J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2016 Dec;18(4):355-362. 10.7461/jcen.2016.18.4.355.
Y-configuration Stent-assisted Coil Embolization for Wide-necked Intracranial Bifurcation Aneurysms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine and Gyeongsang National, University Hospital, Jinju, Korea. 1coo3004@naver.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University and Institute of Health, Sciences, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2367326
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2016.18.4.355
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The objective of this study was to determine the efficiency and safety of Y configuration stent-assisted coiling with double-closed stents for wide-necked intracranial aneurysms located at arterial bifurcations thorough analysis of a multicenter case series.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective chart review was done on 10 patients who underwent endovascular treatment of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms with Y-configuration stent-assisted coil embolization in three centers from August 2011 to March 2014. The degree of aneurysmal occlusion was assessed using the Raymond scale. Clinical outcomes were assessed before operation, at discharge, and at the last follow-up visit using the Glasgow outcome scale.
RESULTS
The 10 patients included 6 females and 4 males with a mean age of 58.6 years. Indications for treatment included 6 unruptured intracranial aneurysms and 4 ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Five aneurysms were located at the basilar artery bifurcation, four aneurysms were located in an anterior communicating artery, and one aneurysm was in the pericallosal artery. The mean size of the 10 aneurysms was 9.7 mm. All aneurysms had a dome-to-neck ratio of < 1.5 (mean, 0.89). Immediate complications included one thromboembolic event out of the 10 cases. Immediate posttreatment angiograms showed complete occlusion in 1 aneurysm and residual necks in 9 aneurysms. Follow-up results showed 8 complete occlusions and 2 residual necks. No delayed complications were observed during the follow-up period (mean: 20 months).
CONCLUSION
Y configuration using double-closed cell stents is feasible and safe in selected patients. This method is an acceptable option for managing complex wide-necked bifurcations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
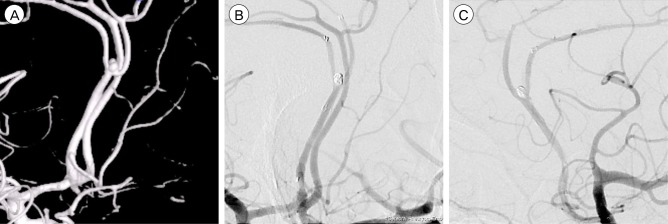
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Y-stent-assisted coiling with Neuroform Atlas stents for wide-necked intracranial bifurcation aneurysms: A preliminary report
Dongkyu Kim, Joonho Chung
J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2022;24(1):1-9. doi: 10.7461/jcen.2021.E2021.06.010.
Reference
-
1. Akgul E, Aksungur E, Balli T, Onan B, Yilmaz DM, Bicakci S, et al. Y-stent-assisted coil embolization of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms. A single center experience. Interv Neuroradiol. 2011; 3. 17(1):36–48. PMID: 21561557.2. Babiker MH, Gonzalez LF, Ryan J, Albuquerque F, Collins D, Elvikis A, et al. Influence of stent configuration on cerebral aneurysm fluid dynamics. J Biomech. 2012; 2. 45(3):440–447. PMID: 22226405.
Article3. Baldi S, Mounayer C, Piotin M, Spelle L, Moret J. Balloon-assisted coil placement in wide-neck bifurcation aneurysms by use of a new, compliant balloon microcatheter. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; Jun-Jul. 24(6):1222–1225. PMID: 12812958.4. Banerjee RK, Gonzalez CF, Cho YI, Picard L. Hemodynamic changes in recurrent intracranial terminal aneurysm after endovascular treatment. Acad Radiol. 1996; 3. 3(3):202–211. PMID: 8796666.
Article5. Bendok BR, Parkinson RJ, Hage ZA, Adel JG, Gounis MJ. The effect of vascular reconstruction device-assisted coiling on packing density, effective neck coverage, and angiographic outcome: an in vitro study. Neurosurgery. 2007; 10. 61(4):835–840. discussion 840-1. PMID: 17986946.6. Cantón G, Levy DI, Lasheras JC. Hemodynamic changes due to stent placement in bifurcating intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2005; 7. 103(1):146–155. PMID: 16121985.
Article7. Cekirge HS, Yavuz K, Geyik S, Saatci I. A novel "Y" stent flow diversion technique for the endovascular treatment of bifurcation aneurysms without endosaccular coiling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 8. 32(7):1262–1268. PMID: 21527573.
Article8. Chow MM, Woo HH, Masaryk TJ, Rasmussen PA. A novel endovascular treatment of a wide-necked basilar apex aneurysm by using a Y-configuration, double-stent technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 3. 25(3):509–512. PMID: 15037483.9. Debrun GM, Aletich VA, Kehrli P, Misra M, Ausman JI, Charbel F. Selection of cerebral aneurysms for treatment using Guglielmi detachable coils: the preliminary University of Illinois at Chicago experience. Neurosurgery. 1998; 12. 43(6):1281–1295. discussion 1296-7. PMID: 9848841.
