Hip Pelvis.
2016 Dec;28(4):254-258. 10.5371/hp.2016.28.4.254.
Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease Misdiagnosed as Relapse of the Infection after Treatment of Periprosthetic Hip Joint Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. oslee@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2364704
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.4.254
Abstract
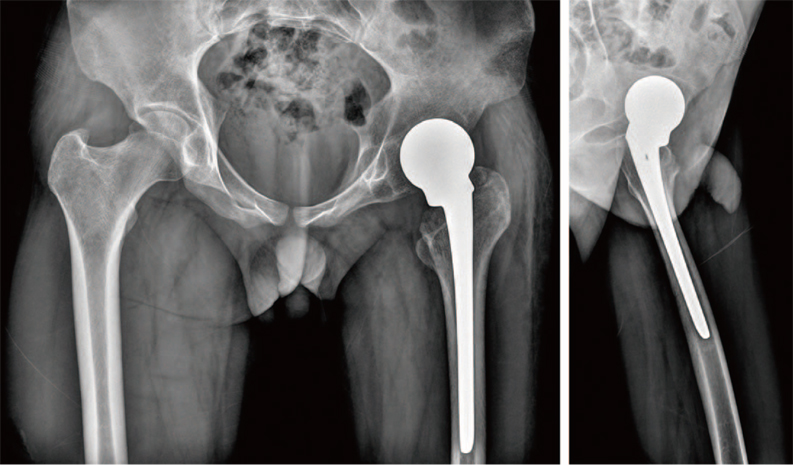
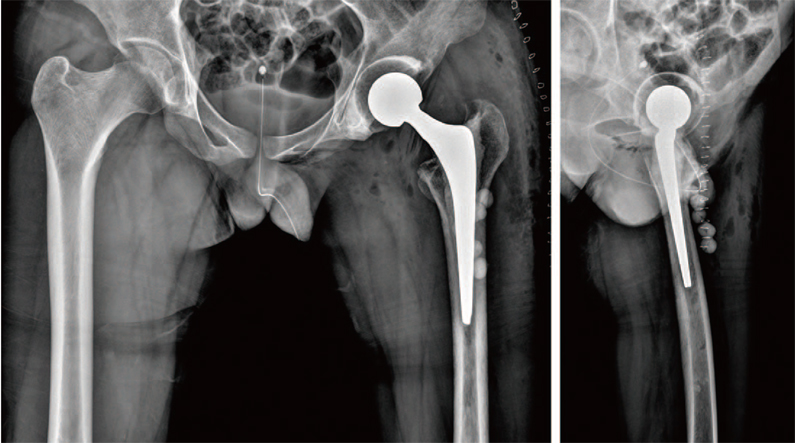
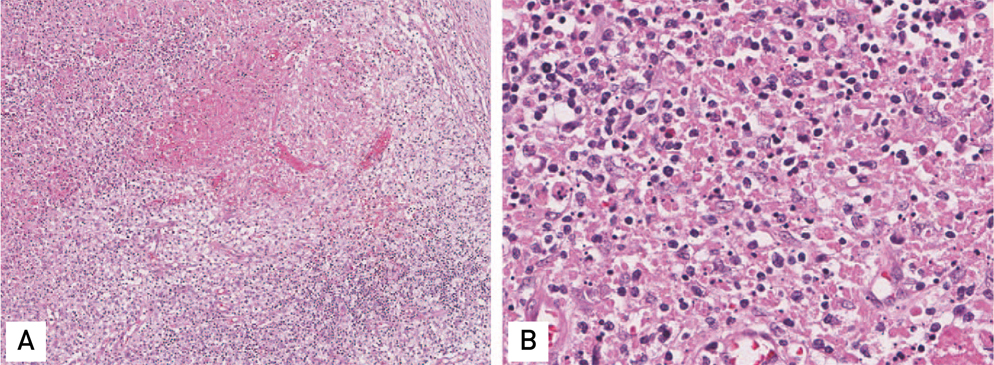
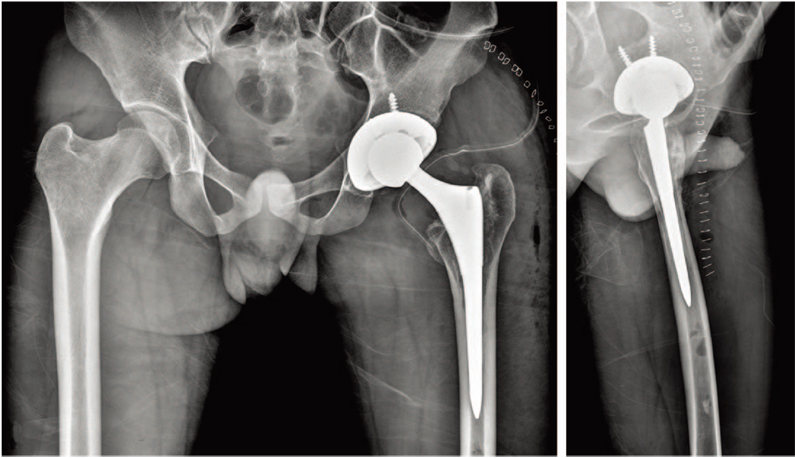
- Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) of the hip can be difficult to treat and can lead to a number of problems including: i) severe functional decline of the hip joint and ii) increasing financial burden for patients due to long treatment periods and the need for repeated surgical interventions. Because there is risk of inadequate control of infection or relapse of a preexisting infection following the treatment of PJI through surgery, it is important to closely observe clinical symptoms such as systemic fever. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease is usually a self-limiting disease characterized by fever and cervical lymphadenopathy. We report one case of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease, with literatures review, that was mistaken for an infection relapse after surgical treatment of the PJI due to sustained fever postoperatively.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ko HS, Bae WH. Treatment of infected total hip arthroplasty. J Korean Hip Soc. 2010; 22:104–110.
Article2. Savarino L, Baldini N, Tarabusi C, Pellacani A, Giunti A. Diagnosis of infection after total hip replacement. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004; 70:139–145.
