J Korean Med Assoc.
2016 Nov;59(11):883-887. 10.5124/jkma.2016.59.11.883.
Fixed-dose combination therapy for cardiovascular prevention
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. shl1106@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2358436
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2016.59.11.883
Abstract
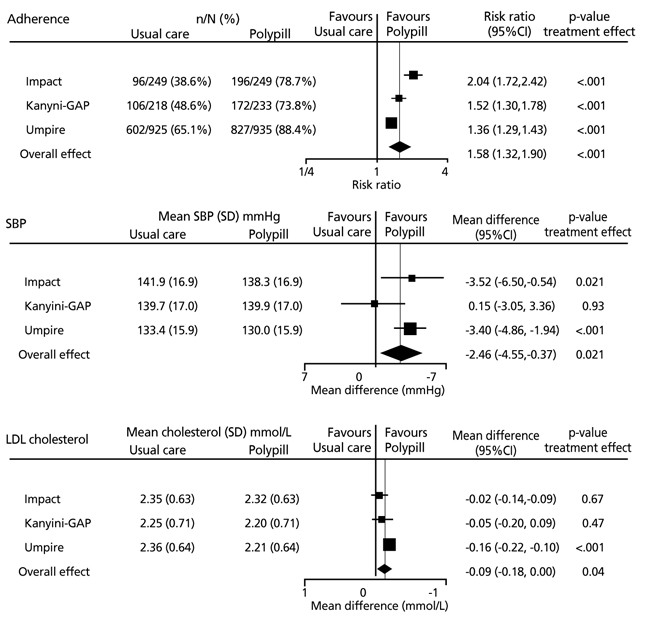
- In patients with high cardiovascular risk, the number of drugs needed is often high, and this may decrease long-term adherence. Therefore, maintaining good adherence and reducing cardiovascular risk is currently an important issue in preventive cardiology. The combination of two different antihypertensive agents is reported to reduce blood pressure more than the doubling of a single agent. In addition, the prevalence of adverse events with two drugs is less than the sum of the number of events associated with each drug. The combination of renin-angiotensin system blockers with statins is a widely used regimen in cardiovascular prevention. Recent clinical trials using a fixed-dose combination of aspirin, statins, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors has revealed better adherence in the combination group than in the group with separately administered drugs. Interestingly, this benefit was more prominent in patients who were under-treated (less adherent) at baseline.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
Antihypertensive Agents
Aspirin
Blood Pressure
Cardiology
Humans
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Patient Compliance
Prevalence
Renin-Angiotensin System
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
Antihypertensive Agents
Aspirin
Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wald DS, Law M, Morris JK, Bestwick JP, Wald NJ. Combination therapy versus monotherapy in reducing blood pressure: meta-analysis on 11,000 participants from 42 trials. Am J Med. 2009; 122:290–300.
Article2. Law MR, Wald NJ, Morris JK, Jordan RE. Value of low dose combination treatment with blood pressure lowering drugs: analysis of 354 randomised trials. BMJ. 2003; 326:1427.
Article3. Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Bohm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Galderisi M, Grobbee DE, Jaarsma T, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, Ruilope LM, Schmieder RE, Sirnes PA, Sleight P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Zannad F, Redon J, Dominiczak A, Narkiewicz K, Nilsson PM, Burnier M, Viigimaa M, Ambrosioni E, Caufield M, Coca A, Olsen MH, Schmieder RE, Tsioufis C, van de Borne P, Zamorano JL, Achenbach S, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, Bueno H, Dean V, Deaton C, Erol C, Fagard R, Ferrari R, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Kirchhof P, Knuuti J, Kolh P, Lancellotti P, Linhart A, Nihoyannopoulos P, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Sirnes PA, Tamargo JL, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Wijns W, Windecker S, Clement DL, Coca A, Gillebert TC, Tendera M, Rosei EA, Ambrosioni E, Anker SD, Bauersachs J, Hitij JB, Caulfield M, De Buyzere M, De Geest S, Derumeaux GA, Erdine S, Farsang C, Funck-Brentano C, Gerc V, Germano G, Gielen S, Haller H, Hoes AW, Jordan J, Kahan T, Komajda M, Lovic D, Mahrholdt H, Olsen MH, Ostergren J, Parati G, Perk J, Polonia J, Popescu BA, Reiner Z, Ryden L, Sirenko Y, Stanton A, Struijker-Boudier H, Tsioufis C, van de Borne P, Vlachopoulos C, Volpe M, Wood DA. 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2013; 34:2159–2219.4. Fihn SD, Gardin JM, Abrams J, Berra K, Blankenship JC, Dallas AP, Douglas PS, Foody JM, Gerber TC, Hinderliter AL, King SB 3rd, Kligfield PD, Krumholz HM, Kwong RY, Lim MJ, Linderbaum JA, Mack MJ, Munger MA, Prager RL, Sabik JF, Shaw LJ, Sikkema JD, Smith CR Jr, Smith SC Jr, Spertus JA, Williams SV. American College of Cardiology Foundation. 2012 ACCF/AHA/ACP/AATS/PCNA/SCAI/STS guideline for the diagnosis and management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines, and the American College of Physicians, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation. 2012; 126:3097–3137.
