Ann Lab Med.
2016 Mar;36(2):85-100. 10.3343/alm.2016.36.2.85.
Systematic Classification of Mixed-Lineage Leukemia Fusion Partners Predicts Additional Cancer Pathways
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute of Pharmaceutical Biology/DCAL, Goethe-University of Frankfurt, Biocenter, Frankfurt/Main, Germany. Rolf.Marschalek@em.uni-frankfurt.de
- KMID: 2373507
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2016.36.2.85
Abstract
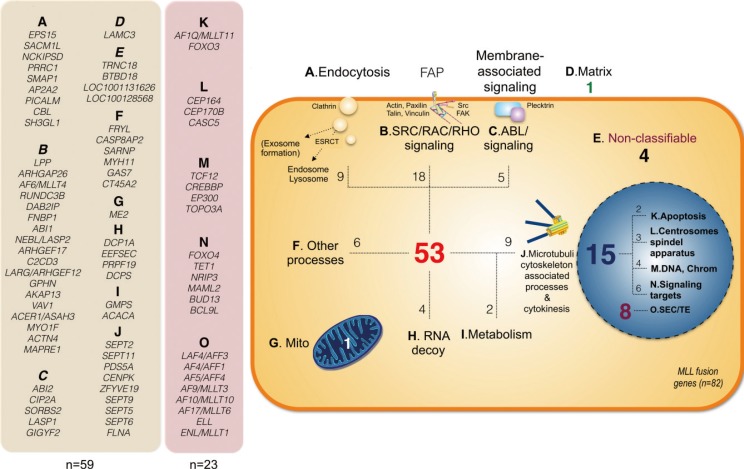
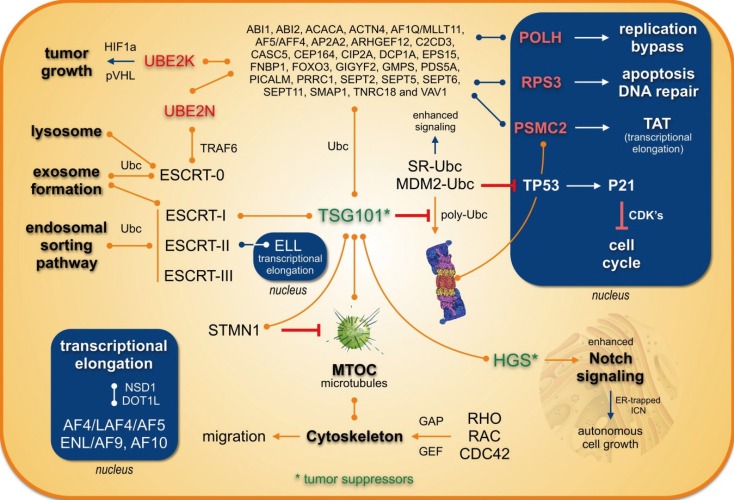
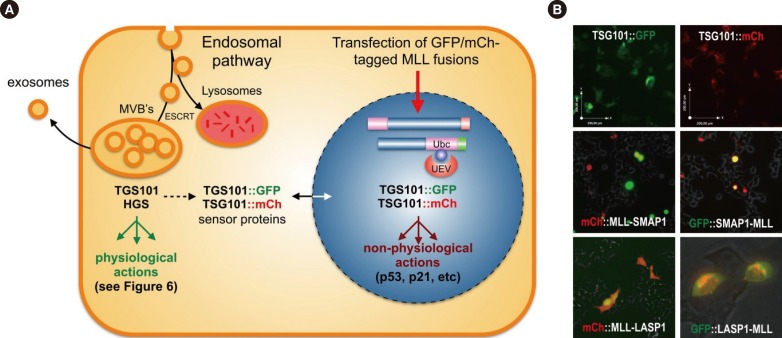
- Chromosomal translocations of the human mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL) gene have been analyzed for more than 20 yr at the molecular level. So far, we have collected about 80 direct MLL fusions (MLL-X alleles) and about 120 reciprocal MLL fusions (X-MLL alleles). The reason for the higher amount of reciprocal MLL fusions is that the excess is caused by 3-way translocations with known direct fusion partners. This review is aiming to propose a solution for an obvious problem, namely why so many and completely different MLL fusion alleles are always leading to the same leukemia phenotypes (ALL, AML, or MLL). This review is aiming to explain the molecular consequences of MLL translocations, and secondly, the contribution of the different fusion partners. A new hypothesis will be posed that can be used for future research, aiming to find new avenues for the treatment of this particular leukemia entity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nilson I, Löchner K, Siegler G, Greil J, Beck JD, Fey GH, et al. Exon/intron structure of the human ALL-1 (MLL) gene involved in translocations to chromosomal region 11q23 and acute leukaemias. Br J Haematol. 1996; 93:966–972. PMID: 8703835.2. Ziemin-van der Poel S, McCabe NR, Gill HJ, Espinosa R 3rd, Patel Y, Harden A, et al. Identification of a gene, MLL, that spans the breakpoint in 11q23 translocations associated with human leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991; 88:10735–10739. PMID: 1720549.3. Corral J, Lavenir I, Impey H, Warren AJ, Forster A, Larson TA, et al. An Mll-AF9 fusion gene made by homologous recombination causes acute leukemia in chimeric mice: a method to create fusion oncogenes. Cell. 1996; 85:853–861. PMID: 8681380.4. Lavau C, Szilvassy SJ, Slany R, Cleary ML. Immortalization and leukemic transformation of a myelomonocytic precursor by retrovirally transduced HRX-ENL. EMBO J. 1997; 16:4226–4237. PMID: 9250666.5. DiMartino JF, Miller T, Ayton PM, Landewe T, Hess JL, Cleary ML, et al. A carboxy-terminal domain of ELL is required and sufficient for immortalization of myeloid progenitors by MLL-ELL. Blood. 2000; 96:3887–3893. PMID: 11090074.6. DiMartino JF, Ayton PM, Chen EH, Naftzger CC, Young BD, Cleary ML. The AF10 leucine zipper is required for leukemic transformation of myeloid progenitors by MLL-AF10. Blood. 2002; 99:3780–3785. PMID: 11986236.7. So CW, Karsunky H, Wong P, Weissman IL, Cleary ML. Leukemic transformation of hematopoietic progenitors by MLL-GAS7 in the absence of Hoxa7 or Hoxa9. Blood. 