Article3. Workgroup Convened by the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. New definition for periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26:1136–1138.4. Cho YJ, Kim KI, Chun YS, et al. Treatment of infected hip arthroplasty with antibiotic-loaded cement spacers. J Korean Hip Soc. 2009; 21:148–155.
Article5. Czaplicki AP, Borger JE, Politi JR, Chambers BT, Taylor BC. Evaluation of postoperative fever and leukocytosis in patients after total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26:1387–1389.
Article6. Jamal AB. Kikuchi fujimoto disease. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2012; 5:63–66.
Article7. Kucukardali Y, Solmazgul E, Kunter E, Oncul O, Yildirim S, Kaplan M. Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: analysis of 244 cases. Clin Rheumatol. 2007; 26:50–54.
Article8. Hur CR, Park CE, Hong JY, Shon WY. Change of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protenin (CRP) after hip arthroplasty. J Korean Hip Soc. 2005; 17:188–194.9. Lu X, Jin J, Lin J, Qian W, Weng X. Course of fever and potential infection after total joint replacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015; 23:1870–1876.
Article10. Ward DT, Hansen EN, Takemoto SK, Bozic KJ. Cost and effectiveness of postoperative fever diagnostic evaluation in total joint arthroplasty patients. J Arthroplasty. 2010; 25:6 Suppl. 43–48.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Periprosthetic Joint Infection after Hip Revision Arthroplasty
- Periprosthetic Hip Joint Infection with Flavonifractor plautii: A Literature Review and Case Report
- Three Concurrent Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Case Report and Literature Review
- A Case Report of Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease with Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Periprostetic Joint Infection Caused by Salmonella: Case Reports of Two Azathioprine and Prednisolone Induced-immunocompromised Patients