Ann Lab Med.
2015 May;35(3):387-389. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.3.387.
Identification of p.Glu131Lys Mutation in the IHH Gene in a Korean Patient With Brachydactyly Type A1
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. changski@skku.edu
- 2Department of Radiology, Woorisoa Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Thyroid Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. swkimmd@skku.edu
- KMID: 2363219
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.3.387
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
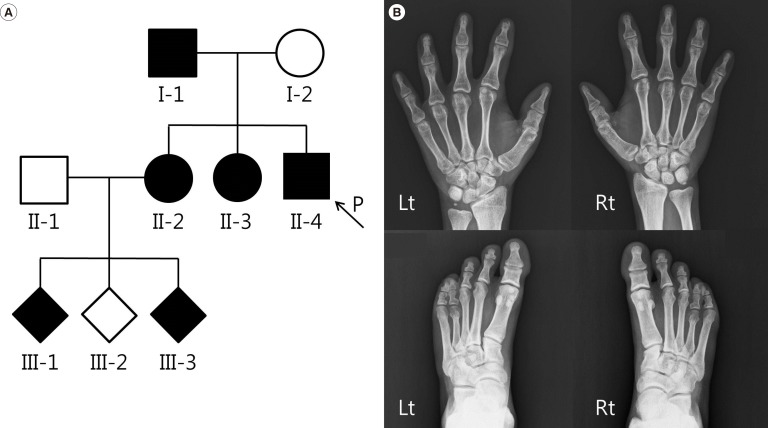
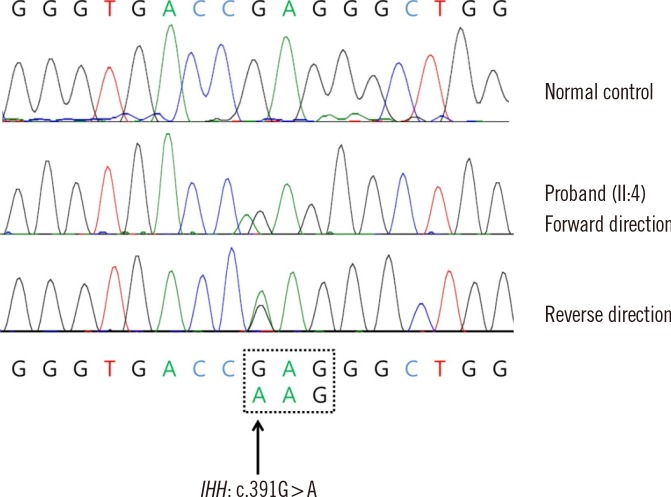
Figure
Reference
-
2. Utine GE, Breckpot J, Thienpont B, Alanay Y, Aksoy C, Boduroğlu K, et al. A second patient with Tsukahara syndrome: type A1 brachydactyly, short stature, hearing loss, microcephaly, mental retardation and ptosis. Am J Med Genet A. 2010; 152A:947–949. PMID: 20358606.
Article3. Gao B, Hu J, Stricker S, Cheung M, Ma G, Law KF, et al. A mutation in Ihh that causes digit abnormalities alters its signalling capacity and range. Nature. 2009; 458:1196–1200. PMID: 19252479.
Article4. Armour CM, McCready ME, Baig A, Hunter AG, Bulman DE. A novel locus for brachydactyly type A1 on chromosome 5p13.3-p13.2. J Med Genet. 2002; 39:186–188. PMID: 11897820.
Article5. Byrnes AM, Racacho L, Nikkel SM, Xiao F, MacDonald H, Underhill TM, et al. Mutations in GDF5 presenting as semidominant brachydactyly A1. Hum Mutat. 2010; 31:1155–1162. PMID: 20683927.
Article6. Byrnes AM, Racacho L, Grimsey A, Hudgins L, Kwan AC, Sangalli M, et al. Brachydactyly A-1 mutations restricted to the central region of the N-terminal active fragment of Indian Hedgehog. Eur J Hum Genet. 2009; 17:1112–1120. PMID: 19277064.
Article7. Yang X, She C, Guo J, Yu AC, Lu Y, Shi X, et al. A locus for brachydactyly type A-1 maps to chromosome 2q35-q36. Am J Hum Genet. 2000; 66:892–903. PMID: 10712204.
Article8. Vortkamp A, Lee K, Lanske B, Segre GV, Kronenberg HM, Tabin CJ. Regulation of rate of cartilage differentiation by Indian hedgehog and PTH-related protein. Science. 1996; 273:613–622. PMID: 8662546.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A familial case with brachydactyly type C with a GDF5 mutation
- Identification of a GDF5 Mutation in a Korean Patient with Brachydactyly Type C without Foot Involvement
- A frameshift mutation in the TRPS1 gene showing a mild phenotype of trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type 1
- Trichorhinophalangeal Syndrome Type III Associated with a Novel Missense Mutation in the TRPS1 Gene
- Identification of a novel mutation in a patient with pseudohypoparathyroidism type Ia