Ann Lab Med.
2017 Jul;37(4):362-364. 10.3343/alm.2017.37.4.362.
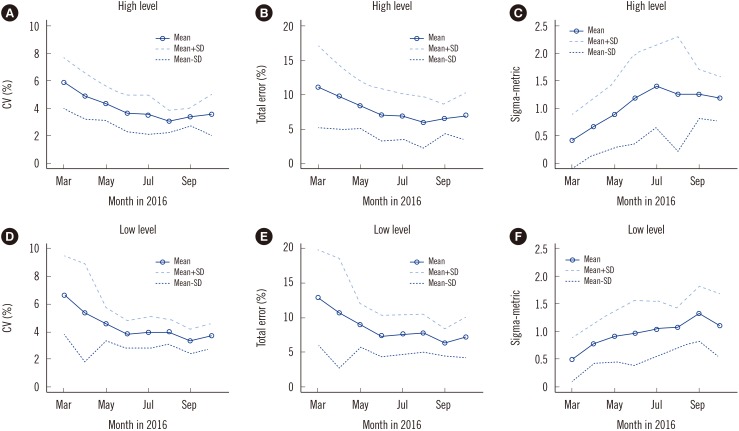
Development and Application of a Laboratory-Developed Quality Control Program for Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems: A Single Institute Experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Hospital Information, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea.
- 3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea. mddaniel@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2376800
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2017.37.4.362
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Updated on Oct 2016. http://www.R-project.org.2. Westgard JO. Desirable Biological Variation Database specifications. Updated on Oct 2014. https://www.westgard.com/biodatabase1.htm.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Application of Continuous Glucose Monitoring System (CGMS) and Patient Education
- Development of Blood Culture and Quality Improvement
- Development of Cell Phone Application for Blood Glucose Self-Monitoring Based on ISO/IEEE 11073 and HL7 CCD
- Installation of Network-Connected Point-of-Care Blood Glucose Meters
- Performance Evaluation of B. Braun Omnitest 5 Blood Glucose Monitoring System for Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose