J Korean Med Sci.
2016 May;31(5):724-728. 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.5.724.
Translation and Validation of a Korean Version of the Xerostomia Inventory in Patients with Primary Sjögren's Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. rapark@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2373669
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2016.31.5.724
Abstract
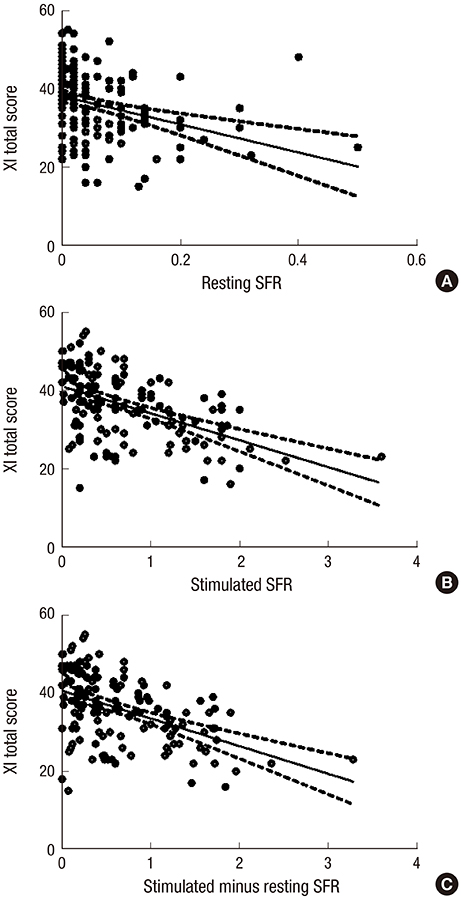
- This study was conducted to generate and validate a cross-culturally adapted Korean version of the xerostomia inventory (XI), an 11-item questionnaire designed to measure the severity of xerostomia. The original English version of the XI was translated into Korean according to the guidelines for cross-cultural adaptation of health-related quality-of-life measures. Among a prospective cohort of primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS) in Korea, 194 patients were analyzed. Internal consistency was evaluated by using Cronbach's alpha, and test-retest reliability was obtained by using an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) analysis. Construct validity was investigated by performing a correlation analysis between XI total score and salivary flow rate (SFR). Cronbach's alpha for internal consistency was 0.868, and the ICC for test-retest reliability ranged from 0.48 to 0.827, with a median value of 0.72. Moderate negative correlations between XI score and stimulated SFR, unstimulated SFR, and differential (stimulated minus unstimulated) SFR were observed (Spearman's rho, Ï = -0.515, -0.447, and -0.482, respectively; P < 0.001). The correlation analysis between the visual analogue scale (VAS) score of overall dryness and SFR indicated a smaller Ï value (-0.235 [P = 0.006], -0.243 [P = 0.002], and -0.252 [P = 0.003], respectively), which supports that XI more accurately reflects the degree of xerostomia in the pSS patients. In conclusion, the Korean version of the XI is a reliable tool to estimate the severity of xerostomia in patients with pSS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mavragani CP, Moutsopoulos NM, Moutsopoulos HM. The management of Sjögren’s syndrome. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006; 2:252–261.2. Patel R, Shahane A. The epidemiology of Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Epidemiol. 2014; 6:247–255.3. Kim JY, Park SH, Kim SK, Hyun DS, Kum YS, Jung KJ, Choe JY. Lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a case report. Korean J Intern Med. 2011; 26:108–111.4. Kim SM, Waters P, Vincent A, Kim SY, Kim HJ, Hong YH, Park KS, Min JH, Sung JJ, Lee KW. Sjogren’s syndrome myelopathy: spinal cord involvement in Sjogren’s syndrome might be a manifestation of neuromyelitis optica. Mult Scler. 2009; 15:1062–1068.5. Kim YK, Song HC, Kim WY, Yoon HE, Choi YJ, Ki CS, Park CW, Yang CW, Kim J, Kim YS, et al. Acquired Gitelman syndrome in a patient with primary Sjögren syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008; 52:1163–1167.6. Cho SG, Yi JH, Han SW, Kim HJ. Electrolyte imbalances and nephrocalcinosis in acute phosphate poisoning on chronic type 1 renal tubular acidosis due to Sjögren’s syndrome. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:336–339.7. Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, Daniels TE, Fox PC, Fox RI, Kassan SS, et al. Classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002; 61:554–558.8. Shiboski SC, Shiboski CH, Criswell L, Baer A, Challacombe S, Lanfranchi H, Schiødt M, Umehara H, Vivino F, Zhao Y, et al. American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a data-driven, expert consensus approach in the Sjögren’s International Collaborative Clinical Alliance cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:475–487.9. Hay EM, Thomas E, Pal B, Hajeer A, Chambers H, Silman AJ. Weak association between subjective symptoms or and objective testing for dry eyes and dry mouth: results from a population based study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998; 57:20–24.10. Thomson WM, Chalmers JM, Spencer AJ, Williams SM. The Xerostomia Inventory: a multi-item approach to measuring dry mouth. Community Dent Health. 1999; 16:12–17.11. Cho HJ, Yoo JJ, Yun CY, Kang EH, Lee HJ, Hyon JY, Song YW, Lee YJ. The EULAR Sjogren’s syndrome patient reported index as an independent determinant of health-related quality of life in primary Sjogren’s syndrome patients: in comparison with non-Sjogren’s sicca patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013; 52:2208–2217.12. Serrano C, Fariña MP, Pérez C, Fernández M, Forman K, Carrasco M. Translation and validation of a Spanish version of the xerostomia inventory. Gerodontology. Forthcoming. 2015.13. da Mata AD, da Silva Marques DN, Freitas FM, de Almeida Rato Amaral JP, Trindade RT, Barcelos FA, Vaz Patto JM. Translation, validation, and construct reliability of a Portuguese version of the Xerostomia Inventory. Oral Dis. 2012; 18:293–298.14. He SL, Wang JH, Li M. Validation of the Chinese version of the Summated Xerostomia Inventory (SXI). Qual Life Res. 2013; 22:2843–2847.15. Bland JM, Altman DG. Cronbach’s alpha. BMJ. 1997; 314:572.16. Thomson WM, Williams SM. Further testing of the xerostomia inventory. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000; 89:46–50.17. Borges BC, Fulco GM, Souza AJ, de Lima KC. Xerostomia and hyposalivation: a preliminary report of their prevalence and associated factors in Brazilian elderly diabetic patients. Oral Health Prev Dent. 2010; 8:153–158.18. Leung KC, McMillan AS, Wong MC, Leung WK, Mok MY, Lau CS. The efficacy of cevimeline hydrochloride in the treatment of xerostomia in Sjögren’s syndrome in southern Chinese patients: a randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study. Clin Rheumatol. 2008; 27:429–436.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rehabilitation using twin-stage method for a Sjögren's syndrome patient with severe discoloration and attrition on upper and lower anterior teeth
- A Case of Treatment with Steroid and Hydrochloroquine of Thrombocytopenia in Primary Sjögren's Syndrome
- Longitudinal Changes of the European League Against Rheumatism Sjögren's Syndrome Patient Reported Index in Korean Patients with Primary Sjögren's Syndrome
- A Case of Sjögren-Larsson Syndrome
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Xerostomia