Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2015 Mar;7(2):118-123. 10.4168/aair.2015.7.2.118.
Three-Year Follow-up Results of Sublingual Immunotherapy in Patients With Allergic Rhinitis Sensitized to House Dust Mites
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. csrhee@snu.ac.kr
- 3Graduate School of Immunology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Sensory Organ Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Institute of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Seoul National University Biomedical Research Institute, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2365539
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2015.7.2.118
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study investigated the long-term efficacy, safety, and compliance associated with sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) in Korean patients with allergic rhinitis sensitized to house dust mites.
METHODS
This is a retrospective cohort study. A total of 164 patients who were sensitized to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and Dermatophagoides farinae and who received SLIT were enrolled between November 2007 and January 2010. Each patient was followed up using a diary card, on which a symptom score, rescue medication score, and adverse events (AEs) were recorded.
RESULTS
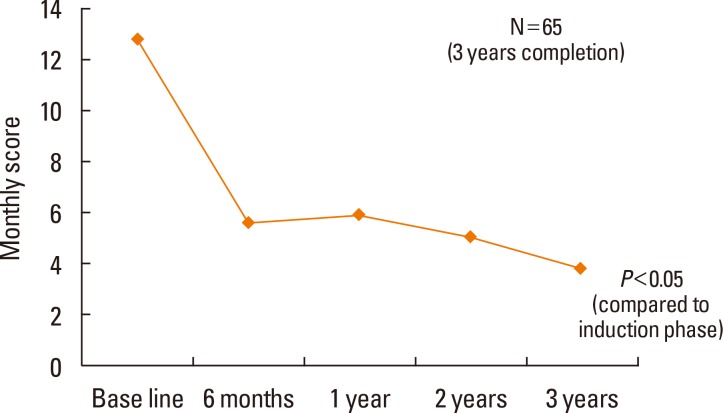
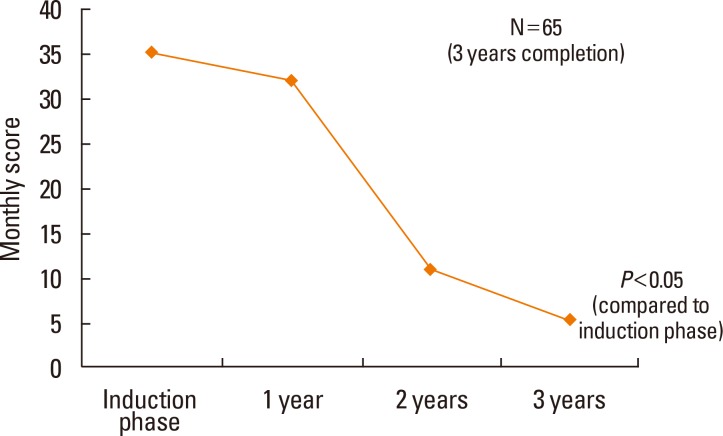
All allergic rhinitis symptoms improved after 3 years of SLIT (P<0.05), and the rescue medication score decreased with time (P<0.05). The incidence of AEs associated with SLIT was 31% (51 of 164 patients) during the first month of therapy, and there were no severe AEs. The dropout rate was 19.5% (32 of 164 patients) during the first month, 34% (56 of 164 patients) after 6 months, and 41% (68 of 164 patients) after 1 year of SLIT. The 3-year compliance rate was approximately 40% (65 of 164 patients). The most common causes of dropout during the first month of SLIT were high cost and inconvenience. The improvement in allergic symptoms was the most common cause of dropout after 6 months.
CONCLUSIONS
Allergic symptoms significantly decreased after 1 year of SLIT treatment, and this effect was sustained after 2 or 3 years of treatment. By increasing compliance through patient education, the 3-year use of SLIT for house dust mite allergies may be effective in the management of allergic rhinitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Survey of Korean Physicians’ Prescription Patterns for Allergic Rhinitis
Min Young Seo, Dong-Kyu Kim, Hye Mi Jee, Young Min Ahn, Yong Min Kim, Sang Duk Hong
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;10(4):332-337. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2017.00143.
Reference
-
1. Saporta D. Sublingual immunotherapy: a novel, albeit not so new, immunotherapy treatment modality. Am J Rhinol. 2008; 22:253–257. PMID: 18211743.
Article2. Wise SK, Schlosser RJ. Subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis: what is the evidence? Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2012; 26:18–22. PMID: 22391071.
Article3. Bahceciler NN, Cobanoglu N. Subcutaneous versus sublingual immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis and/or asthma. Immunotherapy. 2011; 3:747–756. PMID: 21668312.
Article4. Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 2008; 63(Suppl 86):8–160. PMID: 18331513.5. Compalati E, Passalacqua G, Bonini M, Canonica GW. The efficacy of sublingual immunotherapy for house dust mites respiratory allergy: results of a GA2LEN meta-analysis. Allergy. 2009; 64:1570–1579. PMID: 19796205.6. Kiel MA, Röder E, Gerth van Wijk R, Al MJ, Hop WC, Rutten-van Mölken MP. Real-life compliance and persistence among users of subcutaneous and sublingual allergen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 132:353–360.e2. PMID: 23651609.