Article5. Jang JY, Lee SH, Kim BS, Seo HS, Kim WS, Ahn Y, Lee NH, Koh KK, Kang TS, Jo SH, Hong BK, Bae JH, Yang HM, Cha KS, Kim BS, Kwak CH, Cho DK, Kim U, Zo JH, Kang DH, Pyun WB, Chun KJ, Namgung J, Cha TJ, Juhn JH, Jung Y, Jang Y. Additive beneficial effects of valsartan combined with rosuvastatin in the treatment of hypercholesterolemic hypertensive patients. Korean Circ J. 2015; 45:225–233.
Article6. Thom S, Poulter N, Field J, Patel A, Prabhakaran D, Stanton A, Grobbee DE, Bots ML, Reddy KS, Cidambi R, Bompoint S, Billot L, Rodgers A. UMPIRE Collaborative Group. Effects of a fixed-dose combination strategy on adherence and risk factors in patients with or at high risk of CVD: the UMPIRE randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013; 310:918–929.
Article7. Selak V, Elley CR, Bullen C, Crengle S, Wadham A, Rafter N, Parag V, Harwood M, Doughty RN, Arroll B, Milne RJ, Bramley D, Bryant L, Jackson R, Rodgers A. Effect of fixed dose combination treatment on adherence and risk factor control among patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease: randomised controlled trial in primary care. BMJ. 2014; 348:g3318.
Article8. Patel A, Cass A, Peiris D, Usherwood T, Brown A, Jan S, Neal B, Hillis GS, Rafter N, Tonkin A, Webster R, Billot L, Bompoint S, Burch C, Burke H, Hayman N, Molanus B, Reid CM, Shiel L, Togni S, Rodgers A. Kanyini Guidelines Adherence with the Polypill (Kanyini GAP) Collaboration. A pragmatic randomized trial of a Polypill-based strategy to improve use of indicated preventive treatments in people at high cardiovascular disease risk. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2015; 22:920–930.
Article9. Castellano JM, Sanz G, Penalvo JL, Bansilal S, Fernandez-Ortiz A, Alvarez L, Guzman L, Linares JC, Garcia F, D'Aniello F, Arnaiz JA, Varea S, Martinez F, Lorenzatti A, Imaz I, Sanchez-Gomez LM, Roncaglioni MC, Baviera M, Smith SC Jr, Taubert K, Pocock S, Brotons C, Farkouh ME, Fuster V. A Polypill strategy to improve adherence: results from the FOCUS project. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 64:2071–2082.10. Webster R, Patel A, Selak V, Billot L, Bots ML, Brown A, Bullen C, Cass A, Crengle S, Raina Elley C, Grobbee DE, Neal B, Peiris D, Poulter N, Prabhakaran D, Rafter N, Stanton A, Stepien S, Thom S, Usherwood T, Wadham A, Rodgers A. SPACE Collaboration. Effectiveness of fixed dose combination medication ('Polypills') compared with usual care in patients with cardiovascular disease or at high risk: a prospective, indi-vidual patient data meta-analysis of 3140 patients in six coun-tries. Int J Cardiol. 2016; 205:147–156.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of SGLT2 inhibitor/metformin fixed dose combination in Korea
- Recent Update on Fixed Combinations of Antihypertensive Agents
- Radioiodine Therapy: Review of the Empiric Fixed Dose Approaches and Their Selective Applications
- Combination therapy of hypertension
- Does Combination Therapy of Aspirin Plus Antiplatelet Therapy Increase the Risk of Upper Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage?