Ann Dermatol.
2017 Feb;29(1):108-110. 10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.108.
Are Peripheral Natural Killer Cells and Interleukin-21 Interrelated in Psoriasis Pathogenesis?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt. doaasalahhegab@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University, Tanta, Egypt.
- KMID: 2368041
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.108
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
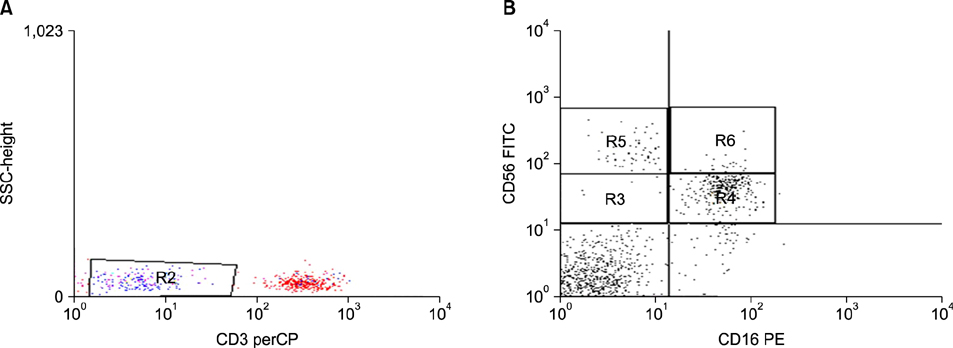
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim J, Krueger JG. The immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. Dermatol Clin. 2015; 33:13–23.
Article2. Spolski R, Leonard WJ. Interleukin-21: a double-edged sword with therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014; 13:379–395.
Article3. Ottaviani C, Nasorri F, Bedini C, de Pità O, Girolomoni G, Cavani A. CD56brightCD16(-) NK cells accumulate in psoriatic skin in response to CXCL10 and CCL5 and exacerbate skin inflammation. Eur J Immunol. 2006; 36:118–128.
Article4. Li Q, Ye LJ, Ren HL, Huyan T, Li J, Shi JL, et al. Multiple effects of IL-21 on human NK cells in ex vivo expansion. Immunobiology. 2015; 220:876–888.
Article5. Sarra M, Caruso R, Cupi ML, Monteleone I, Stolfi C, Campione E, et al. IL-21 promotes skin recruitment of CD4(+) cells and drives IFN-γ-dependent epidermal hyperplasia. J Immunol. 2011; 186:5435–5442.
Article6. Dunphy S, Gardiner CM. NK cells and psoriasis. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011; 2011:248317.
Article7. Son SW, Kim EO, Ryu ES, Kim TJ, Kim JN, Choi JE, et al. Upregulation of Fas and downregulation of CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptors on circulating natural killer cells in patients with new-onset psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 161:281–288.
Article8. Sivori S, Cantoni C, Parolini S, Marcenaro E, Conte R, Moretta L, et al. IL-21 induces both rapid maturation of human CD34+ cell precursors towards NK cells and acquisition of surface killer Ig-like receptors. Eur J Immunol. 2003; 33:3439–3447.
Article9. Toomey JA, Gays F, Foster D, Brooks CG. Cytokine requirements for the growth and development of mouse NK cells in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 2003; 74:233–242.
Article10. Strengell M, Matikainen S, Sirén J, Lehtonen A, Foster D, Julkunen I, et al. IL-21 in synergy with IL-15 or IL-18 enhances IFN-gamma production in human NK and T cells. J Immunol. 2003; 170:5464–5469.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An experimental study on the enhanced cytolytic effects of natural killer cells by interleukin 2
- Increased Th2-like Invariant Natural Killer T cells in Peripheral Blood From Patients With Asthma
- A Role of Natural Killer T Cells for the Pathogenesis of Asthma
- A Study of Natural Killer Cell Activities , T Cells and T Cell Subsets in Vitiligo
- Lymphokine-activated killer(LAK) Cell Activity and Phenotypic Characterization in Peripheral Lymphocytes of Patients with Cervical Cancer