2004; 103:3192–3199. PMID: 15070702.8. Krivtsov AV, Feng Z, Lemieux ME, Faber J, Vempati S, Sinha AU, et al. H3K79 methylation profiles define murine and human MLL-AF4 leukemias. Cancer Cell. 2008; 14:355–368. PMID: 18977325.9. Bursen A, Schwabe K, Rüster B, Henschler R, Ruthardt M, Dingermann T, et al. The AF4-MLL fusion protein is capable of inducing ALL in mice without requirement of MLL-AF4. Blood. 2010; 115:3570–3579. PMID: 20194896.10. Greaves M. When one mutation is all it takes. Cancer Cell. 2015; 27:433–434. PMID: 25873168.11. Jude CD, Climer L, Xu D, Artinger E, Fisher JK, Ernst P. Unique and independent roles for MLL in adult hematopoietic stem cells and progenitors. Cell Stem Cell. 2007; 1:324–337. PMID: 18371366.12. Arai S, Yoshimi A, Shimabe M, Ichikawa M, Nakagawa M, Imai Y, et al. Evi-1 is a transcriptional target of mixed-lineage leukemia oncoproteins in hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2011; 117:6304–6314. PMID: 21190993.13. Huang X, Spencer GJ, Lynch JT, Ciceri F, Somerville TD, Somervaille TC. Enhancers of Polycomb EPC1 and EPC2 sustain the oncogenic potential of MLL leukemia stem cells. Leukemia. 2014; 28:1081–1091. PMID: 24166297.14. Zhou J, Wu J, Li B, Liu D, Yu J, Yan X, et al. PU.1 is essential for MLL leukemia partially via crosstalk with the MEIS/HOX pathway. Leukemia. 2014; 28:1436–1448. PMID: 24445817.15. Park SM, Gönen M, Vu L, Minuesa G, Tivnan P, Barlowe TS, et al. Musashi2 sustains the mixed-lineage leukemia-driven stem cell regulatory program. J Clin Invest. 2015; 125:1286–1298. PMID: 25664853.16. Meyer C, Hofmann J, Burmeister T, Gröger D, Park TS, Emerenciano M, et al. The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias in 2013. Leukemia. 2013; 27:2165–2176. PMID: 23628958.17. Balgobind BV, Raimondi SC, Harbott J, Zimmermann M, Alonzo TA, Auvrignon A, et al. Novel prognostic subgroups in childhood 11q23/MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia: results of an international retrospective study. Blood. 2009; 114:2489–2496. PMID: 19528532.18. Ayton PM, Cleary ML. Transformation of myeloid progenitors by MLL oncoproteins is dependent on Hoxa7 and Hoxa9. Genes Dev. 2003; 17:2298–2307. PMID: 12952893.19. Ernst P, Mabon M, Davidson AJ, Zon LI, Korsmeyer SJ. An Mll-dependent Hox program drives hematopoietic progenitor expansion. Curr Biol. 2004; 14:2063–2069. PMID: 15556871.20. 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. Abecasis GR, Altshuler D, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, et al. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature. 2010; 467:1061–1073. PMID: 20981092.21. Reichel M, Gillert E, Nilson I, Siegler G, Greil J, Fey GH, et al. Fine structure of translocation breakpoints in leukemic blasts with chromosomal translocation t(4;11): the DNA damage-repair model of translocation. Oncogene. 1998; 17:3035–3044. PMID: 9881706.22. Gillert E, Leis T, Repp R, Reichel M, Hösch A, Breitenlohner I, et al. A DNA damage repair mechanism is involved in the origin of chromosomal translocations t(4;11) in primary leukemic cells. Oncogene. 1999; 18:4663–4671. PMID: 10467413.23. Stephens PJ, Greenman CD, Fu B, Yang F, Bignell GR, Mudie LJ, et al. Massive genomic rearrangement acquired in a single catastrophic event during cancer development. Cell. 2011; 144:27–40. PMID: 21215367.24. Djabali M, Selleri L, Parry P, Bower M, Young BD, Evans GA. A trithorax-like gene is interrupted by chromosome 11q23 translocations in acute leukaemias. Nat Genet. 