J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2017 Apr;58(4):449-454. 10.3341/jkos.2017.58.4.449.
Clinical Features of Strabismus in Patients with Unilateral Pediatric Cataract
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kris9352@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2376601
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2017.58.4.449
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The incidence rate and clinical features of strabismus and factors affecting onset of strabismus were evaluated in patients with unilateral pediatric cataract.
METHODS
A total of 42 patients who underwent lens removal for treatment of unilateral cataract between January 1996 and January 2011 were evaluated. Patients were divided into 3 groups (Ortho/Ortho, Ortho/Strabismus, and Strabismus/Strabismus) according to preoperative and postoperative ocular alignment. Age at surgery, visual acuity, amblyopia, and spherical equivalent were compared among the 3 groups.
RESULTS
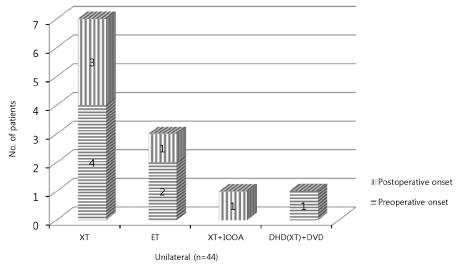
Of the total patients, 7 had strabismus preoperatively and 5 developed postoperative strabismus. Thus, a total of 12 patients had postoperative strabismus. Preoperatively, 5 patients had exotriopa and 2 patients had esotropia. Postoperatively, 9 patients had exotropia and 3 patients had esotropia. Exotropia was more common than esotropia. In comparison of the 3 groups, postoperative visual acuity was significantly low, and differences in visual acuity between normal eye and cataract eye were significantly larger in the Ortho/Strabismus group. There were no significant differences among the 3 groups in age at surgery, amblyopia, or spherical equivalent.
CONCLUSIONS
In the patients with unilateral pediatric cataract, exotropia was the most common type. Because there is a high possibility of postoperative strabismus in patients who had lower postoperative visual acuity, careful observation is needed in these patients.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim HY, Lee YJ, Yu YS. Treatment and prognosis of cataract in children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:1544–1551.2. Ahn JH, Kim WS. Surgical techniques and postoperative complications in pediatric cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:1049–1056.3. Ahn JH, Kim WS, Lee SJ. Factors affecting stereopsis after pediatric cataract surgery. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2008; 49:493–498.4. France TD, Frank JW. The association of strabismus and aphakia in children. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1984; 21:223–226.5. Hiles DA, Sheridan SJ. Strabismus associated with infantile cataracts. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1977; 17:193–202.6. Oh MJ, Min WK, Min BM. The association of strabismus and congenital cataract. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1989; 30:611–615.7. Spanou N, Alexopoulos L, Manta G, et al. Strabismus in pediatric lens disorders. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2011; 48:163–166.8. Demirkilinc Biler E, Bozbiyik DI, Uretmen O, Kose S. Strabismus in infants following congenital cataract surgery. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015; 253:1801–1807.9. Lambert SR, Lynn M, Drews-Botsch C, et al. A comparison of grating visual acuity, strabismus, and reoperation outcomes among children with aphakia and pseudophakia after unilateral cataract surgery during the first six months of life. J AAPOS. 2001; 5:70–75.10. Awner S, Buckley EG, DeVaro JM, Seaber JH. Unilateral pseudophakia in children under 4 years. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1996; 33:230–236.11. Bradford GM, Keech RV, Scotte WE. Factor affecting visual outcome after surgery for bilateral congenital cataracts. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994; 117:58–64.12. Rogers GL, Tishler CL, Tsou BH, et al. Visual acuities in infants with congenital cataracts operated on prior to 6 months of age. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99:999–1003.13. Cheng KP, Hiles DA, Biglan AW, Pettapiece MC. Visual results after early surgical treatment of unilateral congenital cataract. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:903–910.14. Lyle TK, Jackson S. Lyle and Jackson's Practical Orthoptics in the Treatment of Squint (and Other Anomalies of Binocular Vision). 5th ed. London: HK Lewis & Co Ltd;1967. p. 47.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Association of Strabismus and Congenital Cataract
- Factors Associated with Strabismus after Cataract Extraction and Primary Intraocular Lense Implantation in Congenital Cataracts
- Factors Affecting Stereopsis After Pediatric Cataract Surgery
- Four Cases of Strabismus presenting after Cataract Surgery
- Two Cases of Congenital Aniridia