Korean J Ophthalmol.
2015 Jun;29(3):209-211. 10.3341/kjo.2015.29.3.209.
Delayed Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Following Acute Primary Angle Closure
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. kkn9901700@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2363763
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2015.29.3.209
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
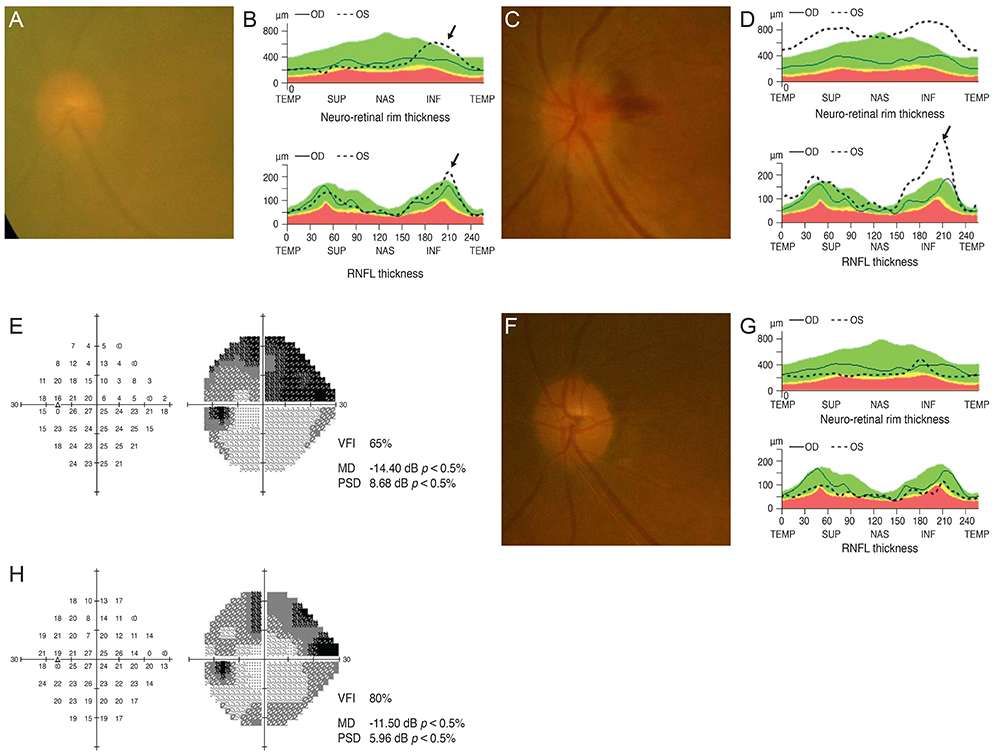
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nahum Y, Newman H, Kurtz S, Rachmiel R. Nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy in a patient with primary acute angle-closure glaucoma. Can J Ophthalmol. 2008; 43:723–724.2. Choudhari NS, George R, Kankaria V, Sunil GT. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy precipitated by acute primary angle closure. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2010; 58:437–440.3. Kuriyan AE, Lam BL. Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy secondary to acute primary-angle closure. Clin Ophthalmol. 2013; 7:1233–1238.4. Hayreh SS. Ischemic optic neuropathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2009; 28:34–62.5. Hayreh SS. Blood supply of the optic nerve head and its role in optic atrophy, glaucoma, and oedema of the optic disc. Br J Ophthalmol. 1969; 53:721–748.6. Tsai JC, Lin PW, Teng MC, Lai IC. Longitudinal changes in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness after acute primary angle closure measured with optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007; 48:1659–1664.7. Hayreh SS. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. V. Optic disc edema an early sign. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981; 99:1030–1040.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropethy
- A Case of Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy after Bilateral Selective Neck Dissection
- Subretinal Fluid Collection in Patient With Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy: A Case Report
- A Case of Subtype Giant Cell Arteritis Without Symptoms of Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
- Bilateral Delayed Nonarteritic Anterior Ischemic Neuropathy Following Acute Primary Angle-closure Crisis