neurilemomas). Cancer. 1969; 24:355–366. PMID: 5796779.
Article2. Mrugala MM, Batchelor TT, Plotkin SR. Peripheral and cranial nerve sheath tumors. Curr Opin Neurol. 2005; 18:604–610. PMID: 16155448.
Article3. Nah YW, Suh JH, Choi DH, Ko BK, Nam CW, Kim GY, et al. Benign retroperitoneal schwannoma: surgical consideration. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005; 52:1681–1684. PMID: 16334756.4. Kapila K, Mathur S, Verma K. Schwannomas: a pitfall in the diagnosis of pleomorphic adenomas on fine-needle aspiration cytology. Diagn Cytopathol. 2002; 27:53–59. PMID: 12112817.
Article5. Pinson CW, ReMine SG, Fletcher WS, Braasch JW. Long-term results with primary retroperitoneal tumors. Arch Surg. 1989; 124:1168–1173. PMID: 2802979.
Article6. Petrucciani N, Sirimarco D, Magistri P, Antolino L, Gasparrini M, Ramacciato G. Retroperitoneal schwannomas: advantages of laparoscopic resection. Review of the literature and case presentation of a large paracaval benign schwannoma (with video). Asian J Endosc Surg. 2015; 8:78–82. PMID: 25598061.
Article7. Kitano S, Iso Y, Moriyama M, Sugimachi K. Laparoscopy-assisted Billroth I gastrectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1994; 4:146–148. PMID: 8180768.8. Kakisako K, Sato K, Adachi Y, Shiraishi N, Miyahara M, Kitano S. Laparoscopic colectomy for Dukes A colon cancer. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2000; 10:66–70. PMID: 10789575.
Article9. Ploussard G, Xylinas E, Paul A, Gillion N, Salomon L, Allory Y, et al. Is robot assistance affecting operating room time compared with pure retroperitoneal laparoscopic radical prostatectomy? J Endourol. 2009; 23:939–943. PMID: 19473064.
Article10. Cadeddu MO, Mamazza J, Schlachta CM, Seshadri PA, Poulin EC. Laparoscopic excision of retroperitoneal tumors: technique and review of the laparoscopic experience. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2001; 11:144–147. PMID: 11330383.11. Kang CM, Kim DH, Lee WJ. Ten years of experience with resection of left-sided pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: evolution and initial experience to a laparoscopic approach. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:1533–1541. PMID: 20054579.
Article12. Okuyama T, Tagaya N, Saito K, Takahashi S, Shibusawa H, Oya M. Laparoscopic resection of a retroperitoneal pelvic schwannoma. J Surg Case Rep. 2014; (1):DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjt122.
Article13. Pazouki A, Khalaj A, Shapoori P, Vaziri M, Najafi L. Laparoscopic resection of a retroperitoneal schwannoma. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2011; 21:e326–e328. PMID: 22146184.
Article14. Choi KS, Chung JC, Kim HC. Feasibility and outcomes of laparoscopic enucleation for pancreatic neoplasms. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2014; 87:285–289. PMID: 25485235.
Article15. Daneshmand S, Youssefzadeh D, Chamie K, Boswell W, Wu N, Stein JP, et al. Benign retroperitoneal schwannoma: a case series and review of the literature. Urology. 2003; 62:993–997. PMID: 14665342.
Article16. Foote MN, Luongo V, Marino ER. Benign giant retroperitoneal neurilemmoma. Ann Surg. 1963; 157:719–724. PMID: 13958661.
Article17. Yoshino T, Yoneda K. Laparoscopic resection of a retroperitoneal ancient schwannoma: a case report and review of the literature. Anticancer Res. 2008; 28(5B):2889–2891. PMID: 19031930.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Retroperitoneal Neurilemmoma Presenting as an Adnexal Mass
- A Case of Retroperitoneal Neurilemmoma
- Retroperitoneal Neurilemmoma: A Report of 2 Cases
- A Case of Retroperitoneal Neurilemmoma
- Affiliation and corresponding author correction: Laparoscopic resection of retroperitoneal benign neurilemmoma