J Korean Med Sci.
2017 Mar;32(3):457-464. 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.3.457.
Clinical Characteristics of Transplant-associated Encephalopathy in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Asan Medical Center Children's Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. tsko@amc.seoul.kr
- 3Department of Pediatrics, CHA Gangnam Medical Center, CHA University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2366642
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2017.32.3.457
Abstract
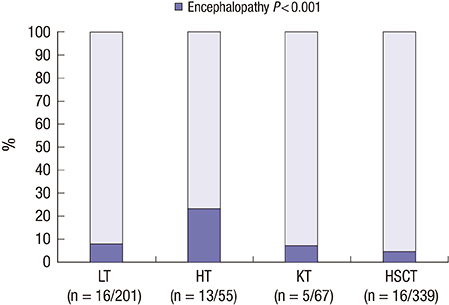
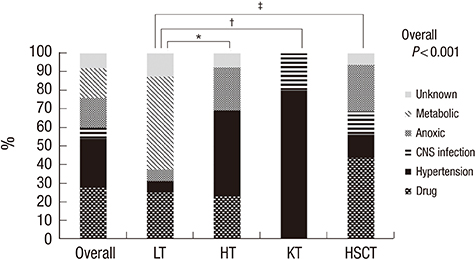
- We aimed to analyze characteristics of encephalopathy after both hematopoietic stem cell and solid organ pediatric transplantation. We retrospectively reviewed medical records of 662 pediatric transplant recipients (201 with liver transplantation [LT], 55 with heart transplantation [HT], and 67 with kidney transplantation [KT], 339 with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation [HSCT]) who received their graft organs at Asan Medical Center between January 2000 and July 2014. Of the 662 patients, 50 (7.6%) experienced encephalopathy after transplantation. The incidence of encephalopathy was significantly different according to the type of organ transplant: LT, 16/201 (8.0%), HT, 13/55 (23.6%), KT, 5/67 (7.5%), and HSCT, 16/339 (4.7%) (P < 0.001). Drug-induced encephalopathy (n = 14) was the most common encephalopathy for all transplant types, but particularly after HSCT. Hypertensive encephalopathy was the most common after KT and HT, whereas metabolic encephalopathy was the most common after LT. The median time to encephalopathy onset also differed according to the transplant type: 5 days after KT (range 0-491 days), 10 days after HT (1-296 days), 49.5 days after HSCT (9-1,405 days), and 39 days after LT (1-1,092 days) (P = 0.018). The mortality rate among patients with encephalopathy was 42.0% (n = 21/50). Only 5 patients died of neurologic complications. Transplant-associated encephalopathy presented different characteristics according to the type of transplant. Specialized diagnostic approach for neurologic complications specific to the type of transplant may improve survival and quality of life in children after transplantation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Brain Diseases*
Brain Diseases, Metabolic
Child*
Chungcheongnam-do
Heart
Heart Transplantation
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Humans
Hypertensive Encephalopathy
Incidence
Kidney
Kidney Transplantation
Liver
Liver Transplantation
Medical Records
Mortality
Quality of Life
Retrospective Studies
Transplant Recipients
Transplantation
Transplants
Figure
Reference
-
1. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration. OPTN/SRTR 2012 annual data report [Internet]. accessed on 28 January 2016. Available at http://srtr.transplant.hrsa.gov/annual_reports/2012/Default.aspx.2. Kang JM, Kim YJ, Kim JY, Cho EJ, Lee JH, Lee MH, Lee SH, Sung KW, Koo HH, Yoo KH. Neurologic complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children: analysis of prognostic factors. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015; 21:1091–1098.3. Ghosh PS, Kwon C, Klein M, Corder J, Ghosh D. Neurologic complications following pediatric renal transplantation. J Child Neurol. 2014; 29:793–798.4. Faraci M, Lanino E, Dini G, Fondelli MP, Morreale G, Dallorso S, Manzitti C, Calevo MG, Gaggero R, Castagnola E, et al. Severe neurologic complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Neurology. 2002; 59:1895–1904.5. Lee YJ, Yum MS, Kim EH, Choi HW, Oh SH, Kim DY, Kim KM, Ko TS. Risk factors for neurological complications and their correlation with survival following pediatric liver transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2014; 18:177–184.6. Koh KN, Park M, Kim BE, Im HJ, Seo JJ. Early central nervous system complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Korean J Hematol. 2010; 45:164–170.7. Ghaus N, Bohlega S, Rezeig M. Neurological complications in liver transplantation. J Neurol. 2001; 248:1042–1048.8. Pless M, Zivkovic SA. Neurologic complications of transplantation. Neurologist. 2002; 8:107–120.9. Senzolo M, Ferronato C, Burra P. Neurologic complications after solid organ transplantation. Transpl Int. 2009; 22:269–278.10. Iguchi A, Kobayashi R, Yoshida M, Kaneda M, Watanabe N, Cho Y, Arioka H, Naito H, Shikano T, Ishikawa Y. Neurological complications after stem cell transplantation in childhood. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999; 24:647–652.11. Andrews BT, Hershon JJ, Calanchini P, Avery GJ 2nd, Hill JD. Neurologic complications of cardiac transplantation. West J Med. 1990; 153:146–148.12. Jeong MY, Cho YK, Kim SY, Kim YO, Kim CJ, Kook H, Woo YJ, Hwang TJ. Neurologic complications after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Korean J Pediatr. 2004; 47:978–985.13. Zivković S. Neuroimaging and neurologic complications after organ transplantation. J Neuroimaging. 2007; 17:110–123.14. Pruitt AA, Graus F, Rosenfeld MR. Neurological complications of transplantation: part I: hematopoietic cell transplantation. Neurohospitalist. 