J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2017 Feb;60(2):146-154. 10.3340/jkns.2016.0607.002.
Semi-Jailing Technique Using a Neuroform3 Stent for Coiling of Wide-Necked Intracranial Aneurysms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea.
- 3Diagnostic Radiology, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea. drcello6193@nate.com
- KMID: 2374875
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.0607.002
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
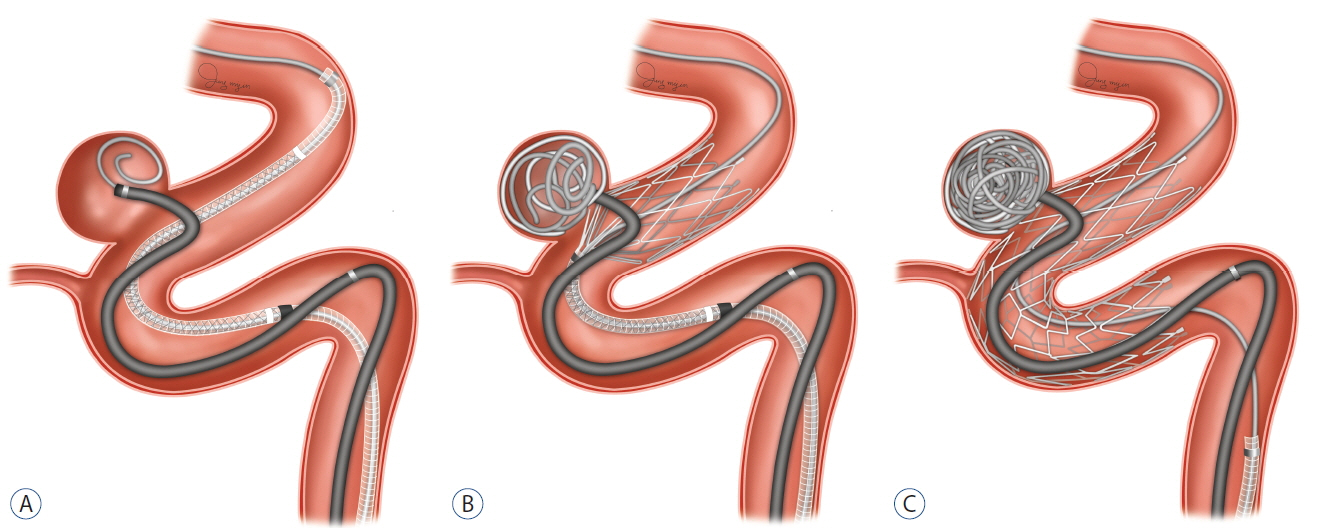
The semi-jailing technique (SJT) provides stent-assisted remodeling of the aneurysm neck during coil embolization without grasping the coil delivery microcatheter. We retrospectively evaluated the efficacy and safety of SJT using a Neuroform3 stent for coiling of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms.
METHODS
We collected the clinical and radiological data between January 2009 and June 2015 of the wide-necked aneurysms treated with SJT using a Neuroform3 stent.
RESULTS
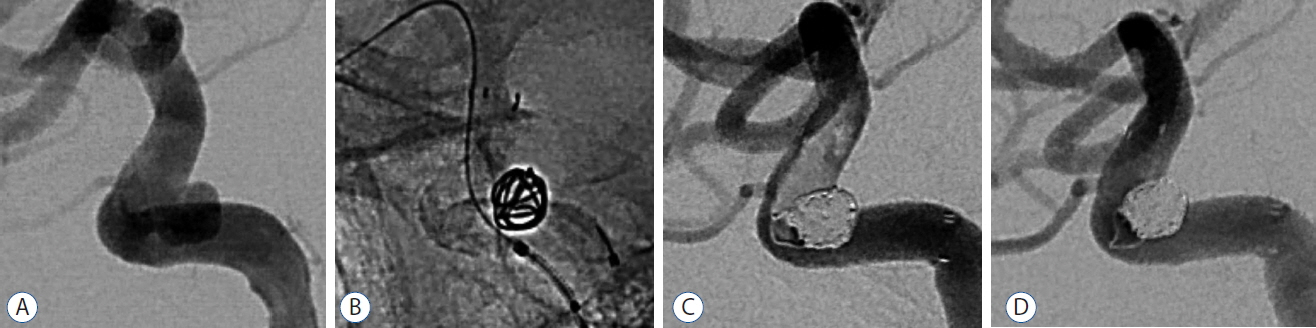
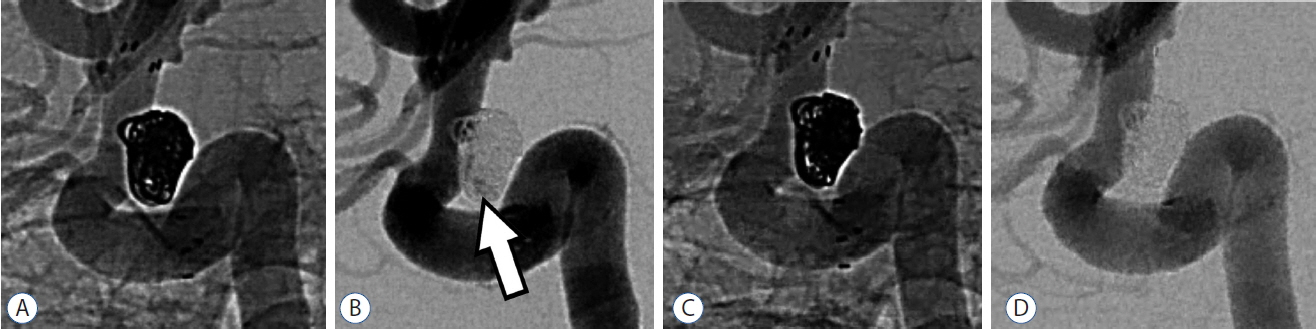
SJT using a Neuroform3 stent was attempted in 70 wide-necked aneurysms (68 patients). There were 56 unruptured and 14 ruptured aneurysms. The size of aneurysm ranged from 1.7 to 28.1 mm (mean 6.1 mm). The immediate angiographic results were complete occlusion in 55 aneurysms (78.6%), neck remnant in 7 (10.0%), and aneurysm remnant in 8 (11.4%). Overall, periprocedural complications occurred in 13 patients (19.1%), including asymptomatic thromboembolism in 7 (10.3%), symptomatic thromboembolism in 4 (5.9%), and symptomatic hemorrhagic complications in 2 (2.9%). Conventional angiography follow-up was obtained in 55 (78.6%) of 70 aneurysms (mean, 10.9 months). The result showed progressive occlusion in 7 aneurysms (12.7%) and recanalization in 1 aneurysm (1.8%). At the end of the observation period (mean, 17.5 months), all 54 patients without subarachnoid hemorrhage showed excellent clinical outcomes (modified Rankin Scale [mRS] 0), except two (mRS 1 or 2) and seven of 14 patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage remained symptom-free (mRS 0).
