Ann Lab Med.
2017 Jan;37(1):28-33. 10.3343/alm.2017.37.1.28.
Comparison of Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (ACR) Between ACR Strip Test and Quantitative Test in Prediabetes and Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Health Promotion Research Institute, Korea Association of Health Promotion, Seoul, Korea. cellonah@hanmail.net
- 2MEDIcheck LAB, Korea Association of Health Promotion, Cheongju, Korea.
- KMID: 2373610
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2017.37.1.28
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Albuminuria is generally known as a sensitive marker of renal and cardiovascular dysfunction. It can be used to help predict the occurrence of nephropathy and cardiovascular disorders in diabetes. Individuals with prediabetes have a tendency to develop macrovascular and microvascular pathology, resulting in an increased risk of retinopathy, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic renal diseases. We evaluated the clinical value of a strip test for measuring the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) in prediabetes and diabetes.
METHODS
Spot urine samples were obtained from 226 prediabetic and 275 diabetic subjects during regular health checkups. Urinary ACR was measured by using strip and laboratory quantitative tests.
RESULTS
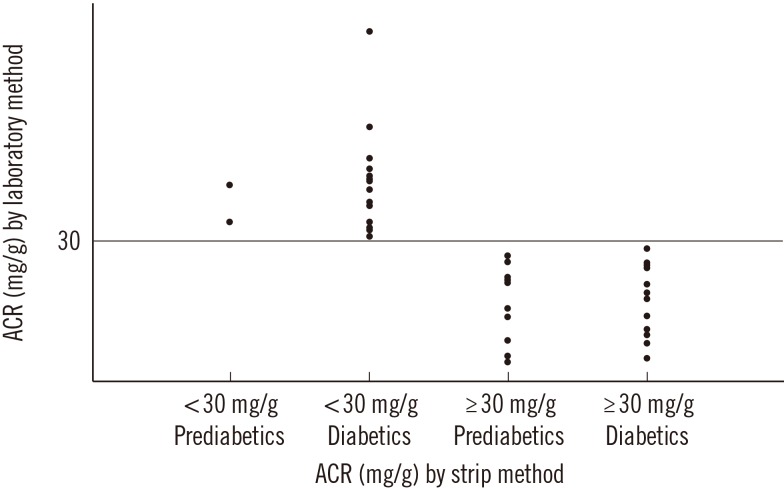
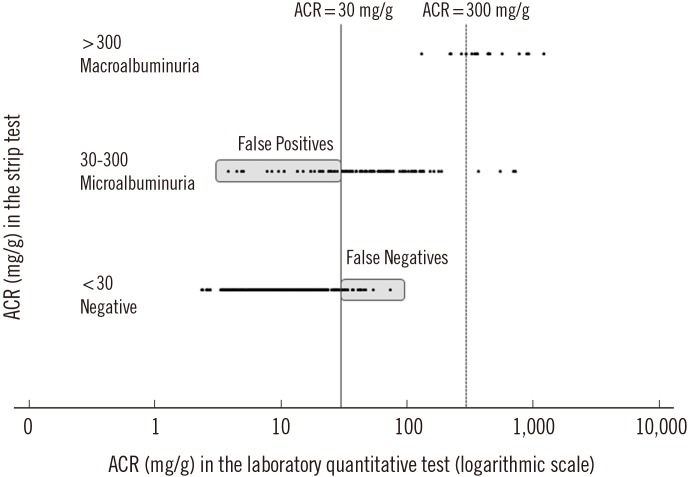
The positive rates of albuminuria measured by using the ACR strip test were 15.5% (microalbuminuria, 14.6%; macroalbuminuria, 0.9%) and 30.5% (microalbuminuria, 25.1%; macroalbuminuria, 5.5%) in prediabetes and diabetes, respectively. In the prediabetic population, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and overall accuracy of the ACR strip method were 92.0%, 94.0%, 65.7%, 99.0%, and 93.8%, respectively; the corresponding values in the diabetic population were 80.0%, 91.6%, 81.0%, 91.1%, and 88.0%, respectively. The median [interquartile range] ACR values in the strip tests for measurement ranges of <30, 30-300, and >300 mg/g were 9.4 [6.3-15.4], 46.9 [26.5-87.7], and 368.8 [296.2-575.2] mg/g, respectively, using the laboratory method.
CONCLUSIONS
The ACR strip test showed high sensitivity, specificity, and negative predictive value, suggesting that the test can be used to screen for albuminuria in cases of prediabetes and diabetes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Performance Evaluation of MEDITAPE UC-11A Strip Test in Estimating the Urine Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio and Urine Protein-to-Creatinine Ratio
Shinae Yu, Sae Am Song, Kyung Ran Jun, Jeong Nyeo Lee
Lab Med Online. 2020;10(1):52-57. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2020.10.1.52.Relationship between Hypertension and Mircroalbuminuria according to Obesity Status in Prediabetes
Jieun Chu, Seon Cho, Suyoung Kim, Eunjoo Kwon, Eun-Hee Nah
Korean J Health Promot. 2019;19(4):202-209. doi: 10.15384/kjhp.2019.19.4.202.
