J Korean Soc Radiol.
2017 Jan;76(1):48-53. 10.3348/jksr.2017.76.1.48.
Comparison of the Therapeutic Effect between a Transforaminal along with a Caudal Epidural Injection, as Well as Two-Level Transforaminal Epidural Injections in a Radiculopathy Patient
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Konyang University Hospital, Deajeon, Korea. radbass@paran.com
- 2Department of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2365051
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2017.76.1.48
Abstract
- PURPOSE
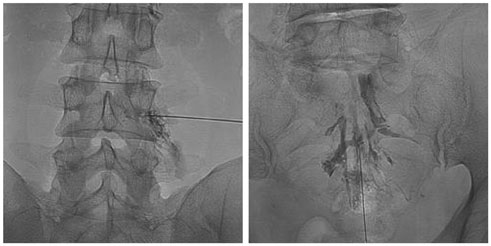
The aim of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic effect of a transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) along with a caudal epidural steroid injection (ESI), compared to two-level TFESIs in a multi-level radiculopathy patient.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 895 lumbar ESIs were performed in 492 patients with multi-level radiculopathy from January 2012 to January 2015. Before injections were performed, the initial Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) score was assessed in all patients, categorized into no pain (excellent), mild (good, NRS: 1-3), moderate (fair, NRS: 4-6), and severe pain (poor, NRS: 7-10). Therapeutic effects were examined for two groups: one-level TFESI along with caudal and ESI two-level TFESIs. Patient outcomes were assessed by NRS in a serial follow-up at one, three, and six months.
RESULTS
One TFESI along with caudal ESI was performed in 274 patients and two TFESIs for 218. For the former group with one TFESI along with caudal ESI, excellent results were shown: 219 (79.9%) patients after one month, 200 (72.9%) after three, and 193 (70.4%) after six months. In the patient group with two TFESIs (n = 218) the outcomes were also very good: 152 (69.7%) after one month, 131 (60.0%) after three months, and 123 (56.4%) patients after six months. The therapeutic effect of one TFESI along with caudal ESI was better than two TFESIs in for one, threes, and six months (p < 0.01).
CONCLUSION
Transforaminal epidural steroid with caudal epidural injection is a more effective tool for lumbosacral radiculopathy than two level transforaminal injections in multi-level radiculopathy patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vad VB, Bhat AL, Lutz GE, Cammisa F. Transforaminal epidural steroid injections in lumbosacral radiculopathy: a prospective randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:11–16.2. Silbergleit R, Mehta BA, Sanders WP, Talati SJ. Imaging-guided injection techniques with fluoroscopy and CT for spinal pain management. Radiographics. 2001; 21:927–939.3. Frymoyer JW, Wiesel SW. The adult and pediatric spine. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2004. p. 929–944.4. Cyteval C, Fescquet N, Thomas E, Decoux E, Blotman F, Taourel P. Predictive factors of efficacy of periradicular corticosteroid injections for lumbar radiculopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:978–982.5. Robecchi A, Capra R. [Hydrocortisone (compound F); first clinical experiments in the field of rheumatology]. Minerva Med. 1952; 43:1259–1263.6. Goebert HW Jr, Jallo SJ, Gardner WJ, Wasmuth CE. Painful radiculopathy treated with epidural injections of procaine and hydrocortisone acetate: results in 113 patients. Anesth Analg. 1961; 40:130–134.7. Pfirrmann CW, Oberholzer PA, Zanetti M, Boos N, Trudell DJ, Resnick D, et al. Selective nerve root blocks for the treatment of sciatica: evaluation of injection site and effectiveness--a study with patients and cadavers. Radiology. 2001; 221:704–711.8. Rydevik B, Garfin S. Spinal nerve root compression. In : Szabo RM, editor. Nerve compression syndromes: diagnosis and treatment. New York: Slack Medical;1989; 247–261.9. Wong DA, Errico T, Saal J, Sims W, Watters W, et al. Clinical guideline on low back pain. Rosemont, IL: American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons;1996. p. 147–161.10. Botwin KP, Gruber RD, Bouchlas CG, Torres-Ramos FM, Sanelli JT, Freeman ED, et al. Fluoroscopically guided lumbar transformational epidural steroid injections in degenerative lumbar stenosis: an outcome study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2002; 81:898–905.11. Simotas AC, Dorey FJ, Hansraj KK, Cammisa F Jr. Nonoperative treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis. Clinical and outcome results and a 3-year survivorship analysis. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:197–120. discussions 203-204.12. Jamison RN, VadeBoncouer T, Ferrante FM. Low back pain patients unresponsive to an epidural steroid injection: identifying predictive factors. Clin J Pain. 1991; 7:311–317.13. Manchikanti L. Transforaminal lumbar epidural steroid injections. Pain Physician. 2000; 3:374–398.14. Lew HL, Coelho P, Chou LH. Preganglionic approach to transforaminal epidural steroid injections. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 83:378.15. Benzon HT. Epidural steroid injections for low back pain and lumbosacral radiculopathy. Pain. 1986; 24:277–295.16. Lee JW, Kim SH, Choi JY, Yeom JS, Kim KJ, Chung SK, et al. Transforaminal epidural steroid injection for lumbosacral radiculopathy: preganglionic versus conventional approach. Korean J Radiol. 2006; 7:139–144.17. Delport EG, Cucuzzella AR, Marley JK, Pruitt CM, Fisher JR. Treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis with epidural steroid injections: a retrospective outcome study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004; 85:479–484.18. Manchikanti L, Cash KA, McManus CD, Pampati V, Abdi S. Preliminary results of a randomized, equivalence trial of fluoroscopic caudal epidural injections in managing chronic low back pain: part 4--spinal stenosis. Pain Physician. 2008; 11:833–848.19. Botwin K, Brown LA, Fishman M, Rao S. Fluoroscopically guided caudal epidural steroid injections in degenerative lumbar spine stenosis. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:547–558.20. Fukusaki M, Kobayashi I, Hara T, Sumikawa K. Symptoms of spinal stenosis do not improve after epidural steroid injection. Clin J Pain. 1998; 14:148–151.21. Kim S, Lee JW, Chai JW, Lee GY, You JY, Kang HS, et al. Fluoroscopy-guided intra-articular facet joint steroid injection for the management of low back pain: therapeutic effectiveness and arthrographic pattern. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2015; 73:172–180.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection and Lumbar/Caudal Epidural Steroid Injection for the Treatment of Lumbosacral Radiculopathy
- Comparison of the Effects between Interlaminar Epidural Block and Transforaminal Epidural Block under C-arm Guide in Lumbar Disc Herniated Radiculopathy
- Acute Cervical Subdural Hematoma with Quadriparesis after Cervical Transforaminal Epidural Block
- Oblique interlaminar lumbar epidural steroid injection for management of low back pain with lumbosacral radicular pain: A case report
- Evaluation of Contrast Flow Patterns with Fluoroscopic Guided Lumbar Transforaminal Epidural Injections