J Korean Med Sci.
2016 May;31(5):822-823. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.5.822.
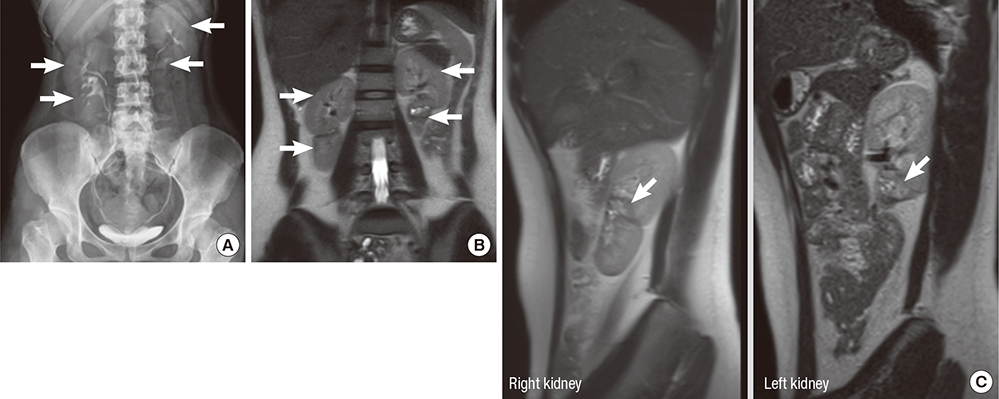
Bilateral Supernumerary Kidney
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Wan Fang Hospital, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan. wingchan@tmu.edu.tw
- 2Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan.
- KMID: 2373685
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.5.822
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Favorito LA, Morais AR. Evaluation of supernumerary kidney with fusion using magnetic resonance image. Int Braz J Urol. 2012; 38:428–429.2. Keskin S, Batur A, Keskin Z, Koc A, Firat Ozcan I. Bilateral supernumerary kidney: a very rare presentation. Iran J Radiol. 2014; 11:e11069.3. Bernik TR, Ravnic DJ, Bernik SF, Wallack MK. Ectopic supernumerary kidney, a cause of para-aortic mass: case report and review. Am Surg. 2001; 67:657–659.4. Conrad GR, Loes DJ. Ectopic supernumerary kidney. Functional assessment using radionuclide imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 1987; 12:253–257.