J Breast Cancer.
2015 Jun;18(2):173-180. 10.4048/jbc.2015.18.2.173.
Axillary Lymph Node-to-Primary Tumor Standard Uptake Value Ratio on Preoperative 18F-FDG PET/CT: A Prognostic Factor for Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University School of Medicine, Guri, Korea.
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kbomsahn@ewha.ac.kr
- 3Clinical Research Institute, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2374533
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2015.18.2.173
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study assessed the axillary lymph node (ALN)-to-primary tumor maximum standard uptake value (SUVmax) ratio (ALN/T SUV ratio) in invasive ductal breast cancer (IDC) on preoperative 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG PET/CT) to determine the effectiveness in predicting recurrence-free survival (RFS).
METHODS
One hundred nineteen IDC patients (mean age, 50.5+/-10.5 years) with pathologically proven ALN involvement without distant metastasis and preoperative FDG PET/CT were enrolled in the study. SUVmax values of the ALN and primary tumor were obtained on FDG PET/CT, and ALN/T SUV ratio was calculated. Several factors were evaluated for their effectiveness in predicting RFS. These included several parameters on FDG PET/CT as well as several clinicopathological parameters: pathologic tumor/node stage; nuclear and histological grade; hormonal state; status with respect to human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, mindbomb E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (MIB-1), and p53; primary tumor size; and ALN size.
RESULTS
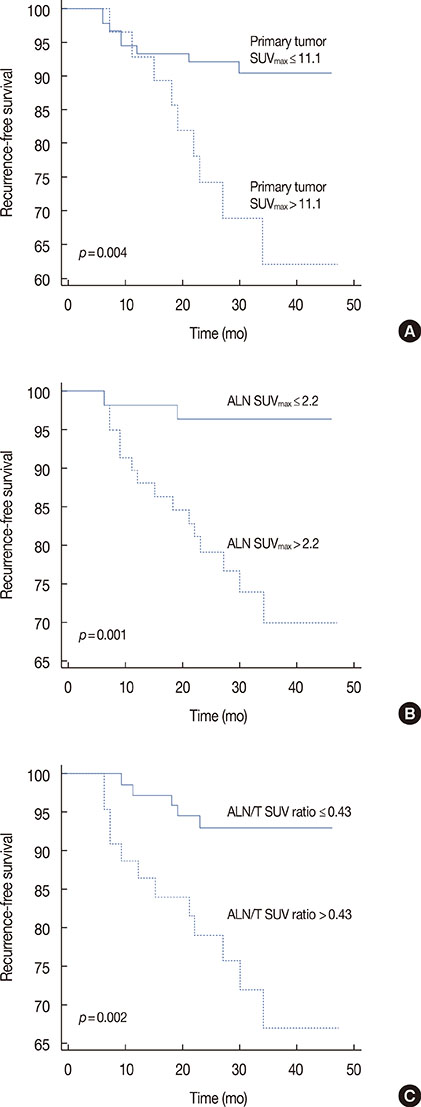
Among 119 patients with breast cancer, 17 patients (14.3%) experienced relapse during follow-up (mean follow-up, 28.4 months). The ALN/T SUV ratio of the group with disease recurrence was higher than that of the group without recurrence (0.97+/-1.60 and 0.45+/-0.40, respectively, p=0.005). Univariate analysis showed that the primary tumor SUVmax, ALN SUVmax, ALN/T SUV ratio, ALN status, nuclear and histological grade, estrogen receptor (ER) status, and MIB-1 status were predictors for RFS. Among these variables, ALN/T SUV ratio with hazard ratio of 4.20 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.74-10.13) and ER status with hazard ratio of 4.33 (95% CI, 1.06-17.71) were predictors for RFS according to multivariate analysis (p=0.002 and p=0.042, respectively).
CONCLUSION
Our study demonstrated that ALN/T SUV ratio together with ER status was an independent factor for predicting relapse in IDC with metastatic ALN. ALN/T SUV ratio on preoperative FDG PET/CT may be a useful marker for selecting IDC patients that need adjunct treatment to prevent recurrence.