2013; 3:24–38.15. Pruitt AA, Graus F, Rosenfeld MR. Neurological complications of solid organ transplantation. Neurohospitalist. 2013; 3:152–166.16. Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, Pessin MS, Lamy C, Mas JL, Caplan LR. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:494–500.17. Belvís R, Martí-Fàbregas J, Cocho D, García-Bargo MD, Franquet E, Agudo R, Brosa V, Campreciós M, Puig M, Martí-Vilalta JL. Cerebrovascular disease as a complication of cardiac transplantation. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2005; 19:267–271.18. Jarquin-Valdivia AA, Wijdicks EF, McGregor C. Neurologic complications following heart transplantation in the modern era: decreased incidence, but postoperative stroke remains prevalent. Transplant Proc. 1999; 31:2161–2162.19. Burra P, Senzolo M, Pizzolato G, Tursi V, Livi U, Chierichetti F, Dam M. Frontal cerebral blood flow is impaired in patients with heart transplantation. Transpl Int. 2002; 15:459–462.20. Massaro AR, Dutra AP, Almeida DR, Diniz RV, Malheiros SM. Transcranial Doppler assessment of cerebral blood flow: effect of cardiac transplantation. Neurology. 2006; 66:124–126.21. van Mook WN, Rennenberg RJ, Schurink GW, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Mess WH, Hofman PA, de Leeuw PW. Cerebral hyperperfusion syndrome. Lancet Neurol. 2005; 4:877–888.22. Schwartz RB. Hyperperfusion encephalopathies: hypertensive encephalopathy and related conditions. Neurologist. 2002; 8:22–34.23. Yu S, Liebeskind DS, Dua S, Wilhalme H, Elashoff D, Qiao XJ, Alger JR, Sanossian N, Starkman S, Ali LK, et al. Postischemic hyperperfusion on arterial spin labeled perfusion MRI is linked to hemorrhagic transformation in stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015; 35:630–637.24. Agildere AM, Başaran C, Cakir B, Ozgül E, Kural F, Haberal M. Evaluation of neurologic complications by brain MRI in kidney and liver transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2006; 38:611–618.25. Dhar R, Young GB, Marotta P. Perioperative neurological complications after liver transplantation are best predicted by pre-transplant hepatic encephalopathy. Neurocrit Care. 2008; 8:253–258.26. Sotil EU, Gottstein J, Ayala E, Randolph C, Blei AT. Impact of preoperative overt hepatic encephalopathy on neurocognitive function after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2009; 15:184–192.27. Parasole R, Petruzziello F, Menna G, Mangione A, Cianciulli E, Buffardi S, Marchese L, Nastro A, Misuraca A, Poggi V. Central nervous system complications during treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a single pediatric institution. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010; 51:1063–1071.28. Baytan B, Evim MS, Güler S, Güneş AM, Okan M. Acute central nervous system complications in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Neurol. 2015; 53:312–318.29. Gruhn N, Larsen FS, Boesgaard S, Knudsen GM, Mortensen SA, Thomsen G, Aldershvile J. Cerebral blood flow in patients with chronic heart failure before and after heart transplantation. Stroke. 2001; 32:2530–2533.30. Baluarte HJ, Gruskin AB, Ingelfinger JR, Stablein D, Tejani A. Analysis of hypertension in children post renal transplantation--a report of the North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study (NAPRTCS). Pediatr Nephrol. 1994; 8:570–573.31. Tejani A. Post-transplant hypertension and hypertensive encephalopathy in renal allograft recipients. Nephron. 1983; 34:73–78.32. Büscher R, Vester U, Wingen AM, Hoyer PF. Pathomechanisms and the diagnosis of arterial hypertension in pediatric renal allograft recipients. Pediatr Nephrol. 2004; 19:1202–1211.33. Uckan D, Cetin M, Yigitkanli I, Tezcan I, Tuncer M, Karasimav D, Oguz KK, Topçu M. Life-threatening neurological complications after bone marrow transplantation in children. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005; 35:71–76.34. Weber C, Schaper J, Tibussek D, Adams O, Mackenzie CR, Dilloo D, Meisel R, Göbel U, Laws HJ. Diagnostic and therapeutic implications of neurological complications following paediatric haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008; 41:253–259.35. Maschke M, Dietrich U, Prumbaum M, Kastrup O, Turowski B, Schaefer UW, Diener HC. Opportunistic CNS infection after bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999; 23:1167–1176.36. Zivković SA. Neurologic complications after liver transplantation. World J Hepatol. 2013; 5:409–416.37. Alejaldre A, Delgado-Mederos R, Santos MÁ, Martí-Fàbregas J. Cerebrovascular complications after heart transplantation. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2010; 6:214–217.38. Wijdicks EF, Torres VE, Schievink WI, Sterioff S. Cerebral hemorrhage in recipients of renal transplantation. Mayo Clin Proc. 1999; 74:1111–1112.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Wernicke's Encephalopathy with Hyperemesis Gravidarum
- A Study on Prognostic Factors in Children with Encephalopathy
- MR Imaging of Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy:A Report of Two Cases
- Hypertensive Encephalopathy in a 10-year-old Boy with Ureteral Stone
- Acute Acquired Metabolic Encephalopathy Based on Diffusion MRI: Note of an Error