J Korean Med Sci.
2015 Dec;30(12):1828-1835. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.12.1828.
Early Caffeine Use in Very Low Birth Weight Infants and Neonatal Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. 19890022@kuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 2359968
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.12.1828
Abstract
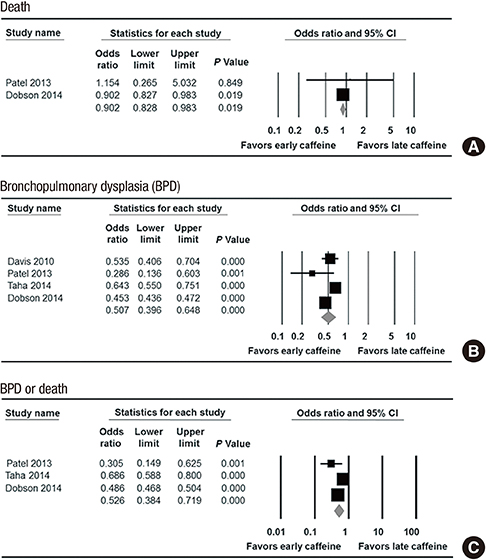
- The use of caffeine citrate for treatment of apnea in very low birth weight infants showed short-term and long-term benefits. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature was undertaken to document the effect providing caffeine early (0-2 days of life) compared to providing caffeine late (> or =3 days of life) in very low birth weight infants on several neonatal outcomes, including bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). We searched MEDLINE, the EMBASE database, the Cochrane Library, and KoreaMed for this meta-analysis. The quality of the included studies was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale and Jadad's scale. Studies were included if they examined the effect of the early use of caffeine compared with the late use of caffeine. Two reviewers screened the candidate articles and extracted the data from the full-text of all of the included studies. We included a total of 59,136 participants (range 58,997-59,136; variable in one study) from a total of 5 studies. The risk of death (odds ratio [OR], 0.902; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.828 to 0.983; P=0.019), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) (OR, 0.507; 95% CI, 0.396 to 0.648; P<0.001), and BPD or death (OR, 0.526; 95% CI, 0.384 to 0.719; P<0.001) were lower in the early caffeine group. Early caffeine use was not associated with a risk of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) and NEC requiring surgery. This meta-analysis suggests that early caffeine use has beneficial effects on neonatal outcomes, including mortality and BPD, without increasing the risk of NEC.
MeSH Terms
-
Apnea/*drug therapy
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia/drug therapy
Caffeine/*administration & dosage/adverse effects
Citrates/*administration & dosage/adverse effects
Enterocolitis, Necrotizing/etiology
Humans
Infant
Infant Mortality
Infant, Newborn
Infant, Very Low Birth Weight
Risk Factors
Treatment Outcome
Caffeine
Citrates
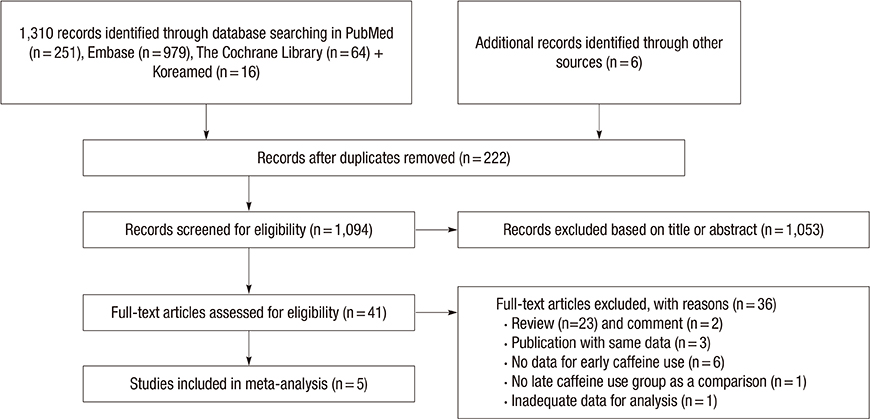
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Hemodynamic Effects on Systemic Blood Flow and Ductal Shunting Flow after Loading Dose of Intravenous Caffeine in Preterm Infants according to the Patency of Ductus Arteriosus
Jihye Hwang, Yu Seon Kim, Jeong Hee Shin, Byung Min Choi
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(4):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e25.