Article7. Chang H, Han DH, Mo JH, Kim JW, Kim DY, Lee CH, et al. Early compliance and efficacy of sublingual immunotherapy in patients with allergic rhinitis for house dust mites. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2009; 2:136–140. PMID: 19784406.
Article8. Kim ST, Han DH, Moon IJ, Lee CH, Min YG, Rhee CS. Clinical and immunologic effects of sublingual immunotherapy on patients with allergic rhinitis to house-dust mites: 1-year follow-up results. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2010; 24:271–275. PMID: 20819465.
Article9. Milián E, Díaz AM. Allergy to house dust mites and asthma. P R Health Sci J. 2004; 23:47–57. PMID: 15125219.10. Canonica GW, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bousquet J, Bousquet PJ, Lockey RF, Malling HJ, et al. Recommendations for standardization of clinical trials with Allergen Specific Immunotherapy for respiratory allergy. A statement of a World Allergy Organization (WAO) taskforce. Allergy. 2007; 62:317–324. PMID: 17298350.
Article11. Canonica GW, Bousquet J, Casale T, Lockey RF, Baena-Cagnani CE, Pawankar R, et al. Sub-lingual immunotherapy: World Allergy Organization Position Paper 2009. Allergy. 2009; 64(Suppl 91):1–59. PMID: 20041860.12. Calderon MA, Casale TB, Nelson HS, Demoly P. An evidence-based analysis of house dust mite allergen immunotherapy: a call for more rigorous clinical studies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 132:1322–1336. PMID: 24139829.13. Tonnel AB, Scherpereel A, Douay B, Mellin B, Leprince D, Goldstein N, et al. Allergic rhinitis due to house dust mites: evaluation of the efficacy of specific sublingual immunotherapy. Allergy. 2004; 59:491–497. PMID: 15080829.
Article14. Pauli G, Bessot JC, Bigot H, Delaume G, Hordle DA, Hirth C, et al. Clinical and immunologic evaluation of tyrosine-adsorbed Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus extract: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984; 74:524–535. PMID: 6208231.15. Eifan AO, Akkoc T, Yildiz A, Keles S, Ozdemir C, Bahceciler NN, et al. Clinical efficacy and immunological mechanisms of sublingual and subcutaneous immunotherapy in asthmatic/rhinitis children sensitized to house dust mite: an open randomized controlled trial. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010; 40:922–932. PMID: 20100188.
Article16. Röder E, Berger MY, de Groot H, Gerth van Wijk R. Sublingual immunotherapy in youngsters: adherence in a randomized clinical trial. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:1659–1667. PMID: 18631346.
Article17. Passalacqua G, Musarra A, Pecora S, Amoroso S, Antonicelli L, Cadario G, et al. Quantitative assessment of the compliance with a once-daily sublingual immunotherapy regimen in real life (EASY Project: Evaluation of A novel SLIT formulation during a Year). J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:946–948. PMID: 16630956.
Article18. Cox L. Sublingual immunotherapy - Is there a role? Is the US ready for sublingual immunotherapy? [Internet]. Miami (FL): World Allergy Organization;2006. cited 2006 Mar 3. Available from: http://www.worldallergy.org/educational_programs/world_allergy_forum/miamibeach2006/cox.php.19. Mun SJ, Shin JM, Han DH, Kim JW, Kim DY, Lee CH, et al. Efficacy and safety of a once-daily sublingual immunotherapy without escalation regimen in house dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013; 3:177–183. PMID: 23044892.
Article20. Smith H, White P, Annila I, Poole J, Andre C, Frew A. Randomized controlled trial of high-dose sublingual immunotherapy to treat seasonal allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114:831–837. PMID: 15480323.
Article21. Di Lorenzo G, Mansueto P, Pacor ML, Rizzo M, Castello F, Martinelli N, et al. Evaluation of serum s-IgE/total IgE ratio in predicting clinical response to allergen-specific immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:1103–1110. 1110.e1–1110.e4. PMID: 19356792.
Article22. Caffarelli C, Cardinale F, Povesi C, Chinellato I, Sterpeto Loffredo M. Optimal duration of SLIT. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2009; 22:17–22. PMID: 19944005.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Update of Sublingual Immunotherapy for Allergic Rhinitis
- Outcome of Sublingual Immunotherapy in Patients With Allergic Rhinitis Sensitive to House Dust Mites
- Sublingual Immunotherapy in Asian Children: 2-Year Follow-Up Results
- Distribution of House Dust Mites in the Bedroom of Patients with Allergic Rhinitis in Pusan Area
- Staloral(R) in Adult Patients with Allergic Rhinitis