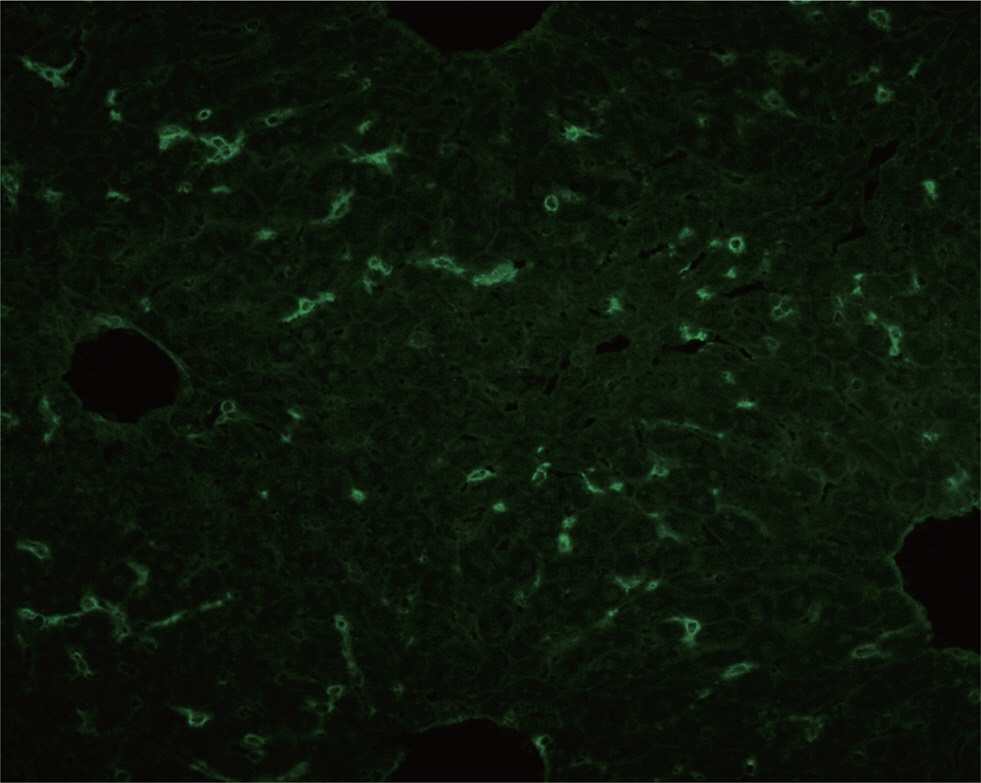
Lab Med Online.
2017 Jan;7(1):37-40. 10.3343/lmo.2017.7.1.37.
Case of Bile Canalicular Antibody in a Korean Patient with Alcoholic Hepatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hanyang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. tykim@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Hanyang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2363005
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2017.7.1.37
Abstract
- Bile canalicular antibody (BCA) was first reported in 1969. Many studies of BCA were performed in the 1970s and 1980s and revealed that BCA has a highly positive rate in chronic active hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC). These studies suggested that BCA can be useful in the diagnosis of these liver diseases. However, BCA is almost negative in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. We report a case of BCA in a 50-yr-old woman with a history of heavy alcohol consumption. The patient's serum levels of aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase were increased, leading to a diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis. The patient was evaluated for liver disease. Anti-mitochondria antibody, anti-smooth muscle antibody, and anti-liver kidney microsomal antibody tests were conducted, yielding negative results. However, during this testing process, the patient's serum was incidentally found to be positive for BCA at a titer of 1:160. This is the first case report of BCA in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Diederichsen H. Hetero-antibody against bile canaliculi in patients with chronic, clinically active hepatitis. Acta Med Scand. 1969; 186:299–302.
Article2. MacSween RN, Armstrong EM, Gray KG, Mason M. Bile canalicular antibody in primary biliary cirrhosis and in other liver diseases. Lancet. 1973; 1:1419–21.
Article3. Kurki P, Miettinen A, Linder E, Pikkarainen P, Vuoristo M, Salaspuro MP. Different types of smooth muscle antibodies in chronic active hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis: their diagnostic and prognostic signifcance. Gut. 1980; 21:878–84.4. Diederichsen H, Riisom K, Andersen I, Hage E. Antibodies to isolated hepatocytes in chronic active liver disease. Identifcation and diagnostic signifcance of bile canalicular antibodies. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1986; 21:146–50.5. Fischer JT, Petz LD, Garratty G, Cooper NR. Correlations between quantitative assay of red cell-bound C3, serologic reactions, and hemolytic anemia. Blood. 1974; 44:359–73.
Article6. Tuma DJ, Klassen LW. Immune responses to acetaldehyde-protein adducts: Role in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1992; 103:1969–73.
Article7. Stieger B, Meier Y, Meier PJ. The bile salt export pump. Pfugers Arch. 2007; 453:611–20.
Article8. Jara P, Hierro L, Martínez-Fernández P, Alvarez-Doforno R, Yánez F, Diaz MC, et al. Recurrence of bile salt export pump defciency after liver transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:1359–67.9. Pauli-Magnus C, Meier PJ. Hepatocellular transporters and cholestasis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005; 39:S103–10.
Article10. Borst P, de Wolf C, van de Wetering K. Multidrug resistance-associated proteins 3, 4, and 5. Pfugers Arch. 2007; 453:661–73.
Article11. Smit JJ, Schinkel AH, Oude Elferink RP, Groen AK, Wagenaar E, van Deemter L, et al. Homozygous disruption of the murine mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene leads to a complete absence of phospholipid from bile and to liver disease. Cell. 1993; 75:451–62.
Article12. Torok NJ. Update on alcoholic hepatitis. Biomolecules. 2015; 5:2978–86.
Article13. Dunn W, Angulo P, Sanderson S, Jamil LH, Stadheim L, Rosen C, et al. Utility of a new model to diagnose an alcohol basis for steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2006; 131:1057–63.
Article14. Altamirano J, Miquel R, Katoonizadeh A, Abraldes JG, Duarte-Rojo A, Louvet A, et al. A histologic scoring system for prognosis of patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146:1231–9.15. Naveau S, Giraud V, Borotto E, Aubert A, Capron F, Chaput JC. Excess weight risk factor for alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 1997; 25:108–11.
Article16. Carithers RL Jr, Herlong HF, Diehl AM, Shaw EW, Combes B, Fallon HJ, et al. Methylprednisolone therapy in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis. A randomized multicenter trial. Ann Intern Med. 1989; 110:685–90.17. Dunn W, Jamil LH, Brown LS, Wiesner RH, Kim WR, Menon KV, et al. MELD accurately predicts mortality in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatology. 2005; 41:353–8.
Article18. Dominguez M, Rincón D, Abraldes JG, Miquel R, Colmenero J, Bellot P, et al. A new scoring system for prognostic stratifcation of patients with alcoholic hepatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008; 103:2747–56.19. Louvet A, Naveau S, Abdelnour M, Ramond MJ, Diaz E, Fartoux L, et al. The Lille model: A new tool for therapeutic strategy in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis treated with steroids. Hepatology. 2007; 45:1348–54.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Alcoholic Hepatitis
- The Role of Bile Acid Receptors in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases
- Liver in Systemic Lupus Erythematous: Clinicopathological analysis of 8 cases
- Prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen(HBsAg), anti-hepatitis C virus(HCV) antibody-treponemal antibody and anti-HIV-1 antibody in donor's bloods
- A Case of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Mimicking Acute Hepatitis B in the Clinic, Republic of Korea