J Korean Diabetes.
2016 Dec;17(4):282-287. 10.4093/jkd.2016.17.4.282.
A Case of Diabetic Ketoacidosis Caused by Dapsone-Induced Acute Pancreatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Research Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Cha Gumi Medical Center, CHA University, Gumi, Korea. sungwoocap@naver.com
- KMID: 2362988
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2016.17.4.282
Abstract
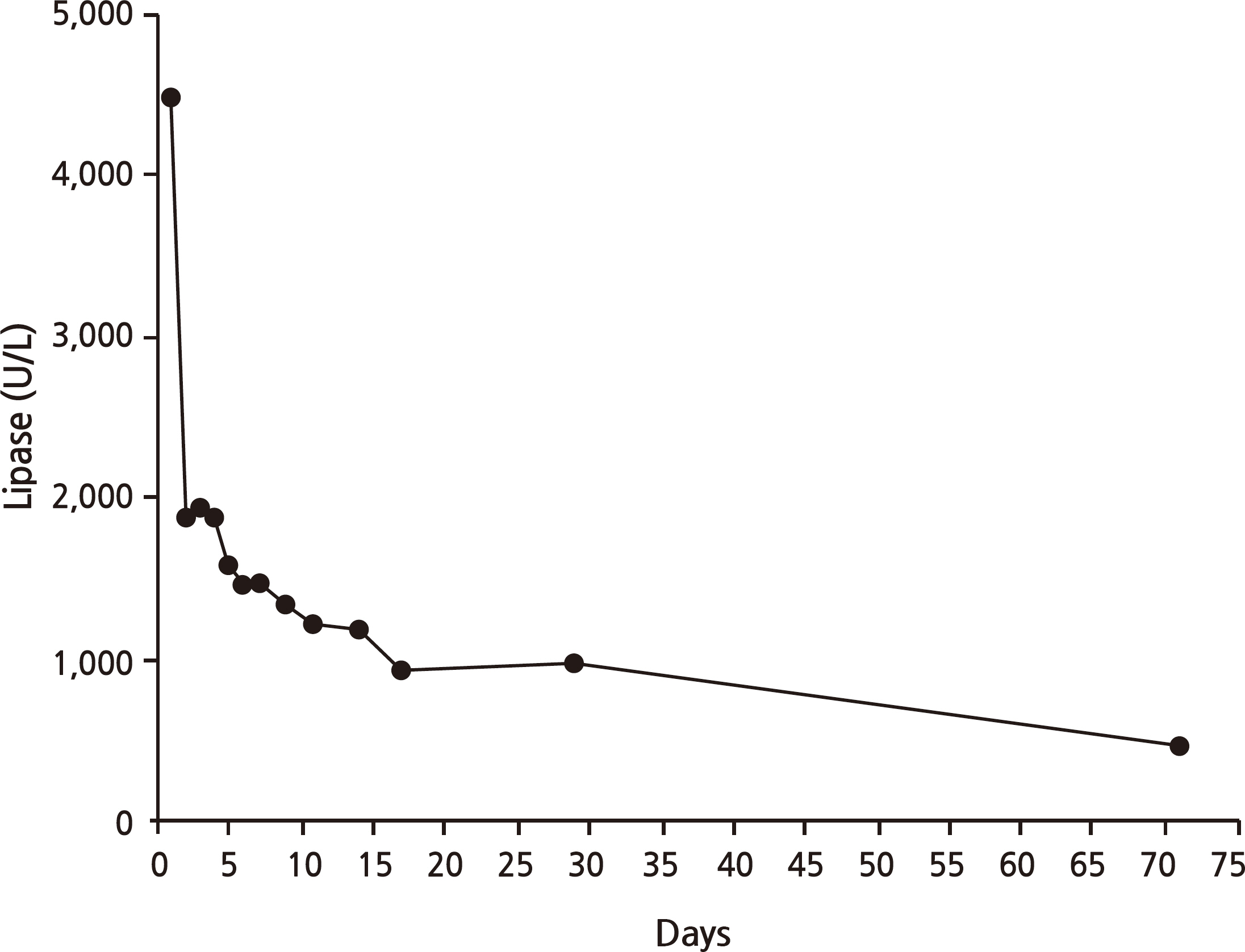
- Drug-induced pancreatitis accounts for 0.1~2.0% of all pancreatitis cases. Generally, the mechanism of drug-induced pancreatitis is an immune reaction, accumulation of toxic material, and/or ischemia. However, how dapsone causes pancreatitis remains unclear. A 61-year-old man presented with a 2-week history of epigastric discomfort. He had taken dapsone for 2 months to treat psoriasis. Laboratory findings showed high blood glucose levels and metabolic acidosis; however, hemoglobin A1c was low. Serum amylase and lipase levels were elevated to 125/4,479 U/L. Abdominal computed tomography was indicative of pancreatitis. There was no causative history of pancreatitis and no other medication history except dapsone. Thus, we reached a diagnosis of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) followed by dapsone-induced pancreatitis. The patient fasted and was treated with insulin administration and fluid hydration in accordance with treatment guidelines. After treatment, amylase and lipase decreased and symptoms subsided, but insulin injection was required to control blood glucose levels. Drug-induced pancreatitis is a very rare adverse effect of dapsone. Only four cases of pancreatitis related to dapsone could be found in a PubMed search. Moreover, diabetes caused by dapsone-induced pancreatitis has not been reported previously. Here, we report a case of DKA caused by dapsoneinduced acute pancreatitis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Coleman MD. Dapsone: modes of action, toxicity and possible strategies for increasing patient tolerance. Br J Dermatol. 1993; 129:507–13.