MeSH Terms
-
Breast Neoplasms*
Electrons
Estrogens
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18*
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Lymph Nodes
Multivariate Analysis
Neoplasm Metastasis
Positron-Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography*
Prognosis
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Recurrence
Ubiquitin-Protein Ligases
Estrogens
Fluorodeoxyglucose F18
Receptor, Epidermal Growth Factor
Ubiquitin-Protein Ligases
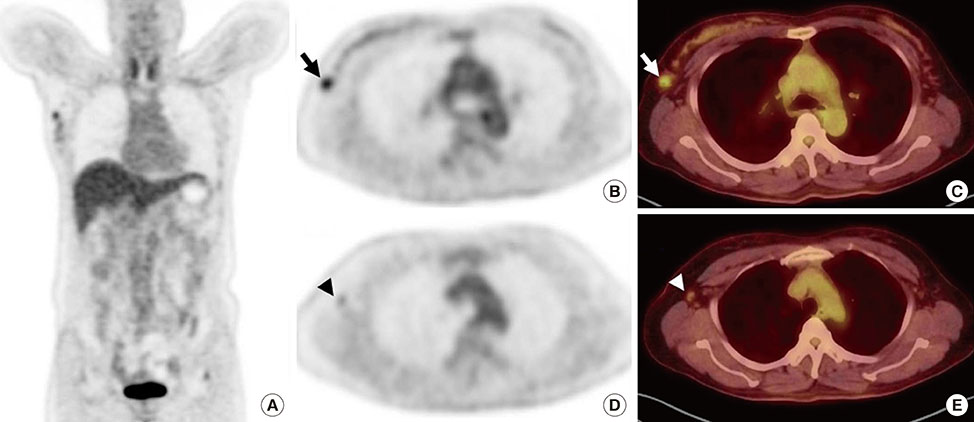
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jatoi I, Miller AB. Why is breast-cancer mortality declining? Lancet Oncol. 2003; 4:251–254.
Article2. Kim JY, Ryu MR, Choi BO, Park WC, Oh SJ, Won JM, et al. The prognostic significance of the lymph node ratio in axillary lymph node positive breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2011; 14:204–212.
Article3. Lale Atahan I, Yildiz F, Ozyigit G, Sari S, Gurkaynak M, Selek U, et al. Percent positive axillary lymph node metastasis predicts survival in patients with non-metastatic breast cancer. Acta Oncol. 2008; 47:232–238.
Article4. Cochet A, Dygai-Cochet I, Riedinger JM, Humbert O, Berriolo-Riedinger A, Toubeau M, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT provides powerful prognostic stratification in the primary staging of large breast cancer when compared with conventional explorations. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014; 41:428–437.
Article5. Oshida M, Uno K, Suzuki M, Nagashima T, Hashimoto H, Yagata H, et al. Predicting the prognoses of breast carcinoma patients with positron emission tomography using 2-deoxy-2-fluoro[18F]-D-glucose. Cancer. 1998; 82:2227–2234.
Article6. Alberini JL, Lerebours F, Wartski M, Fourme E, Le Stanc E, Gontier E, et al. 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) imaging in the staging and prognosis of inflammatory breast cancer. Cancer. 2009; 115:5038–5047.
Article7. Inoue T, Yutani K, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y, Shiba E, Noguchi S. Preoperative evaluation of prognosis in breast cancer patients by [(18)F]2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-glucose-positron emission tomography. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004; 130:273–278.
Article8. Ueda S, Tsuda H, Asakawa H, Shigekawa T, Fukatsu K, Kondo N, et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic relevance of uptake level using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography fusion imaging (18F-FDG PET/CT) in primary breast cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2008; 38:250–258.
Article9. Cerfolio RJ, Bryant AS. Ratio of the maximum standardized uptake value on FDG-PET of the mediastinal (N2) lymph nodes to the primary tumor may be a universal predictor of nodal malignancy in patients with nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007; 83:1826–1829.
Article10. Kaira K, Endo M, Asakura K, Tsuya A, Nakamura Y, Naito T, et al. Ratio of standardized uptake value on PET helps predict response and outcome after chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Nucl Med. 2010; 24:697–705.
Article11. Iskender I, Kadioglu SZ, Kosar A, Atasalihi A, Kir A. Is there any maximum standardized uptake value variation among positron emission tomography scanners for mediastinal staging in non-small cell lung cancer? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2011; 12:965–969.