Article10. Debrun GM, Aletich VA, Kehrli P, Misra M, Ausman JI, Charbel F, et al. Aneurysm geometry: an important criterion in selecting patients for Guglielmi detachable coiling. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 1998; 38(Suppl):1–20.
Article11. Fargen KM, Mocco J, Neal D, Dewan MC, Reavey-Cantwell J, Woo HH, et al. A multicenter study of stent-assisted coiling of cerebral aneurysms with a Y configuration. Neurosurgery. 2013; 9. 73(3):466–472. PMID: 23756744.
Article12. Fiehler J, Byrne JV. Factors affecting outcome after endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Curr Opin Neurol. 2009; 2. 22(1):103–108. PMID: 19155767.
Article13. Horowitz M, Levy E, Sauvageau E, Genevro J, Guterman LR, Hanel R, et al. Intra/extra-aneurysmal stent placement for management of complex and wide-necked-bifurcation aneurysms: eight cases using the waffle cone technique. Neurosurgery. 2006; 4. 58(4 Suppl 2):ONS-258–ONS-262. discussion ONS-262.14. Kono K, Terada T. Hemodynamics of 8 different configurations of stenting for bifurcation aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013; 10. 34(10):1980–1986. PMID: 23578668.
Article15. Lozen A, Manjila S, Rhiew R, Fessler R. Y-stent-assisted coil embolization for the management of unruptured cerebral aneurysms: report of six cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2009; 12. 151(12):1663–1672. PMID: 19618104.
Article16. Lubicz B. Linear stent-assisted coiling: another way to treat very wide-necked intracranial aneurysms. Neuroradiology. 2011; 6. 53(6):457–459. PMID: 21088964.
Article17. Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, Clarke M, Sneade M, Yarnold JA, et al. International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet. 2005; 9. 366(9488):809–817. PMID: 16139655.
Article18. Moret J, Cognard C, Weill A, Castaings L, Rey A. Reconstruction technic in the treatment of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms. Long-term angiographic and clinical results. Apropos of 56 cases. J Neuroradiol. 1997; 6. 24(1):30–44. PMID: 9303942.19. Murayama Y, Nien YL, Duckwiler G, Gobin YP, Jahan R, Frazee J, et al. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of cerebral aneurysms: 11 years' experience. J Neurosurg. 2003; 5. 98(5):959–966. PMID: 12744354.
Article20. Raymond J, Guilbert F, Roy D. Neck-bridge device for endovascular treatment of wide-neck bifurcation aneurysms: initial experience. Radiology. 2001; 11. 221(2):318–326. PMID: 11687670.
Article21. Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A, Georganos SA, Juravsky L, Lambert A, et al. Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke. 2003; 6. 34(6):1398–1403. PMID: 12775880.
Article22. Rhee K, Han MH, Cha SH. Changes of flow characteristics by stenting in aneurysm models: influence of aneurysm geometry and stent porosity. Ann Biomed Eng. 2002; Jul-Aug. 30(7):894–904. PMID: 12398420.
Article23. Saatci I, Geyik S, Yavuz K, Cekirge S. X-configured stent-assisted coiling in the endovascular treatment of complex anterior communicating artery aneurysms: a novel reconstructive technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; Jun-Jul. 32(6):E113–E117. PMID: 20595366.
Article24. Shapiro M, Becske T, Sahlein D, Babb J, Nelson PK. Stent-supported aneurysm coiling: a literature survey of treatment and follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; 1. 33(1):159–163. PMID: 22033717.
Article25. Spiotta AM, Gupta R, Fiorella D, Gonugunta V, Lobo B, Rasmussen PA, et al. Mid-term results of endovascular coiling of wide-necked aneurysms using double stents in a Y configuration. Neurosurgery. 2011; 8. 69(2):421–429. PMID: 21389887.
Article26. Sze DY, Razavi MK, Mitri RK, Regala AC, Dake MD. The "Y" stent: a technique using nitinol stents to treat bifurcations. J Endovasc Ther. 2003; 8. 10(4):780–787. PMID: 14533963.
Article27. Tateshima S, Tanishita K, Hakata Y, Tanoue SY, Vinuela F. Alteration of intraaneurysmal hemodynamics by placement of a self-expandable stent. Laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg. 2009; 7. 111(1):22–27. PMID: 19267529.28. Thorell WE, Chow MM, Woo HH, Masaryk TJ, Rasmussen PA. Y-configured dual intracranial stent-assisted coil embolization for the treatment of wide-necked basilar tip aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2005; 5. 56(5):1035–1040. discussion 1035-40. PMID: 15854251.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Preliminary Results of Y-Stent-Assisted Coil Embolization of Wide-Necked Intracranial Aneurysms: 8 Consecutive Patients
- A Complicated Case of Endovascular Stent Assisted Coil Embolization of an Aneurysm
- Endovascular Treatment of Wide-Necked Intracranial Aneurysms : Techniques and Outcomes in 15 Patients
- Selective Temporary Stent-Assisted Coil Embolization for Intracranial Wide-Necked Small Aneurysms Using Solitaire AB Retrievable Stent
- Y-stent-assisted coiling with Neuroform Atlas stents for wide-necked intracranial bifurcation aneurysms: A preliminary report