1992; 2:113–118. PMID: 1303259.25. Tkachuk DC, Kohler S, Cleary ML. Involvement of a homolog of Drosophila trithorax by 11q23 chromosomal translocations in acute leukemias. Cell. 1992; 71:691–700. PMID: 1423624.26. Gu Y, Nakamura T, Alder H, Prasad R, Canaani O, Cimino G, et al. The t(4;11) chromosome translocation of human acute leukemias fuses the ALL-1 gene, related to Drosophila trithorax, to the AF-4 gene. Cell. 1992; 71:701–708. PMID: 1423625.27. Rasio D, Schichman SA, Negrini M, Canaani E, Croce CM. Complete exon structure of the ALL1 gene. Cancer Res. 1996; 56:1766–1769. PMID: 8620491.28. Meyer C, Kowarz E, Schneider B, Oehm C, Klingebiel T, Dingermann T, et al. Genomic DNA of leukemic patients: target for clinical diagnosis of MLL rearrangements. Biotechnol J. 2006; 1:656–663. PMID: 16892314.29. Rössler T, Marschalek R. An alternative splice process renders the MLL protein either into a transcriptional activator or repressor. Pharmazie. 2013; 68:601–607. PMID: 23923644.30. Zeisig DT, Bittner CB, Zeisig BB, García-Cuéllar MP, Hess JL, Slany RK. The eleven-nineteen-leukemia protein ENL connects nuclear MLL fusion partners with chromatin. Oncogene. 2005; 24:5525–5532. PMID: 15856011.31. Bitoun E, Oliver PL, Davies KE. The mixed-lineage leukemia fusion partner AF4 stimulates RNA polymerase II transcriptional elongation and mediates coordinated chromatin remodeling. Hum Mol Genet. 2007; 16:92–106. PMID: 17135274.32. Mueller D, García-Cuéllar MP, Bach C, Buhl S, Maethner E, Slany RK. Misguided transcriptional elongation causes mixed lineage leukemia. PLoS Biol. 2009; 7:e1000249. PMID: 19956800.33. Benedikt A, Baltruschat S, Scholz B, Bursen A, Arrey TN, Meyer B, et al. The leukemogenic AF4-MLL fusion protein causes P-TEFb kinase activation and altered epigenetic signatures. Leukemia. 2011; 25:135–144. PMID: 21030982.34. Hsieh JJ, Cheng EH, Korsmeyer SJ. Taspase1: a threonine aspartase required for cleavage of MLL and proper HOX gene expression. Cell. 2003; 115:293–303. PMID: 14636557.35. Adler HT, Nallaseth FS, Walter G, Tkachuk DC. HRX leukemic fusion proteins form a heterocomplex with the leukemia-associated protein SET and protein phosphatase 2A. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272:28407–28414. PMID: 9353299.36. Adler HT, Chinery R, Wu DY, Kussick SJ, Payne JM, Fornace AJ Jr, et al. Leukemic HRX fusion proteins inhibit GADD34-induced apoptosis and associate with the GADD34 and hSNF5/INI1 proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1999; 19:7050–7060. PMID: 10490642.37. Nakamura T, Mori T, Tada S, Krajewski W, Rozovskaia T, Wassell R, et al. ALL-1 is a histone methyltransferase that assembles a supercomplex of proteins involved in transcriptional regulation. Mol Cell. 2002; 10:1119–1128. PMID: 12453419.38. Yokoyama A, Kitabayashi I, Ayton PM, Cleary ML, Ohki M. Leukemia proto-oncoprotein MLL is proteolytically processed into 2 fragments with opposite transcriptional properties. Blood. 