J Korean Acad Oral Health.
2016 Dec;40(4):270-276. 10.11149/jkaoh.2016.40.4.270.
Remineralisation effect of 1,500 ppm fluoride-containing toothpaste in enamel early caries lesion
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive & Public Health Dentistry, Chonnam National University School of Dentistry, Gwangju, Korea. sjhong@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Dental Science Research Institute, Chonnam National University School of Dentistry, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3LG Household & Health Care Research Park, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2366494
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11149/jkaoh.2016.40.4.270
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
We compared the effects of a 1,500 ppm fluoride-containing toothpaste and a 1,000 ppm fluoride-containing toothpaste, which were revised up to the recent revision, and evaluated their effects on the tooth surface after adding bamboo salt to the preparations.
METHODS
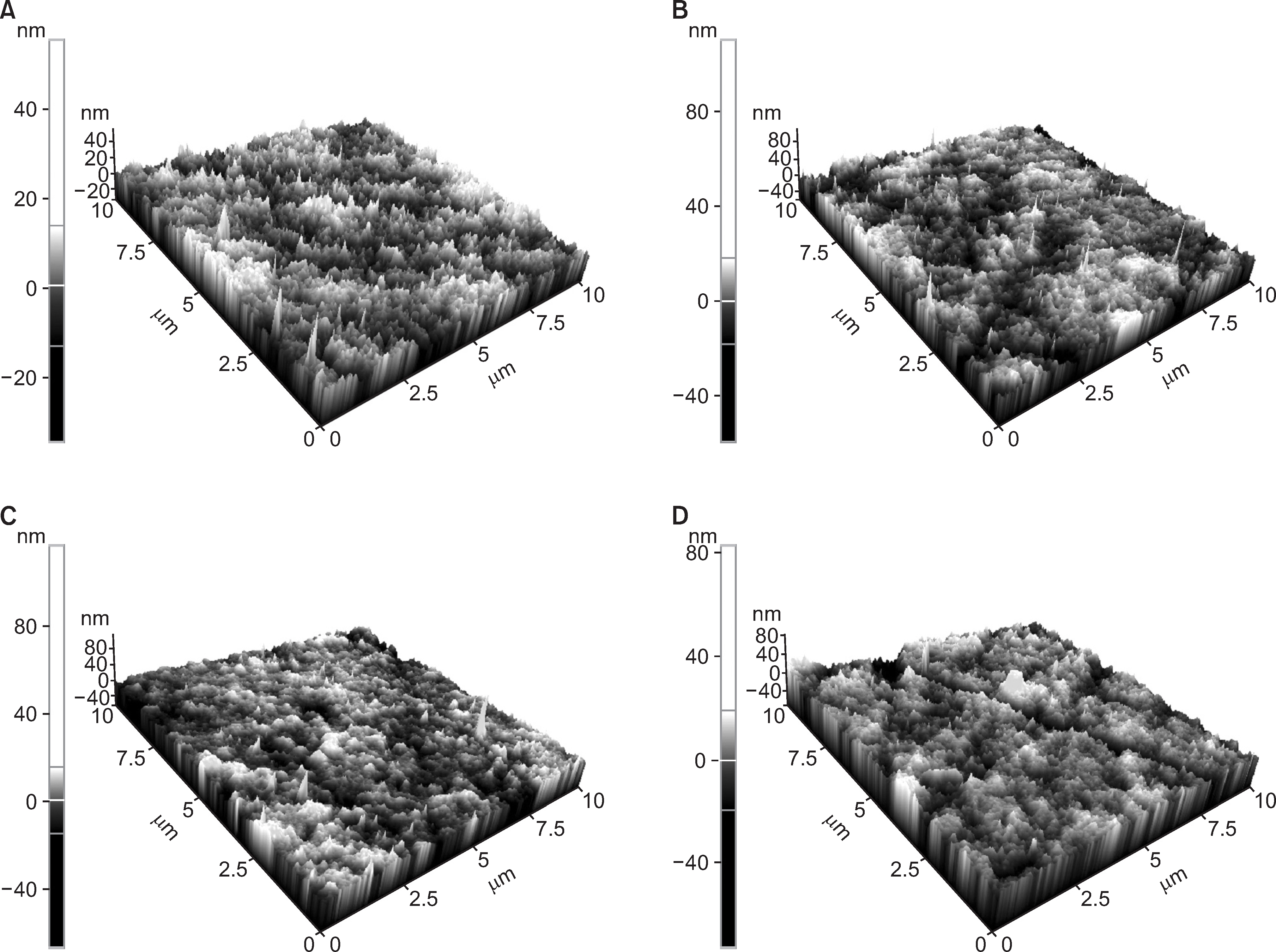
Experimental early artificial caries specimens were subjected to one of four treatments (n=12 per treatment group): 1,500 ppm NaF, 2% bamboo salt+1,000 ppm NaF, 1,000 ppm NaF, and control treatment. The specimens were exposed to the experimental toothpaste, artificial saliva, and demineralized solution. The treated specimens were analyzed using Vickers surface hardness testing, scanning electron microscopy, and atomic force microscopy.
RESULTS
The toothpaste with a high fluoride concentration (1,500 ppm NaF) showed more remineralization than did the toothpaste with a low fluoride concentration (1,000 ppm NaF). The 2% bamboo salt+1,000 ppm NaF group showed remineralization similar to the 1,500 ppm NaF group and higher surface microhardness than the 1,000 ppm NaF group.
