Korean J Crit Care Med.
2017 Feb;32(1):74-78. 10.4266/kjccm.2016.00409.
Recurrent Aspiration Pneumonia due to Anterior Cervical Osteophyte
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine,Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 2Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Chuncheon, Korea. zzaracat@yuhs.ac
- 3Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Gangneung Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
- KMID: 2371157
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2016.00409
Abstract
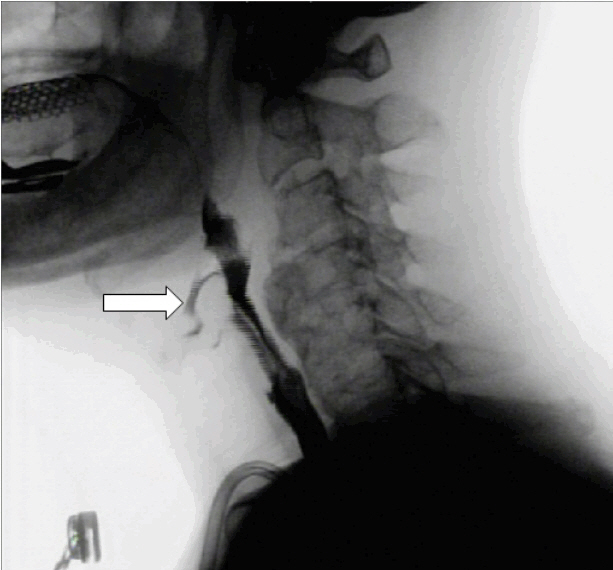
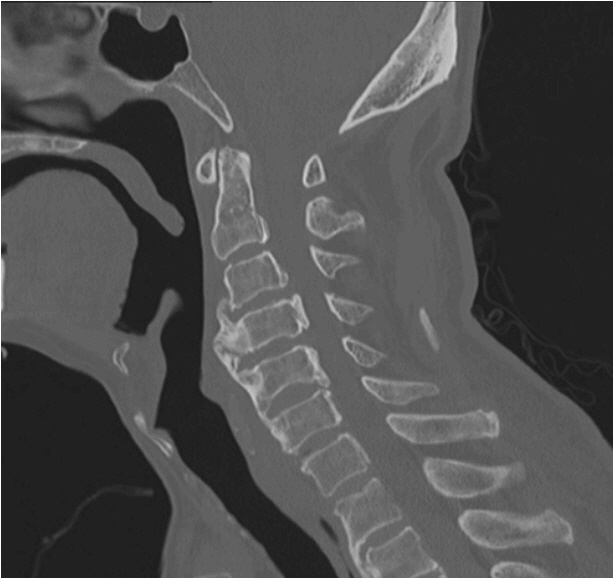
- A 74-year-old man presented with recurrent vomiting and aspiration pneumonia in the left lower lobe. He entered the intensive care unit to manage the pneumonia and septic shock. Although a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube was implanted for recurrent vomiting, vomiting and aspiration recurred frequently during admission. Subsequently, he complained of neck pain when in an upright position. A videofluoroscopic swallowing study showed compression of the esophagus by cervical osteophytes and tracheal aspiration caused by an abnormality at the laryngeal inlet. Cervical spine X-rays and computed tomography showed anterior cervical osteophytes at the C3-6 levels. Surgical decompression was scheduled, but was cancelled due to his frailty. Unfortunately, further recurrent vomiting and aspiration resulted in respiratory arrest leading to hypoxic brain damage and death. Physicians should consider cervical spine disease, such as diffuse skeletal hyperostosis as an uncommon cause of recurrent aspiration pneumonia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Mazières B. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (Forestier-Rotes-Querol disease): what’s new? Joint Bone Spine. 2013; 80:466–70.
Article2. Hirasawa A, Wakao N, Kamiya M, Takeuchi M, Kawanami K, Murotani K, et al. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in Japan - the first report of measurement by CT and review of the literature. J Orthop Sci. 2016; 21:287–90.