2002; 100:3710–3718. PMID: 12393701.39. Xia ZB, Anderson M, Diaz MO, Zeleznik-Le NJ. MLL repression domain interacts with histone deacetylases, the polycomb group proteins HPC2 and BMI-1, and the corepressor C-terminal-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003; 100:8342–8347. PMID: 12829790.40. Yokoyama A, Wang Z, Wysocka J, Sanyal M, Aufiero DJ, Kitabayashi I, et al. Leukemia proto-oncoprotein MLL forms a SET1-like histone methyltransferase complex with menin to regulate Hox gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 2004; 24:5639–5649. PMID: 15199122.41. Wysocka J, Swigut T, Milne TA, Dou Y, Zhang X, Burlingame AL, et al. WDR5 associates with histone H3 methylated at K4 and is essential for H3 K4 methylation and vertebrate development. Cell. 2005; 121:859–872. PMID: 15960974.42. Dou Y, Milne TA, Tackett AJ, Smith ER, Fukuda A, Wysocka J, et al. Physical association and coordinate function of the H3 K4 methyltransferase MLL1 and the H4 K16 acetyltransferase MOF. Cell. 2005; 121:873–885. PMID: 15960975.43. Dou Y, Milne TA, Ruthenburg AJ, Lee S, Lee JW, Verdine GL, et al. Regulation of MLL1 H3K4 methyltransferase activity by its core components. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006; 13:713–719. PMID: 16878130.44. Milne TA, Kim J, Wang GG, Stadler SC, Basrur V, Whitcomb SJ, et al. Multiple interactions recruit MLL1 and MLL1 fusion proteins to the HOXA9 locus in leukemogenesis. Mol Cell. 2010; 38:853–863. PMID: 20541448.45. Muntean AG, Tan J, Sitwala K, Huang Y, Bronstein J, Connelly JA, et al. The PAF complex synergizes with MLL fusion proteins at HOX loci to promote leukemogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2010; 17:609–621. PMID: 20541477.46. Chang PY, Hom RA, Musselman CA, Zhu L, Kuo A, Gozani O, et al. Binding of the MLL PHD3 finger to histone H3K4me3 is required for MLL-dependent gene transcription. J Mol Biol. 2010; 400:137–144. PMID: 20452361.47. Hom RA, Chang PY, Roy S, Musselman CA, Glass KC, Selezneva AI, et al. Molecular mechanism of MLL PHD3 and RNA recognition by the Cyp33 RRM domain. J Mol Biol. 2010; 400:145–154. PMID: 20460131.48. Wang Z, Song J, Milne TA, Wang GG, Li H, Allis CD, et al. Pro isomerization in MLL1 PHD3-bromo cassette connects H3K4me readout to CyP33 and HDAC-mediated repression. Cell. 2010; 141:1183–1194. PMID: 20541251.49. Schraets D, Lehmann T, Dingermann T, Marschalek R. MLL-mediated transcriptional gene regulation investigated by gene expression profiling. Oncogene. 2003; 22:3655–3668. PMID: 12789274.50. Chen J, Santillan DA, Koonce M, Wei W, Luo R, Thirman MJ, et al. Loss of MLL PHD finger 3 is necessary for MLL-ENL-induced hematopoietic stem cell immortalization. Cancer Res. 2008; 68:6199–6207. PMID: 18676843.51. Muntean AG, Giannola D, Udager AM, Hess JL. The PHD fingers of MLL block MLL fusion protein-mediated transformation. Blood. 2008; 112:4690–4693. PMID: 18796627.52. Hayette S, Tigaud I, Maguer-Satta V, Bartholin L, Thomas X, Charrin C, et al. Recurrent involvement of the MLL gene in adult T-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2002; 99:4647–4649. PMID: 12066788.53. Quigley DI, Wolff DJ. Pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with aberrations of both MLL loci. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2006; 168:77–79. PMID: 16772125.54. Türkmen S, Timmermann B, Bartels G, Gröger D, Meyer C, Schwartz S, et al. Involvement of the MLL gene in adult T-lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2012; 51:1114–1124. PMID: 22927255.55. Broeker PL, Super HG, Thirman MJ, Pomykala H, Yonebayashi Y, Tanabe S, et al. Distribution of 11q23 breakpoints within the MLL breakpoint cluster region in de novo acute leukemia and in treatment-related acute myeloid leukemia: correlation with scaffold attachment regions and topoisomerase II consensus binding sites. Blood. 