CONCLUSION
In this report of 70 aneurysms, SJT using a Neuroform3 stent for coiling of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms showed good technical safety, as well as favorable clinical and angiographic outcomes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Amenta PS, Dalyai RT, Kung D, Toporowski A, Chandela S, Hasan D, et al. Stent-assisted coiling of wide-necked aneurysms in the setting of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage: experience in 65 patients. Neurosurgery. 70:1415–1429. discussion 1429. 2012.
Article2. Benitez RP, Silva MT, Klem J, Veznedaroglu E, Rosenwasser RH. Endovascular occlusion of wide-necked aneurysms with a new intracranial microstent (Neuroform) and detachable coils. Neurosurgery. 54:1359–1367. discussion 1368. 2004.
Article3. Biondi A, Janardhan V, Katz JM, Salvaggio K, Riina HA, Gobin YP. Neuroform stent-assisted coil embolization of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms: strategies in stent deployment and midterm follow-up. Neurosurgery. 61:460–468. discussion 468–469. 2007.4. Byun JS, Kim JK, Lee HY, Hwang SN. Temporary semi-jailing technique for coil embolization of wide-neck aneurysm with small caliber parent artery following incomplete clipping. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 53:241–244. 2013.
Article5. Chung J, Lim YC, Suh SH, Shim YS, Kim YB, Joo JY, et al. Stent-assisted coil embolization of ruptured wide-necked aneurysms in the acute period: incidence of and risk factors for periprocedural complications. J Neurosurg. 121:4–11. 2014.
Article6. Durst CR, Khan P, Gaughen J, Patrie J, Starke RM, Conant P, et al. Direct comparison of Neuroform and Enterprise stents in the treatment of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms. Clin Radiol. 69:e471–e476. 2014.
