J Korean Soc Med Inform.
2009 Mar;15(1):141-151.
Toward the Automatic Generation of the Entry Level CDA Documents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Interdisciplinary Program, College of Engineering, Seoul National University, Korea.
- 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Korea. jinchoi@snu.ac.kr
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
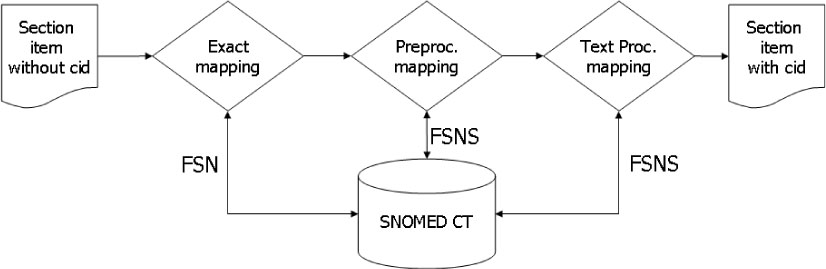
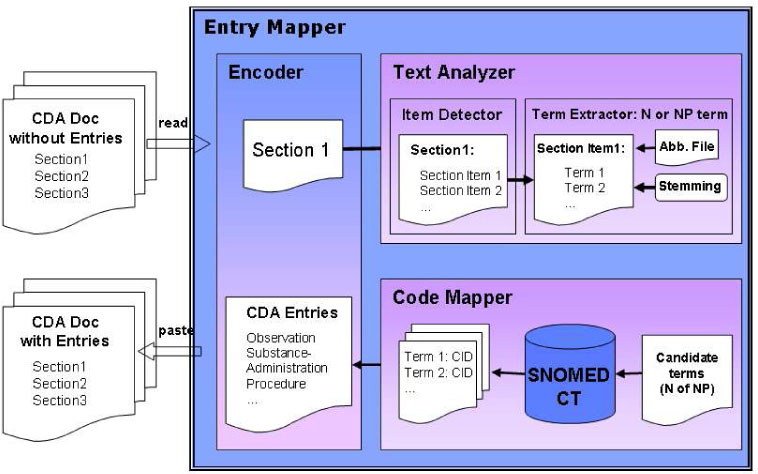
CDA (Clinical Document Architecture) is a markup standard for clinical document exchange. In order to increase the semantic interoperability of documents exchange, the clinical statements in the narrative blocks should be encoded with code values. Natural language processing (NLP) is required in order to transform the narrative blocks into the coded elements in the level 3 CDA documents. In this paper, we evaluate the accuracy of text mapping methods which are based on NLP.
METHODS
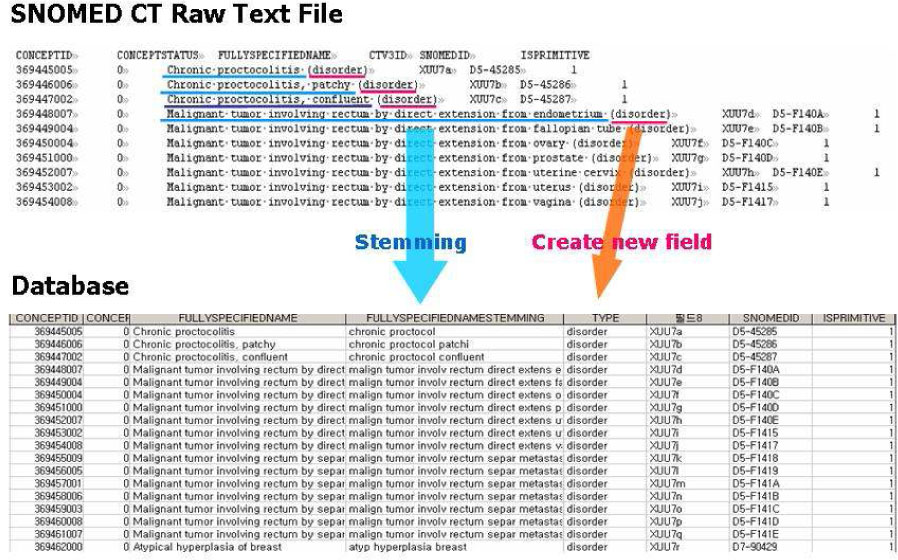
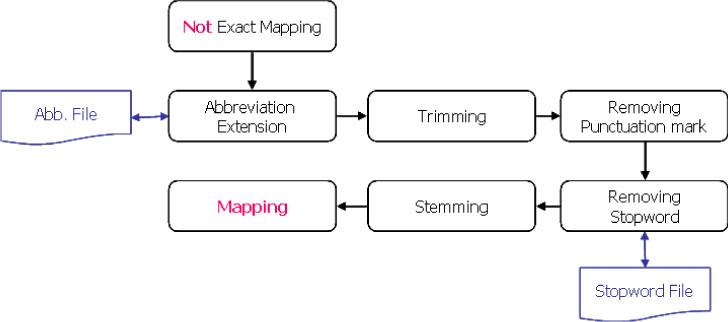
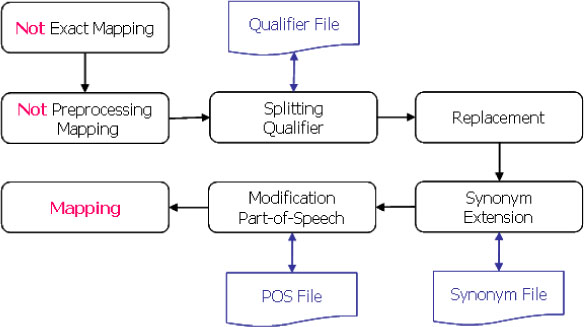
We analyzed about one thousand discharge summaries to know their characteristics and focused the syntactic patterns of the diagnostic sections in the discharge summaries. According to the patterns, different rules were applied for matching code values of Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine Clinical Terms (SNOMED CT).
RESULTS
The accuracy of matching was evaluated using five-hundred discharge summaries. The precision was as follows: 86.5% for diagnosis, 61.8% for chief complaint, 62.7%, for problem list, and 64.8% for discharge medication.
CONCLUSION
The text processing method based on the pattern analysis of a clinical statement can be effectively used for generating CDA entries.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Available at: http://www.hl7.org. Accessed December 13, 2007.2. Available at: http://www.hl7.org/v3ballot/html/welcome/environment/index.htm. Accessed December 13, 2007.3. Paterson GI, Shepherd M, Wang X, Watters C, Zitner D. Using the XML-based clinical document architecture for exchange of structured discharge summaries. Proceedings of the 35th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. 2002. In : 1st AMA National Conference on Child Abuse and Neglect; Jan 7-10; 1200–1209.