Article12. Park J, Byun BH, Noh WC, Lee SS, Kim HA, Kim EK, et al. Lymph node to primary tumor SUV ratio by 18F-FDG PET/CT and the prediction of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2014; 39:e249–e253.
Article13. Kaida H, Toh U, Hayakawa M, Hattori S, Fujii T, Kurata S, et al. The relationship between 18F-FDG metabolic volumetric parameters and clinicopathological factors of breast cancer. Nucl Med Commun. 2013; 34:562–570.
Article14. Boellaard R, O'Doherty MJ, Weber WA, Mottaghy FM, Lonsdale MN, Stroobants SG, et al. FDG PET and PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour PET imaging: version 1.0. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010; 37:181–200.15. Nakajima N, Kataoka M, Sugawara Y, Ochi T, Kiyoto S, Ohsumi S, et al. Volume-based parameters of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography improve disease recurrence prediction in postmastectomy breast cancer patients with 1 to 3 positive axillary lymph nodes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013; 87:738–746.
Article16. Hudis CA, Barlow WE, Costantino JP, Gray RJ, Pritchard KI, Chapman JA, et al. Proposal for standardized definitions for efficacy end points in adjuvant breast cancer trials: the STEEP system. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:2127–2132.
Article17. Seok JW, Kim Y, An YS, Kim BS. The clinical value of tumor FDG uptake for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in breast cancer with clinically negative axillary lymph nodes. Ann Nucl Med. 2013; 27:546–553.
Article18. Elston CW, Ellis IO. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1991; 19:403–410.
Article19. Robbins P, Pinder S, de Klerk N, Dawkins H, Harvey J, Sterrett G, et al. Histological grading of breast carcinomas: a study of interobserver agreement. Hum Pathol. 1995; 26:873–879.
Article20. Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK, Allred DC. Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17:1474–1481.
Article21. Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B, et al. Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann Oncol. 2013; 24:2206–2223.
Article22. Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:118–145.
Article23. Okereke IC, Gangadharan SP, Kent MS, Nicotera SP, Shen C, DeCamp MM. Standard uptake value predicts survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009; 88:911–915.
Article24. Nguyen XC, So Y, Chung JH, Lee WW, Park SY, Kim SE. High correlations between primary tumours and loco-regional metastatic lymph nodes in non-small-cell lung cancer with respect to glucose transporter type 1-mediated 2-deoxy-2-F18-fluoro-D-glucose uptake. Eur J Cancer. 2008; 44:692–698.
Article25. Song BI, Lee SW, Jeong SY, Chae YS, Lee WK, Ahn BC, et al. 18F-FDG uptake by metastatic axillary lymph nodes on pretreatment PET/CT as a prognostic factor for recurrence in patients with invasive ductal breast cancer. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53:1337–1344.
Article26. Ohara M, Shigematsu H, Tsutani Y, Emi A, Masumoto N, Ozaki S, et al. Role of FDG-PET/CT in evaluating surgical outcomes of operable breast cancer: usefulness for malignant grade of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast. 2013; 22:958–963.
Article27. Cheang MC, Treaba DO, Speers CH, Olivotto IA, Bajdik CD, Chia SK, et al. Immunohistochemical detection using the new rabbit monoclonal antibody SP1 of estrogen receptor in breast cancer is superior to mouse monoclonal antibody 1D5 in predicting survival. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:5637–5644.
Article28. Lee J, Im YH, Lee SH, Cho EY, Choi YL, Ko YH, et al. Evaluation of ER and Ki-67 proliferation index as prognostic factors for survival following neoadjuvant chemotherapy with doxorubicin/docetaxel for locally advanced breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008; 61:569–577.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 18F-FDG PET/CT Findings in a Breast Cancer Patient with Concomitant Tuberculous Axillary Lymphadenitis
- Prediction of Axillary Nodal Status according to the Axillary Lymph Node to Primary Breast Tumor Maximum Standardized Uptake Value Ratio on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography
- Preoperative Axillary Staging Using 18F-FDG PET/CT and Ultrasonography in Breast Cancer Patients
- Clinicopathological Characteristics in Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer with Low FDG Uptake in (18)F-FDG PET/CT
- Unusual Contralateral Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in a Second Primary Breast Cancer Detected by FDG PET/CT and Lymphoscintigraphy