Article3. Carlson ML, Archibald DJ, Graner DE, Kasperbauer JL. Surgical management of dysphagia and airway obstruction in patients with prominent ventral cervical osteophytes. Dysphagia. 2011; 26:34–40.
Article4. Kos MP, van Royen BJ, David EF, Mahieu HF. Anterior cervical osteophytes resulting in severe dysphagia and aspiration: two case reports and literature review. J Laryngol Otol. 2009; 123:1169–73.
Article5. Ozkalkanli MY, Katircioglu K, Ozkalkanli DT, Savaci S. Airway management of a patient with Forestier’s disease. J Anesth. 2006; 20:304–6.
Article6. Verlaan JJ, Boswijk PF, de Ru JA, Dhert WJ, Oner FC. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine: an underestimated cause of dysphagia and airway obstruction. Spine J. 2011; 11:1058–67.
Article7. Oppenlander ME, Orringer DA, La Marca F, McGillicuddy JE, Sullivan SE, Chandler WF, et al. Dysphagia due to anterior cervical hyperosteophytosis. Surg Neurol. 2009; 72:266–70. discussion 270-1.
Article8. Nelson RS, Urquhart AC, Faciszewski T. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: a rare cause of Dysphagia, airway obstruction, and dysphonia. J Am Coll Surg. 2006; 202:938–42.
Article9. Resnick D, Shaul SR, Robins JM. Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH): Forestier’s disease with extraspinal manifestations. Radiology. 1975; 115:513–24.
Article10. Seidler TO, Pèrez Alvarez JC, Wonneberger K, Hacki T. Dysphagia caused by ventral osteophytes of the cervical spine: clinical and radiographic findings. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009; 266:285–91.
Article11. Burkus JK. Esophageal obstruction secondary to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis. Orthopedics. 1988; 11:717–20.
Article12. Lecerf P, Malard O. How to diagnose and treat symptomatic anterior cervical osteophytes? Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2010; 127:111–6.
Article13. Aydin E, Akdogan V, Akkuzu B, Kirbas I, Ozgirgin ON. Six cases of Forestier syndrome, a rare cause of dysphagia. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006; 126:775–8.
Article14. Babores M, Finnerty JP. Aspiration pneumonia secondary to giant cervical osteophyte formation (diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis or Forrestier’s disease): a case report. Chest. 1998; 114:1481–2.15. Hassard AD. Cervical ankylosing hyperostosis and airway obstruction. Laryngoscope. 1984; 94:966–8.
Article16. Matan AJ, Hsu J, Fredrickson BA. Management of respiratory compromise caused by cervical osteophytes: a case report and review of the literature. Spine J. 2002; 2:456–9.17. Granville LJ, Musson N, Altman R, Silverman M. Anterior cervical osteophytes as a cause of pharyngeal stage dysphagia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1998; 46:1003–7.
Article18. Kim SK, Choi BR, Kim CG, Chung SH, Choe JY, Joo KB, et al. The prevalence of diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis in Korea. J Rheumatol. 2004; 31:2032–5.19. Pillai S, Littlejohn G. Metabolic factors in diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis - a review of clinical data. Open Rheumatol J. 2014; 8:116–28.
Article20. Zhang C, Ruan D, He Q, Wen T, Yang P. Progressive dysphagia and neck pain due to diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis of the cervical spine: a case report and literature review. Clin Interv Aging. 2014; 9:553–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Dysphagia Caused by Anterior Cervical Osteophytes: Different Surgical Outcomes in Three Cases
- Dysphagia Caused by an Anterior Cervical Osteophyte: A Case Report
- Surgical Treatments on Patients with Anterior Cervical Hyperostosis-Derived Dysphagia
- A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis
- Temporarily Aggravated Dysphagia Following Osteophytectomy and Fixation in a Patient with Cervical Osteophyte