Clin Orthop Surg.
2016 Sep;8(3):237-242. 10.4055/cios.2016.8.3.237.
Total Hip Arthroplasty around the Inception of the Interface Bioactive Bone Cement Technique
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tominaga Hospital, H. Oonishi Memorial Joint Replacement Institute, Osaka, Japan.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Osaka Saiseikai Nakatsu Hospital, Osaka, Japan. LU7H-OOHS@asahi-net.or.jp
- KMID: 2374267
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.3.237
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
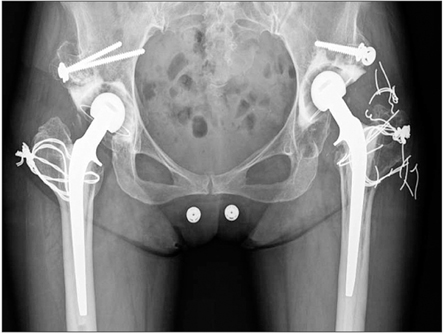
To augment cement-bone fixation, Dr. Hironobu Oonishi attempted additional physicochemical bonding through interposition of osteoconductive crystal hydroxyapatite (HA) granules at the cement-bone interface in 1982. He first used the interface bioactive bone cement (IBBC) technique in 12 selected patients (12 hips) in 1982 (first stage) and followed them for 2 years. In 1985, the technique was applied in 25 total hip arthroplasty (THA) patients (second stage) and the effects were investigated by comparing the side with the IBBC technique and the other side without the IBBC technique. He has employed this technique in all THA patients since 1987 (third stage).
METHODS
In the IBBC technique, HA granules (2 to 3 g) were smeared on the bone surface just before the acetabular and femoral components were cemented. In the first stage, 12 hips were operated using the IBBC technique in 1982. In the second stage, THA was performed without the IBBC technique on one side and with the IBBC technique on the other side within 1 year in 25 patients. In the third stage, THA was performed with the IBBC technique in 285 hips in 1987.
RESULTS
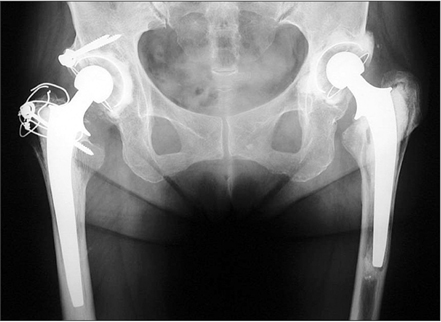
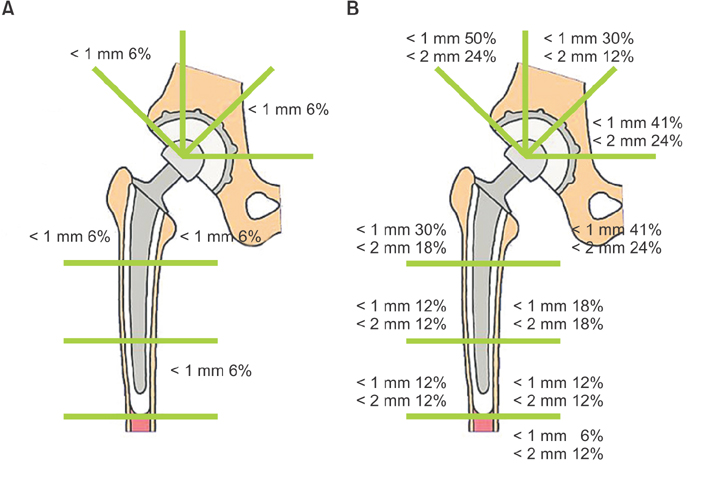
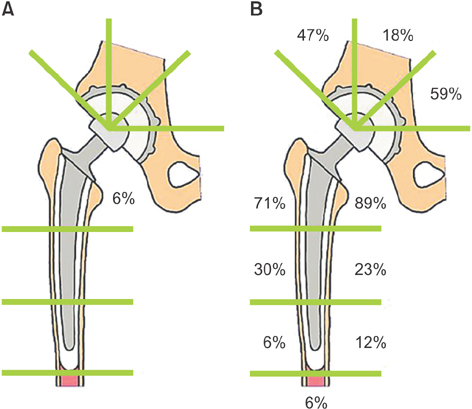
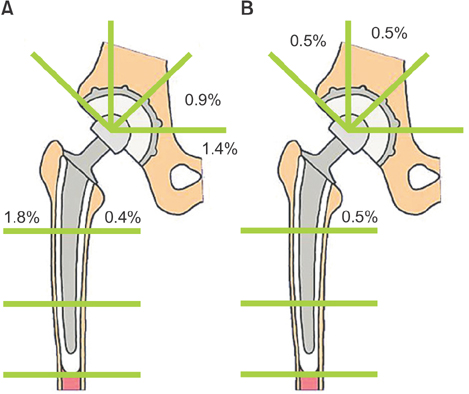
In the first stage patients, implant loosening was not detected at 30 years after operation. In the second stage patients, revision was required in 7 hips without the IBBC technique due to cup loosening (5 hips) and stem loosening (2 hips), whereas no hip was revised after THA with the IBBC technique at 26 years after operation. In the third stage patients, the incidence of radiolucent lines and osteolysis was very few at 25 years after operation.