Article7. Fargen KM, Hoh BL, Welch BG, Pride GL, Lanzino G, Boulos AS, et al. Long-term results of enterprise stent-assisted coiling of cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 71:239–244. discussion 244. 2012.
Article8. Fernandez Zubillaga A, Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Duckwiler GR. Endovascular occlusion of intracranial aneurysms with electrically detachable coils: correlation of aneurysm neck size and treatment results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 15:815–820. 1994.9. Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Han P, McDougall CG. Preliminary experience using the Neuroform stent for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 54:6–16. discussion 16–17. 2004.
Article10. Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Woo H, Rasmussen PA, Masaryk TJ, McDougall CG. Neuroform stent assisted aneurysm treatment: evolving treatment strategies, complications and results of long term follow-up. J Neurointerv Surg. 2:16–22. 2010.
Article11. Gao X, Liang G, Li Z, Qu H, Wei X. Stent-assisted coil embolization of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms using a semi-deployment technique: angiographic and clinical outcomes in 31 consecutive patients. Interv Neuroradiol. 16:385–393. 2010.
Article12. Heller RS, Malek AM. Parent vessel size and curvature strongly influence risk of incomplete stent apposition in enterprise intracranial aneurysm stent coiling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 32:1714–1720. 2011.
Article13. Heller RS, Miele WR, Do-Dai DD, Malek AM. Crescent sign on magnetic resonance angiography revealing incomplete stent apposition: correlation with diffusion-weighted changes in stent-mediated coil embolization of aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 115:624–632. 2011.
Article14. Hong B, Patel NV, Gounis MJ, DeLeo MJ 3rd, Linfante I, Wojak JC, et al. Semi-jailing technique for coil embolization of complex, wide-necked intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 65:1131–1138. discussion 1138–1139. 2009.
Article15. Howington JU, Hanel RA, Harrigan MR, Levy EI, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN. The Neuroform stent, the first microcatheter-delivered stent for use in the intracranial circulation. Neurosurgery. 54:2–5. 2004.
Article16. Kadkhodayan Y, Rhodes N, Blackburn S, Derdeyn CP, Cross DT 3rd, Moran CJ. Comparison of Enterprise with Neuroform stent-assisted coiling of intracranial aneurysms. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 200:872–878. 2013.
Article17. Kim BM, Kim DJ, Kim DI. Stent application for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Neurointervention. 6:53–70. 2011.
Article18. Krischek O, Miloslavski E, Fischer S, Shrivastava S, Henkes H. A comparison of functional and physical properties of self-expanding intracranial stents [Neuroform3, Wingspan, Solitaire, Leo+, Enterprise]. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 54:21–28. 2011.
Article19. Lopes D, Sani S. Histological postmortem study of an internal carotid artery aneurysm treated with the Neuroform stent. Neurosurgery. 56:E416. discussion E416. 2005.
Article20. Meckel S, Singh TP, Undren P, Ramgren B, Nilsson OG, Phatouros C, et al. Endovascular treatment using predominantly stent-assisted coil embolization and antiplatelet and anticoagulation management of ruptured blood blister-like aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 32:764–771. 2011.
Article21. Mocco J, Snyder KV, Albuquerque FC, Bendok BR, Alan SB, Carpenter JS, et al. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms with the Enterprise stent: a multicenter registry. J Neurosurg. 110:35–39. 2009.
Article22. Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A, Georganos SA, Juravsky L, Lambert A, et al. Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke. 34:1398–1403. 2003.
Article23. Tahtinen OI, Vanninen RL, Manninen HI, Rautio R, Haapanen A, Niskakangas T, et al. Wide-necked intracranial aneurysms: treatment with stent-assisted coil embolization during acute (<72 hours) subarachnoid hemorrhage--experience in 61 consecutive patients. Radiology. 253:199–208. 2009.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Temporary Semi-Jailing Technique Avoiding Inevitable Antiplatelet Medication for Coil Embolization of Wide-necked Cerebral Aneurysms
- Y-Stenting Endovascular Treatment for Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysms : A Single-Institution Experience in Korea
- A Complicated Case of Endovascular Stent Assisted Coil Embolization of an Aneurysm
- Physiologic Flow Diversion Coiling Technique for Wide-Necked Aneurysms with an Asymmetric Bidirectional Flow at the Aneurysm Neck
- Solitaire AB Stent-Assisted Coiling of Wide-Neck Micro Aneurysms