Reference
-
1. Gannon BA. Theophylline or caffeine: which is best for apnea of prematurity? Neonatal Netw. 2000; 19:33–36.2. Aranda JV, Beharry K, Valencia GB, Natarajan G, Davis J. Caffeine impact on neonatal morbidities. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010; 23:20–23.3. Sacré L, Vandenplas Y. Xanthines in apnea of premature infants. Influence on gastroesophageal reflux. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1987; 44:383–385.4. Picone S, Bedetta M, Paolillo P. Caffeine citrate: when and for how long. A literature review. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012; 25:11–14.5. Schmidt B, Roberts RS, Davis P, Doyle LW, Barrington KJ, Ohlsson A, Solimano A, Tin W. Caffeine for Apnea of Prematurity Trial Group. Caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:2112–2121.6. Schmidt B, Roberts RS, Davis P, Doyle LW, Barrington KJ, Ohlsson A, Solimano A, Tin W. Caffeine for Apnea of Prematurity Trial Group. Long-term effects of caffeine therapy for apnea of prematurity. N Engl J Med. 2007; 357:1893–1902.7. Haskó G, Cronstein BN. Adenosine: an endogenous regulator of innate immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004; 25:33–39.8. Kilicdag H, Daglioglu YK, Erdogan S, Zorludemir S. Effects of caffeine on neuronal apoptosis in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014; 27:1470–1475.9. Rivkees SA, Wendler CC. Adverse and protective influences of adenosine on the newborn and embryo: implications for preterm white matter injury and embryo protection. Pediatr Res. 2011; 69:271–278.10. Doyle LW, Cheong J, Hunt RW, Lee KJ, Thompson DK, Davis PG, Rees S, Anderson PJ, Inder TE. Caffeine and brain development in very preterm infants. Ann Neurol. 2010; 68:734–742.11. Horrigan LA, Kelly JP, Connor TJ. Immunomodulatory effects of caffeine: friend or foe? Pharmacol Ther. 2006; 111:877–892.12. Martin RJ, Wang K, Köroğlu O, Di Fiore J, Kc P. Intermittent hypoxic episodes in preterm infants: do they matter? Neonatology. 2011; 100:303–310.13. Chavez Valdez R, Ahlawat R, Wills-Karp M, Nathan A, Ezell T, Gauda EB. Correlation between serum caffeine levels and changes in cytokine profile in a cohort of preterm infants. J Pediatr. 2011; 158:57–64.e1.14. Davis PG, Schmidt B, Roberts RS, Doyle LW, Asztalos E, Haslam R, Sinha S, Tin W. Caffeine for Apnea of Prematurity Trial Group. Caffeine for Apnea of Prematurity trial: benefits may vary in subgroups. J Pediatr. 2010; 156:382–387.15. Dobson NR, Patel RM, Smith PB, Kuehn DR, Clark J, Vyas-Read S, Herring A, Laughon MM, Carlton D, Hunt CE. Trends in caffeine use and association between clinical outcomes and timing of therapy in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr. 2014; 164:992–998.e3.16. Taha D, Kirkby S, Nawab U, Dysart KC, Genen L, Greenspan JS, Aghai ZH. Early caffeine therapy for prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014; 27:1698–1702.17. Patel RM, Leong T, Carlton DP, Vyas-Read S. Early caffeine therapy and clinical outcomes in extremely preterm infants. J Perinatol. 2013; 33:134–140.18. Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996; 17:1–12.19. Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, Tugwell P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyse. accessed on 4 September 2014. Available at http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.20. Abbasi S, Aden U, Allan W, Bada H, Barks J, Bauer C, Bizzarro M, Carlo W, Chen X, Cummings J. Early caffeine is associated with decreased IVH in very low birth weight neonate. Platform Session 2: (#9-16) [abstract]. Ann Neurol. 2010; 68:S88–S90.21. Aranda JV, Gorman W, Bergsteinsson H, Gunn T. Efficacy of caffeine in treatment of apnea in the low-birth-weight infant. J Pediatr. 1977; 90:467–472.22. Steer PA, Henderson-Smart DJ. Caffeine versus theophylline for apnea in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000; CD000273.23. Henderson-Smart DJ, Steer PA. Caffeine versus theophylline for apnea in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000; CD000273.24. Sreenan C, Etches PC, Demianczuk N, Robertson CM. Isolated mental developmental delay in very low birth weight infants: association with prolonged doxapram therapy for apnea. J Pediatr. 2001; 139:832–837.25. Kassim Z, Greenough A, Rafferty GF. Effect of caffeine on respiratory muscle strength and lung function in prematurely born, ventilated infants. Eur J Pediatr. 2009; 168:1491–1495.26. Chavez-Valdez R, Wills-Karp M, Ahlawat R, Cristofalo EA, Nathan A, Gauda EB. Caffeine modulates TNF-alpha production by cord blood monocytes: the role of adenosine receptors. Pediatr Res. 2009; 65:203–208.27. Weichelt U, Cay R, Schmitz T, Strauss E, Sifringer M, Bührer C, Endesfelder S. Prevention of hyperoxia-mediated pulmonary inflammation in neonatal rats by caffeine. Eur Respir J. 2013; 41:966–973.28. Martin RJ, Di Fiore JM, Macfarlane PM, Wilson CG. Physiologic basis for intermittent hypoxic episodes in preterm infants. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012; 758:351–358.29. Ogden BE, Murphy SA, Saunders GC, Pathak D, Johnson JD. Neonatal lung neutrophils and elastase/proteinase inhibitor imbalance. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984; 130:817–821.30. Pryds O, Schneider S. Aminophylline reduces cerebral blood flow in stable, preterm infants without affecting the visual evoked potential. Eur J Pediatr. 1991; 150:366–369.31. Lampkin SJ, Turner AM, Lakshminrusimha S, Mathew B, Brown J, Fominaya CE, Johnson KK. Association between caffeine citrate exposure and necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2013; 70:603–608.32. Henderson-Smart DJ, De Paoli AG. Prophylactic methylxanthine for prevention of apnoea in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010; CD000432.33. Erenberg A, Leff RD, Haack DG, Mosdell KW, Hicks GM, Wynne BA. Caffeine citrate for the treatment of apnea of prematurity: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Pharmacotherapy. 2000; 20:644–652.34. Bancalari E. Caffeine for apnea of prematurity. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:2179–2181.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fluconazole prophylaxis against invasive candidiasis in very low and extremely low birth weight preterm neonates: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Changes in Neonatal Epidemiology during the Last 3 Decades in Korea
- Clinical Study of Prematurity and Low Birth Weight Infants
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants
- Changes in neonatal outcomes in Korea