1996; 87:1912–1922. PMID: 8634439.56. Cimino G, Rapanotti MC, Biondi A, Elia L, Lo Coco F, Price C, et al. Infant acute leukemias show the same biased distribution of ALL1 gene breaks as topoisomerase II related secondary acute leukemias. Cancer Res. 1997; 57:2879–2883. PMID: 9230194.57. Felix CA, Hosler MR, Slater DJ, Parker RI, Masterson M, Whitlock JA, et al. MLL genomic breakpoint distribution within the breakpoint cluster region in de novo leukemia in children. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1998; 20:299–308. PMID: 9703001.58. Reichel M, Gillert E, Angermüller S, Hensel JP, Heidel F, Lode M, et al. Biased distribution of chromosomal breakpoints involving the MLL gene in infants versus children and adults with t(4;11) ALL. Oncogene. 2001; 20:2900–2907. PMID: 11420702.59. Wang J, Muntean AG, Hess JL. ECSASB2 mediates MLL degradation during hematopoietic differentiation. Blood. 2012; 119:1151–1161. PMID: 22174154.60. Marschalek R. It takes two-to-leukemia: about addictions and requirements. Leuk Res. 2011; 35:424–425. PMID: 21074267.61. Emerenciano M, Meyer C, Mansur MB, Marschalek R, Pombo-de-Oliveira MS. Brazilian Collaborative Study Group of Infant Acute Leukaemia. The distribution of MLL breakpoints correlates with outcome in infant acute leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2013; 161:224–236. PMID: 23432364.62. Scholz B, Kowarz E, Rössler T, Ahmad K, Steinhilber D, Marschalek R. AF4 and AF4N protein complexes: recruitment of P-TEFb kinase, their interactome and potential functions. Am J Blood Res. 2015; 5:10–24. PMID: 26171280.63. Gaussmann A, Wenger T, Eberle I, Bursen A, Bracharz S, Herr I, et al. Combined effects of the two reciprocal t(4;11) fusion proteins MLL-AF4 and AF4-MLL confer resistance to apoptosis, cell cycling capacity and growth transformation. Oncogene. 2007; 26:3352–3363. PMID: 17130830.64. Eberle I, Pless B, Braun M, Dingermann T, Marschalek R. Transcriptional properties of human NANOG1 and NANOG2 in acute leukemic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010; 38:5384–5395. PMID: 20427424.65. Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006; 126:663–676. PMID: 16904174.66. Smith E, Lin C, Shilatifard A. The super elongation complex (SEC) and MLL in development and disease. Genes Dev. 2011; 25:661–672. PMID: 21460034.67. Luo Z, Lin C, Shilatifard A. The super elongation complex (SEC) family in transcriptional control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012; 13:543–547. PMID: 22895430.68. Zheng X, Güller S, Beissert T, Puccetti E, Ruthardt M. BCR and its mutants, the reciprocal t(9;22)-associated ABL/BCR fusion proteins, differentially regulate the cytoskeleton and cell motility. BMC Cancer. 2006; 6:262. PMID: 17090304.69. Zheng X, Oancea C, Henschler R, Moore MA, Ruthardt M. Reciprocal t(9;22) ABL/BCR fusion proteins: leukemogenic potential and effects on B cell commitment. PLoS One. 2009; 4:e7661. PMID: 19876398.70. Rafiei A, Mian AA, Döring C, Metodieva A, Oancea C, Thalheimer FB, et al. The functional interplay between the t(9;22)-associated fusion proteins BCR/ABL and ABL/BCR in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphatic leukemia. PLoS Genet. 