Article4. Dalmiani S, Marcheschi P, Mazzarisi A. HL7 clinical document architecture to share structured inwide hospital information systems. 2004. In : 22nd International Conference, EurePACS-MIR 2004;5. Heitmann KU, Schweiger R, Dudeck J. Discharge and referral data exchange using global standards-the SCIPHOX project in Germany. Study Health Technol Inform. 2002. 90:679–684.
Article6. Jung SW, Choe MS, Yoo SY, Park HK, Choi JW, et al. Development of CDA authoring Tool: CDA Studio. Proceedings of 7th International Workshop on HEALTHCOM 2005. 2005 June 23-25; 307–310.7. Choe MS, Jung SW, Choi JW. CDA studio: development of an integrated tool for generating CDA documents. Journal of Korean Society of Medical Informatics. 2005. 11:Supplement 2. 130–134.8. Seo HJ, Hong SK, Park JY, Lee JA, Park YR, Kim JH. Presentation of structural constraints for discharge note according to clinical document architecture standard. Journal of Korean Society of Medical Informatics. 2005. 11(2):189–197.
Article9. Kim IK, Lee JY, Kim IK, Cho H, Kwak YS. Clinical document repository system for electronic health record. Journal of Korean Society of Medical Informatics. 2005. 11(2):199–211.
Article10. Aronson AR. Effective mapping of biomedical text to the UMLS metathesaurus: the MetaMap program. 2001. In : AMIA Symposium Hanley & Belfus; 2001; 17–21.11. Huang Y, Lowe H, Hersh W. A pilot study of contextual UMLS indexing to improve the precision of concept-based representation in XML-structured clinical radiology reports. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2003. 10:580–587.
Article12. Friedman C, Shagina L, Lussier Y, Hripcsak G. Automated encoding of clinical documents based on natural language processing. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2004. 11(5):392–402.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- CDA Compression via Automatic Type Inference
- Clinical Document Repository System for Electronic Health Record
- Implementation of Medical Information Exchange System Based on EHR Standard
- The clinical decision analysis using decision tree
- Development Environment for Automatic Generation of Clinical Data Acquisition System