Article2. McKenna KE, Robinson J. The dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome occurring in a patient with dermatitis herpetiformis. Br J Dermatol. 1997; 137:657–8.
Article3. Lawrence WA, Olsen HW, Nickles DJ. Dapsone hepatitis. Arch Intern Med. 1987; 147:175.
Article4. Jha SH, Reddy JA, Dave JK. Dapsoneinduced acute pancreatitis. Ann Pharmacother. 2003; 37:1438–40.
Article5. Navarro-Mingorance A, Castellanos-Alcarria AJ, Ibañez-Micó S, Cervantes-Pardo A, Sánchez-Pedreño P. Dapsoneinduced isolated acute pancreatitis in a child with linear IgA dermatitis. Indian J Pediatr. 2014; 81:735–6.
Article6. Das AK, Jawed Q. Drug-induced acute pancreatitis: a rare manifestation of an incomplete "dapsone syndrome". Indian J Pharmacol. 2014; 46:455–7.
Article7. Corp CC, Ghishan FK. The sulfone syndrome complicated by pancreatitis and pleural effusion in an adolescent receiving dapsone for treatment of acne vulgaris. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1998; 26:103–5.
Article8. Kaurich T. Drug-induced acute pancreatitis. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2008; 21:77–81.
Article9. Nitsche CJ, Jamieson N, Lerch MM, Mayerle JV. Drug induced pancreatitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 24:143–55.
Article10. Trivedi CD, Pitchumoni CS. Drug-induced pancreatitis: an update. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005; 39:709–16.11. Das SL, Singh PP, Phillips AR, Murphy R, Windsor JA, Petrov MS. Newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus after acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Gut. 2014; 63:818–31.
Article12. Gornik I, Vujaklija A, Lukić E, Madzarac G, Gasparović V. Hyperglycemia in sepsis is a risk factor for development of type II diabetes. J Crit Care. 2010; 25:263–9.
Article13. Shen HN, Yang CC, Chang YH, Lu CL, Li CY. Risk of diabetes mellitus after first-attack acute pancreatitis: a national population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015; 110:1698–706.
Article14. Shah AD, Fox RK, Rushakoff RJ. Falsely decreased HbA1c in a type 2 diabetic patient treated with dapsone. Endocr Pract. 2014; 20:e229–32.
Article15. Unnikrishnan R, Anjana RM, Mohan V. Drugs affecting HbA1c levels. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2012; 16:528–31.16. Nebesio CL, Lewis C, Chuang TY. Lack of an association between granuloma annulare and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Br J Dermatol. 2002; 146:122–4.
Article17. Kibsgaard L, Bay B, Deleuran M, Vestergaard C. A retrospective consecutive case-series study on the effect of systemic treatment, length of admission time, and comorbidities in 98 bullous pemphigoid patients admitted to a tertiary centre. Acta Derm Venereol. 2015; 95:307–11.
Article18. Duff M, Demidova O, Blackburn S, Shubrook J. Cutaneous manifestations of diabetes mellitus. Clin Diabetes. 2015; 33:40–8.
Article19. Imagawa A, Hanafusa T, Uchigata Y, Kanatsuka A, Kawasaki E, Kobayashi T, Shimada A, Shimizu I, Toyoda T, Maruyama T, Makino H. Fulminant type 1 diabetes: a nationwide survey in Japan. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:2345–52.20. Hanafusa T, Imagawa A. Fulminant type 1 diabetes: a novel clinical entity requiring special attention by all medical practitioners. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 3:36–45. quiz 2p following 69.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Severe Hypertriglyceridemia in Diabetic Ketoacidosis Accompanied by Acute Pancreatitis: Case Report
- Ketoacidosis with Hypertriglyceridemia-Induced Pancreatitis in a Patient with Gestational Diabetes: A Case Report
- Acute Pancreatitis Complicated with Diabetic Ketoacidosis in a Young Adult without Hypertriglyceridemia: A Case Report
- Concurrent Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Acute Pancreatitis in Mild Hypertriglyceridemia: An Enigmatic Triangle
- A case of transient diabetes mellitus and diabetic ketoacidosis induced by L-asparaginase and prednisolone administration in a patient with relapsed acute lymphocytic leukemia