2015; 11:e1005144. PMID: 25919613.71. Essers MA, Trumpp A. Targeting leukemic stem cells by breaking their dormancy. Mol Oncol. 2010; 4:443–450. PMID: 20599449.72. Walf-Vorderwülbecke V, de Boer J, Horton SJ, van Amerongen R, Proost N, Berns A, et al. Frat2 mediates the oncogenic activation of Rac by MLL fusions. Blood. 2012; 120:4819–4828. PMID: 23074275.73. Wang Z, Smith KS, Murphy M, Piloto O, Somervaille TC, Cleary ML. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 in MLL leukaemia maintenance and targeted therapy. Nature. 2008; 455:1205–1209. PMID: 18806775.74. Maucuer A, Camonis JH, Sobel A. Stathmin interaction with a putative kinase and coiled-coil-forming protein domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995; 92:3100–3104. PMID: 7724523.75. Jackson BC, Ivanova IA, Dagnino L. An ELMO2-RhoG-ILK network modulates microtubule dynamics. Mol Biol Cell. 2015; 26:2712–2725. PMID: 25995380.76. Cassimeris L. The oncoprotein 18/stathmin family of microtubule destabilizers. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2002; 14:18–24. PMID: 11792540.77. Holmfeldt P, Sellin ME, Gullberg M. Upregulated Op18/stathmin activity causes chromosomal instability through a mechanism that evades the spindle assembly checkpoint. Exp Cell Res. 2010; 316:2017–2026. PMID: 20399773.78. Machado-Neto JA, Saad ST, Traina F. Stathmin 1 in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. BMB Rep. 2014; 47:660–665. PMID: 24667172.79. Slagsvold T, Pattni K, Malerød L, Stenmark H. Endosomal and non-endosomal functions of ESCRT proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2006; 16:317–326. PMID: 16716591.80. Webber J, Yeung V, Clayton A. Extracellular vesicles as modulators of the cancer microenvironment. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015; 40:27–34. PMID: 25662446.81. Boyiadzis M, Whiteside TL. Information transfer by exosomes: a new frontier in hematologic malignancies. Blood Rev. 2015; 29:281–290. PMID: 25686749.82. Mathivanan S, Ji H, Simpson RJ. Exosomes: extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J Proteomics. 2010; 73:1907–1920. PMID: 20601276.83. Prokopi M, Kousparou CA, Epenetos AA. The secret role of microRNAs in cancer stem cell development and potential therapy: a Notch-pathway approach. Front Oncol. 2015; 4:389. PMID: 25717438.84. Shilatifard A. Identification and purification of the Holo-ELL complex. Evidence for the presence of ELL-associated proteins that suppress the transcriptional inhibitory activity of ELL. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273:11212–11217. PMID: 9556611.85. Kamura T, Burian D, Khalili H, Schmidt SL, Sato S, Liu WJ, et al. Cloning and characterization of ELL-associated proteins EAP45 and EAP20. a role for yeast EAP-like proteins in regulation of gene expression by glucose. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:16528–16533. PMID: 11278625.86. Kushwah R, Guezguez B, Lee JB, Hopkins CI, Bhatia M. Pleiotropic roles of Notch signaling in normal, malignant, and developmental hematopoiesis in the human. EMBO Rep. 2014; 15:1128–1138. PMID: 25252682.87. Gao X. Ribosomal protein s3: a multifunctional target of attaching/effacing bacterial pathogens. Front Microbiol. 