Reference
-
1. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. The prevalence of retinopathy in impaired glucose tolerance and recent-onset diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program. Diabet Med. 2007; 24:137–144. PMID: 17257275.2. Wingard DL, Barrett-Connor EL, Scheidt-Nave C, McPhillips JB. Prevalence of cardiovascular and renal complications in older adults with normal or impaired glucose tolerance or NIDDM. A population-based study. Diabetes Care. 1993; 16:1022–1025. PMID: 8359095.3. Levitzky YS, Pencina MJ, D'Agostino RB, Meigs JB, Murabito JM, Vasan RS, et al. Impact of impaired fasting glucose on cardiovascular disease: the Framingham Heart Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 51:264–270. PMID: 18206734.4. Ford ES, Zhao G, Li C. Pre-diabetes and the risk for cardiovascular disease: a systematic review of the evidence. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 55:1310–1317. PMID: 20338491.5. Plantinga LC, Crews DC, Coresh J, Miller ER 3rd, Saran R, Yee J, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in US adults with undiagnosed diabetes or prediabetes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010; 5:673–682. PMID: 20338960.6. Dell'Omo G, Penno G, Giorgi D, Di Bello V, Mariani M, Pedrinelli R. Association between high-normal albuminuria and risk factors for cardiovascular and renal disease in essential hypertensive men. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002; 40:1–8. PMID: 12087554.7. Garg JP, Bakris GL. Microalbuminuria: marker of vascular dysfunction, risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Vasc Med. 2002; 7:35–43. PMID: 12083733.8. Wang XL, Lu JM, Pan CY, Tian H, Li CL. A comparison of urinary albumin excretion rate and microalbuminuria in various glucose tolerance subjects. Diabet Med. 2005; 22:332–335. PMID: 15717883.9. Viberti GC, Hill RD, Jarrett RJ, Argyropoulos A, Mahmud U, Keen H. Microalbuminuria as a predictor of clinical nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1982; 1:1430–1432. PMID: 6123720.10. Fioretto P, Caramori ML, Mauer M. The kidney in diabetes: dynamic pathways of injury and repair. The Camillo Golgi Lecture 2007. Diabetologia. 2008; 51:1347–1355. PMID: 18528679.11. Sacks DB, Arnold M, Bakris GL, Bruns DE, Horvath AR, Kirkman MS, et al. Position statement executive summary: guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:1419–1423. PMID: 21617111.12. Jager A, van Hinsbergh VW, Kostense PJ, Emeis JJ, Nijpels G, Dekker JM, et al. C-reactive protein and soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 are associated with elevated urinary albumin excretion but do not explain its link with cardiovascular risk. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002; 22:593–598. PMID: 11950696.13. Lambers Heerspink HJ, Brantsma AH, de Zeeuw D, Bakker SJ, de Jong PE, Gansevoort RT. PREVEND Study Group. Albuminuria assessed from first-morning-void urine samples versus 24-hour urine collections as a predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Am J Epidemiol. 2008; 168:897–905. PMID: 18775924.14. McTaggart MP, Price CP, Pinnock RG, Stevens PE, Newall RG, Lamb EJ. The diagnostic accuracy of a urine albumin-creatinine ratio point-of-care test for detection of albuminuria in primary care. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012; 60:787–794. PMID: 22721931.15. Graziani MS, Gambaro G, Mantovani L, Sorio A, Yabarek T, Abaterusso C, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of a reagent strip for assessing urinary albumin excretion in the general population. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009; 24:1490–1494. PMID: 19037085.16. Le Floch JP, Marre M, Rodier M, Passa P. Interest of Clinitek Microalbumin in screening for microalbuminuria: results of a multicentre study in 302 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab. 2001; 27:36–39. PMID: 11240444.17. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37(Suppl 1):S81–S90. PMID: 24357215.18. Friedman AN, Marrero D, Ma Y, Ackermann R, Narayan KM, Barrett-Connor E, et al. Value of urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio as a predictor of type 2 diabetes in pre-diabetic individuals. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:2344–2348. PMID: 18796622.19. Zhou Y, Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Gu JJ, Ruan XN, Zhao GM, Xu WH, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease across levels of glycemia among adults in Pudong New Area, Shanghai, China. BMC Nephrol. 2013; 14:253. PMID: 24238578.20. Levey AS, Eckardt KU, Tsukamoto Y, Levin A, Coresh J, Rossert J, et al. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005; 67:2089–2100. PMID: 15882252.21. Guy M, Newall R, Borzomato J, Kalra PA, Price C. Diagnostic accuracy of the urinary albumin: creatinine ratio determined by the CLINITEK Microalbumin and DCA 2000+ for the rule-out of albuminuria in chronic kidney disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 399:54–58. PMID: 18834870.22. Omoruyi FO, Mustafa GM, Okorodudu AO, Petersen JR. Evaluation of the performance of urine albumin, creatinine and albumin-creatinine ratio assay on two POCT analyzers relative to a central laboratory method. Clin Chim Acta. 2012; 413:625–629. PMID: 22212624.23. Dutta D, Choudhuri S, Mondal SA, Mukherjee S, Chowdhury S. Urinary albumin : creatinine ratio predicts prediabetes progression to diabetes and reversal to normoglycemia: role of associated insulin resistance, inflammatory cytokines and low vitamin D. J Diabetes. 2014; 6:316–322. PMID: 24251376.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnostic Utility of the URiSCAN 2 ACR Strip as a Point-of-care Test for Estimating Urine Albumin-Creatinine Ratios
- Albumin Creatinine Ratio as Screening Test for Microalbuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Performance Evaluation of the Afinion AS100 Analyzer for Its Use in the Albumin Creatinine Ratio Test
- Proposed Imprecision Quality Goals for Urinary Albumin/Creatinine Ratio
- The Efficacy of Urinary Albumin-to-Osmolality Ratio in Predicting 24-hour Urine Albumin Excretion in Type 2 DM Patients