CONCLUSIONS
The long-term follow-up of THA performed around the inception of the IBBC technique has revealed low incidences of radiolucent lines, osteolysis, and revision surgery.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
*Arthroplasty, Replacement, Hip/adverse effects/instrumentation/methods
*Bone Cements/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Bone-Implant Interface/physiology
Follow-Up Studies
Hip/diagnostic imaging/surgery
Humans
Hydroxyapatites/therapeutic use
Middle Aged
Young Adult
Bone Cements
Hydroxyapatites
Figure
Reference
-
1. Herberts P, Malchau H. How outcome studies have changed total hip arthroplasty practices in Sweden. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; (344):44–60.
Article2. Oonishi H, Kadoya Y, Iwaki H, Kin N. Total hip arthroplasty with a modified cementing technique using hydroxyapatite granules. J Arthroplasty. 2001; 16(6):784–789.
Article3. Oonishi H, Ohashi H, Oonishi H Jr, Kim SC. THA with hydroxyapatite granules at cement-bone interface: 15- to 20-year results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008; 466(2):373–379.4. DeLee JG, Charnley J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; (121):20–32.
Article5. Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC. "Modes of failure" of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; (141):17–27.6. MacDonald W, Swarts E, Beaver R. Penetration and shear strength of cement-bone interfaces in vivo. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (286):283–288.
Article7. Schmalzried TP, Kwong LM, Jasty M, et al. The mechanism of loosening of cemented acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty: analysis of specimens retrieved at autopsy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; (274):60–78.8. Fujita H, Ido K, Matsuda Y, et al. Evaluation of bioactive bone cement in canine total hip arthroplasty. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000; 49(2):273–288.9. Liang B, Fujibayashi S, Fujita H, Ise K, Neo M, Nakamura T. Long-term follow-up study of bioactive bone cement in canine total hip arthroplasty. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2006; 16(4):291–299.10. Ni GX, Lin JH, Chiu PK, Li ZY, Lu WW. Effect of strontiumcontaining hydroxyapatite bone cement on bone remodeling following hip replacement. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010; 21(1):377–384.11. Digas G, Karrholm J, Thanner J. Addition of fluoride to acrylic bone cement does not improve fixation of a total hip arthroplasty stem. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006; 448:58–66.12. Kim SC, Ohashi H, Oonishi H Jr, Oonishi H. Histologic findings at 14 and 18 years after cemented total hip arthroplasty with interface bioactive bone cement technique. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22(7):1067–1069.13. Zyman Z, Weng J, Liu X, Zhang X, Ma Z. Amorphous phase and morphological structure of hydroxyapatite plasma coatings. Biomaterials. 1993; 14(3):225–228.
Article14. Geesink RG. Osteoconductive coatings for total joint arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; (395):53–65.
Article15. Chou L, Marek B, Wagner WR. Effects of hydroxylapatite coating crystallinity on biosolubility, cell attachment efficiency and proliferation in vitro. Biomaterials. 1999; 20(10):977–985.
Article16. Story BJ, Burgess AV, La D, Wagner WR. In vitro stability of a highly crystalline hydroxylapatite coating in a saturated citric acid solution. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999; 48(6):841–847.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- In Vitro Measurement of the Interface Micromotion at the Cemented Total Hip Arthroplasty System with Different Surface Roughness
- Biomechanical analysis of the Effect of Debondign of Cement - Femoral Stem Interface to the Cement - Bone Interface - three - dimensional non - linear finite element analysis -
- Cement Filling Technique to Prevent Greater Trochanter Displacement in Hip Arthroplasty for Femoral Intertrochanteric Fracture: A Technical Note
- Cemented Total Hip Replacement Arthroplasty
- A Review and Description of Acetabular Impaction Bone Grafting: Updating the Traditional Technique