J Korean Assoc Pediatr Surg.
2016 Dec;22(2):54-58. 10.13029/jkaps.2016.22.2.54.
Farber Disease Misdiagnosed as Hemangioendothelioma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatric Surgery, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, Seoul, Korea. spkhy02@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2363025
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13029/jkaps.2016.22.2.54
Abstract
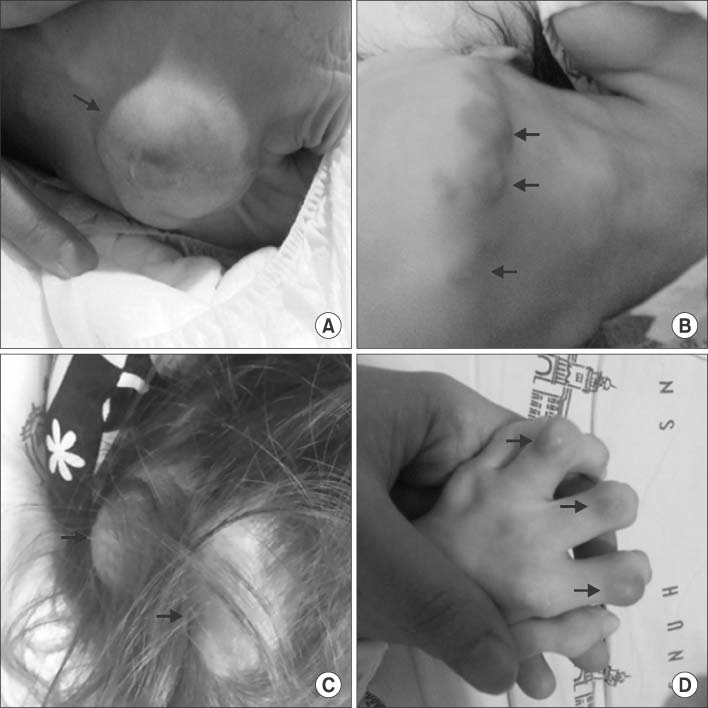
- Farber disease (FD) is a rare lysosomal storage disorder that shows autosomal recessive inheritance. We report the case of a 58-month-old girl with FD, who was misdiagnosed with epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. The patient had undergone five surgeries for sacrococcygeal masses and three surgeries for scalp masses owing to misdiagnosis. Here, we describe this rare case of FD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
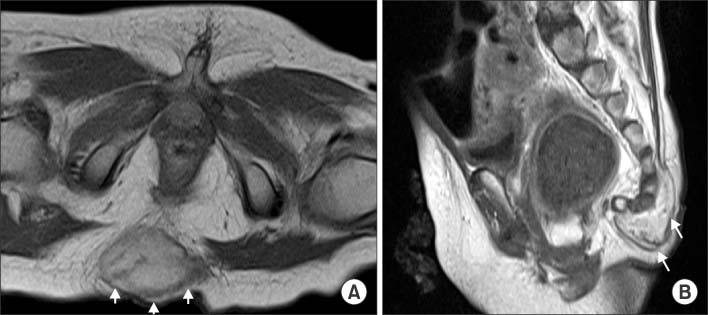
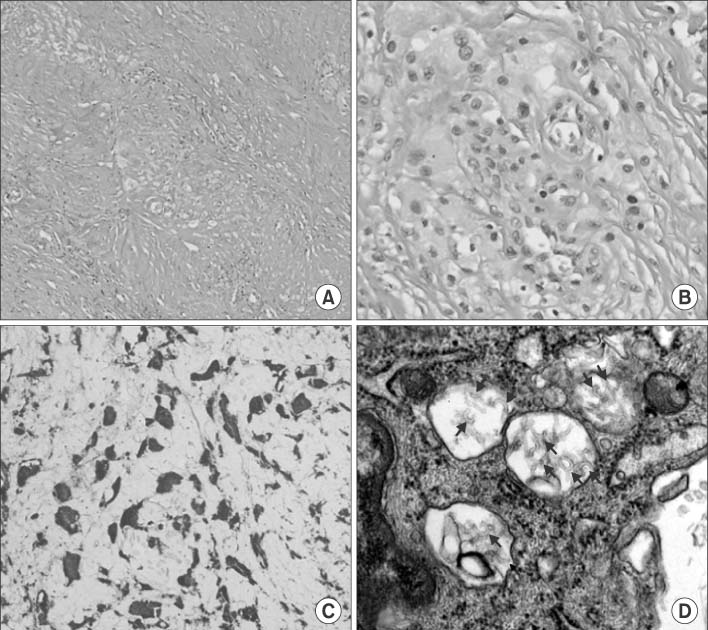
Figure
Reference
-
1. Devi AR, Gopikrishna M, Ratheesh R, Savithri G, Swarnalata G, Bashyam M. Farber lipogranulomatosis: clinical and molecular genetic analysis reveals a novel mutation in an Indian family. J Hum Genet. 2006; 51:811–814.
Article2. Farber disease [Internet]. Paris: Orphanet / INSERM US14;c2015. updated 2015 Jul. cited 2016 Jun 12. Available from: http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?Expert=333.3. Moser HW, Linke T, Fensom AH, Levade T, Sandhoff K. Acid ceramidase deficiency: farber lipogranulomatosis. In : Schriver CR, Beadudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. The metabolic & molecular bases of inherited disease. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2001. p. 3573–3588.4. Yeager AM, Uhas KA, Coles CD, Davis PC, Krause WL, Moser HW. Bone marrow transplantation for infantile ceramidase deficiency (Farber disease). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000; 26:357–363.
Article5. Vormoor J, Ehlert K, Groll AH, Koch HG, Frosch M, Roth J. Successful hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in Farber disease. J Pediatr. 2004; 144:132–134.
Article6. Kayler LK, Merion RM, Arenas JD, Magee JC, Campbell DA, Rudich SM, et al. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver disseminated to the peritoneum treated with liver transplantation and interferon alpha-2B. Transplantation. 2002; 74:128–130.
Article7. Lakkis Z, Kim S, Delabrousse E, Jary M, Nguyen T, Mantion G, et al. Metronomic cyclophosphamide: an alternative treatment for hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. J Hepatol. 2013; 58:1254–1257.
Article8. Cvitanovic-Sojat L, Gjergja Juraski R, Sabourdy F, Fensom AH, Fumic K, Paschke E, et al. Farber lipogranulomatosis type 1--late presentation and early death in a Croatian boy with a novel homozygous ASAH1 mutation. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2011; 15:171–173.9. Ahmad A, Mazhar AU, Anwar M. Farber disease: a rare neurodegenerative disorder. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2009; 19:67–68.10. Fiumara A, Nigro F, Pavone L, Moser HW. Farber disease with prolonged survival. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1993; 16:915–916.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma on the Choana
- Infantile hemangioendothelioma treated with high dose methylprednisolone pulse therapy
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver
- Hemangioendothelioma Developed in Thoracic Vertebra: Report of 1 Case
- Two cases of infantile hemangioendothelioma of the liver