Ann Lab Med.
2016 Jul;36(4):353-357. 10.3343/alm.2016.36.4.353.
In vitro Stability of Heat Shock Protein 27 in Serum and Plasma Under Different Pre-analytical Conditions: Implications for Large-Scale Clinical Studies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Christian Doppler Laboratory for Cardiac and Thoracic Diagnosis and Regeneration, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine II, Division of Cardiology, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria.
- 3Department of Gynaecology and Gynaecological Oncology, Gynecologic Cancer Unit, Comprehensive Cancer Center, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria.
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Konventhospital Barmherzige Brueder Linz, Linz, Austria. thomas.mueller@bs-lab.at
- 5Department of Cardiology, Department of Research and Education, General Hospital Celje, Celje, Slovenia.
- 6Faculty of Medicine, University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia.
- 7Department of Thoracic Surgery, Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria.
- KMID: 2373555
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2016.36.4.353
Abstract
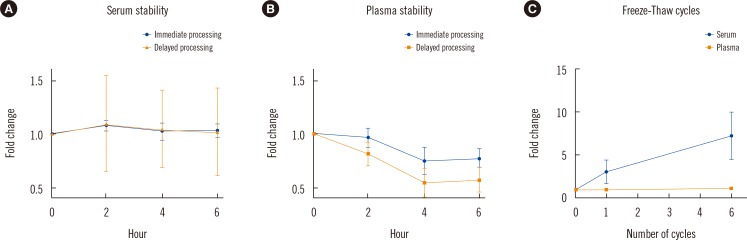
- The effects of storage temperatures, repeated freeze-thaw cycles, or delays in separating plasma or serum from blood samples are largely unknown for heat shock protein 27 (HSP27). We evaluated (1) the imprecision of the HSP27 assay used in this study; (2) the in vitro stability of HSP27 in blood samples stored at 4℃ for up to 6 hr with immediate and delayed serum/plasma separation from cells; and (3) the in vitro stability of HSP27 in blood samples stored at -80℃ after repeated freeze-thaw cycles. The ELISA to detect HSP27 in this study showed a within-run CV of <9% and a total CV of <15%. After 4-6 hr of storage at 4℃, HSP27 concentrations remained stable when using serum tubes irrespective of sample handling, but HSP27 concentrations decreased by 25-45% when using EDTA plasma tubes. Compared with baseline HSP27, one freeze-thaw cycle had no effect on serum concentrations. However, plasma concentrations increased by 3.1-fold after one freeze-thaw cycle and by 7.3-fold after five freeze-thaw cycles. In conclusion, serum is an appropriate biological sample type for use in epidemiological and large-scale clinical studies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mymrikov EV, Seit-Nebi AS, Gusev NB. Large potentials of small heat shock proteins. Physiol Rev. 2011; 91:1123–1159. PMID: 22013208.
Article2. Lianos GD, Alexiou GA, Mangano A, Mangano A, Rausei S, Boni L, et al. The role of heat shock proteins in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015; 360:114–118. PMID: 25721081.
Article3. Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Saber H, Ferns GA. The potential role of heat shock protein 27 in cardiovascular disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2012; 413:15–24. PMID: 21514288.
Article4. Park HK, Park EC, Bae SW, Park MY, Kim SW, Yoo HS, et al. Expression of heat shock protein 27 in human atherosclerotic plaques and increased plasma level of heat shock protein 27 in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Circulation. 2006; 114:886–893. PMID: 16923754.
Article5. Périard JD, Ruell P, Caillaud C, Thompson MW. Plasma Hsp72 (HSPA1A) and Hsp27 (HSPB1) expression under heat stress: influence of exercise intensity. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2012; 17:375–383. PMID: 22222935.
Article6. Gruden G, Carucci P, Lolli V, Cosso L, Dellavalle E, Rolle E, et al. Serum heat shock protein 27 levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013; 18:235–241. PMID: 23073653.
Article7. Jan Ankersmit H, Nickl S, Hoeltl E, Toepker M, Lambers C, Mitterbauer A, et al. Increased serum levels of HSP27 as a marker for incipient chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in young smokers. Respiration. 2012; 83:391–399. PMID: 22469636.
Article8. Son SJ, Lee KS, Chung JH, Chang KJ, Roh HW, Kim SH, et al. Increased plasma levels of heat shock protein 70 associated with subsequent clinical conversion to mild cognitive impairment in cognitively healthy elderly. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0119180. PMID: 25768018.
Article9. Cui X, Xing J, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Luo X, Zhang Z, et al. COPD and levels of Hsp70 (HSPA1A) and Hsp27 (HSPB1) in plasma and lymphocytes among coal workers: a case-control study. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015; 20:473–481. PMID: 25620081.
Article10. Marquez E, Sadowski E, Reese S, Vidyasagar A, Artz N, Fain S, et al. Serum HSP27 is associated with medullary perfusion in kidney allografts. J Nephrol. 2012; 25:1075–1080. PMID: 22383348.
Article11. Hu YF, Yeh HI, Tsao HM, Tai CT, Lin YJ, Chang SL, et al. Electrophysiological correlation and prognostic impact of heat shock protein 27 in atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2012; 5:334–340. PMID: 22354927.
Article12. Sato Y, Harada K, Sasaki M, Yasaka T, Nakanuma Y. Heat shock proteins 27 and 70 are potential biliary markers for the detection of cholangiocarcinoma. Am J Pathol. 2012; 180:123–130. PMID: 22051775.
Article13. Zimmermann M, Mueller T, Dieplinger B, Bekos C, Beer L, Hofbauer H, et al. Circulating heat shock protein 27 as a biomarker for the differentiation of patients with lung cancer and healthy controls--a clinical comparison of different enzyme linked immunosorbent assays. Clin Lab. 2014; 60:999–1006. PMID: 25016706.
Article14. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Evaluation of precision performance of clinical chemistry devices; approved guideline. CLSI document EP5-A. Wayne, PA: CLSI;1999.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 m-RNA in Rat Bladder Overdistended by Diuresis
- Environmental factors regulating the expression of Porphyromonas gingivalis heat shock protein
- The Protective Effect of Induced Heat Shock Protein in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells
- Heat Shock Protein Induction By An Infrared Warm Compression Device
- Expression of Heat Shock Protein 27 and Apoptosis in Renal Cell Carcinomas