CONCLUSIONS
Toothpastes containing 1,500 ppm NaF have a higher preventive effect against dental caries than do toothpastes containing 1,000 ppm NaF. The addition of bamboo salt to fluoride-containing dentifrices improves their effectiveness in preventing dental caries.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Preventive effect of dentifrice containing 1,450 ppm fluoride and sodium pyrophosphate
Min-Ji Park, Ja-Won Cho, Hyun-Jun Yoo, Mi-Hae Yun, Kyong-Hoon Shin, Young-Hoon Park
J Korean Acad Oral Health. 2022;46(2):63-69. doi: 10.11149/jkaoh.2022.46.2.63.
Reference
-
References
1. World Health Organization. Report of a WHO Expert Committee on oral health status and fluoride use. Geneva: World Health Organiza-tion;1994. p. 1–37.2. Shani Ann Mani. Evidence-based clinical recommendation for fluoride use : a review. Arch Orofac Sci. 2009; 4:1–6.3. Horowitz HS. The 2001 CDC recommendations for using fluoride to prevent and control dental caries in the United States. J Public Health Dent. 2003; 63:3–8.
Article4. Marinho VC, Higgins JP, Sheiham A, Logan S. Combinations of topical fluoride (toothpastes, mouthrinses, gels, varnishes) versus single topical fluoride for preventing dental caries in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004; (1). CD002781.
Article5. FDI World Dental Federation. Promoting dental health through fluoride toothpaste 2008. Stockholm: FDI World Dental Federation;2008.6. Murry JJ, Rugg-Gunnn AJ. Fluorides in caries prevention. 2nd ed. Bristol: John Wright & Sons;1982. p. 101–121.7. Ministry of food and drug safety. Medicines etc standard manufacturing standards some revision notices(011-37). Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2011. p. 1–24.8. Kim JH, Jeong SS, Choi CH, Hong SJ. Fluoride concentration of commercial dentifrices and effect of fluoride containing dentifrices on artificial enamel caries. J Korean Acad Oral Health. 2006; 30:56–66.9. FDA 21 CFR Parts 310, 355 and 369 Anticaries drug products for over-the- counter human use; Final monograph. Feder Reg. 1995; 60:52474–52510.10. Korea health promotion foundation. What’s in the toothpaste? Tooth decay prevention? seoul: Korea health promotion founda-tion;2016. p. 1–4.11. Europäische Kommission Scientific Committee on Cosmetic Products and Non-Food Products. Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Cosmetic Products and Non-Food Products Intended for Con- sumers: The safety of fluorine compounds in oral hygiene products for children under age of 6 years. SCCNFP 24th plenary meet-ing. 2003. 1–26.12. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Medicines etc Standard manufacturing standards Some revision notices(014-152). Cheongju: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2014. p. 1–9.13. Ha MO. The effect of bamboo salt on remineralization of subsurface of incipient caries enamel [master’s thesis]. Gwangju: Chonnam National Uni- versity;2016. [Korean].14. Bibby BG. A test of the effect of fluoride-containing dentifrices on dental caries. J Dent Res. 1945; 24:297–303.
Article15. Marthaler TM1, O’Mullane DM, Vrbic V. The prevalence of dental caries in Europe 1990-1995. ORCA Saturday afternoon symposium 1995. Caries Res. 1996; 30:237–255.16. White DJ. Reactivity of fluoride dentifrices with artificial caries II. Effect on subsurface lesions: F uptake, F distribution, surface hardening and remineralization. Caries Res. 1988; 22:27–36.17. Damato FA, Stephen KW KW, Edgar WM. In situ remineralization studies using SMFP and NaF dentifrices. JDR. 1994; 73:(Abstr). 272.18. Hagen AR. The state of fluorine in dentifrice systems. Acta Odont Scand. 1972; 30:167–186.
Article19. Kwon JH, Park HW, Lee JH, Seo HW. The analysis of remineralization effect in fluoride varnish using confocal laser scanning mi-croscpoe. J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent. 2008; 35:57–64.20. Davies GM, Worthington HV, Ellwood RP, Bentley EM, Blinkhorn AS, Taylor GO, et al. A randomised controlled trial of the effectiveness of providing free fluoride toothpaste from the age 12 months on reducing caries in 54-year old children. Community Dent Health. 2002; 19:131–136.21. Ha MO, Choi CH, Youn HJ, Hong SJ. The effect of dentifrice containing bamboo salt on the acid resistance of enamel. J Korean Acad Oral Health. 2010; 34:482–490.22. Kim HL, Lee SJ, Lee JH, Kim IC. Sulfur dioxide, mineral contents and physicochemical properties generated during manufacture of bamboo salt. Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2014; 43:1248–1256.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fluoride Release of Several Types of Fluoride-Containing Restorative Materials According to Fluoride Concentration in Toothpaste
- Antimicrobial activity of dental polishing bur material with fluoride ion
- The effects of the fluoride concentration of acidulated buffer solutions on dentine remineralization
- Effects of dentifrice containing 1,500 ppm F (NaF) on dental erosion
- Comparison in Demineralization Resistance of Resin Infiltration and 1.23% Acidulated Phosphate Fluoride in Bovine Teeth