2011; 2:137. PMID: 21738525.88. Daigle SR, Olhava EJ, Therkelsen CA, Basavapathruni A, Jin L, Boriack-Sjodin PA, et al. Potent inhibition of DOT1L as treatment of MLL-fusion leukemia. Blood. 2013; 122:1017–1025. PMID: 23801631.89. Borkin D, He S, Miao H, Kempinska K, Pollock J, Chase J, et al. Pharmacologic iInhibition of the Menin-MLL interaction blocks progression of MLL leukemia in vivo. Cancer Cell. 2015; 27:589–602. PMID: 25817203.90. Jones WD, Dafou D, McEntagart M, Woollard WJ, Elmslie FV, Holder-Espinasse M, et al. De novo mutations in MLL cause Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2012; 91:358–364. PMID: 22795537.91. Ahmad K, Katryniok C, Scholz B, Merkens J, Löscher D, Marschalek R, et al. Inhibition of class I HDACs abrogates the dominant effect of MLL-AF4 by activation of wild-type MLL. Oncogenesis. 2014; 3:e127. PMID: 25402609.92. Bursen A, Moritz S, Gaussmann A, Moritz S, Dingermann T, Marschalek R. Interaction of AF4 wild-type and AF4.MLL fusion protein with SIAH proteins: indication for t(4;11) pathobiology? Oncogene. 2004; 23:6237–6249. PMID: 15221006.93. Kumar AR, Yao Q, Li Q, Sam TA, Kersey JH. t(4;11) leukemias display addiction to MLL-AF4 but not to AF4-MLL. Leuk Res. 2011; 35:305–309. PMID: 20869771.94. Sanders DS, Muntean AG, Hess JL. Significance of AF4-MLL reciprocal fusion in t(4;11) leukemias? Leuk Res. 2011; 35:299–300. PMID: 20952059.95. Emerenciano M, Kowarz E, Karl K, de Almeida Lopes B, Scholz B, Bracharz S, et al. Functional analysis of the two reciprocal fusion genes MLL-NEBL and NEBL-MLL reveal their oncogenic potential. Cancer Lett. 2013; 332:30–34. PMID: 23340173.96. Wilkinson AC, Ballabio E, Geng H, North P, Tapia M, Kerry J, et al. RUNX1 is a key target in t(4;11) leukemias that contributes to gene activation through an AF4-MLL complex interaction. Cell Rep. 2013; 3:116–127. PMID: 23352661.97. Wächter K, Kowarz E, Marschalek R. Functional characterisation of different MLL fusion proteins by using inducible Sleeping Beauty vectors. Cancer Lett. 2014; 352:196–202. PMID: 25016062.98. Breese EH, Buechele C, Dawson C, Cleary ML, Porteus MH. Use of genome engineering to create patient specific MLL translocations in primary human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. PLoS ONE. 2015; 10:e0136644. PMID: 26351841.99. Sabiani S, Geppert T, Engelbrecht C, Kowarz E, Schneider G, Marschalek R. Unraveling the activation mechanism of Taspase1 which controls the oncogenic AF4-MLL fusion protein. EBioMedicine. 2015; 2:386–395. PMID: 26137584.100. Cao F, Townsend EC, Karatas H, Xu J, Li L, Lee S, et al. Targeting MLL1 H3K4 methyltransferase activity in mixed-lineage leukemia. Mol Cell. 2014; 53:247–261. PMID: 24389101.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Monocytic Leukemia with t(11;17)(q23;q21) Involving a Rearrangement of Mixed Lineage Leukemia Gene
- Surface Marker Analysis in Acute Leukemias
- Biphenotypic acute leukemia or acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage in childhood: clinical characteristics and outcome
- A Case of Lineage Switch from Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia to Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- A clinical study of childhood acute mixed lineage leukemia