J Rheum Dis.
2016 Oct;23(5):321-325. 10.4078/jrd.2016.23.5.321.
A Case of Infectious Arthritis due to Staphylococcus lugdunensis in Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis, Diabetes Mellitus Patient, after Intraarticular Hyaluronic Acid Injection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Anyang SAM Hospital, Anyang, Korea. ninijang@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2356488
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2016.23.5.321
Abstract
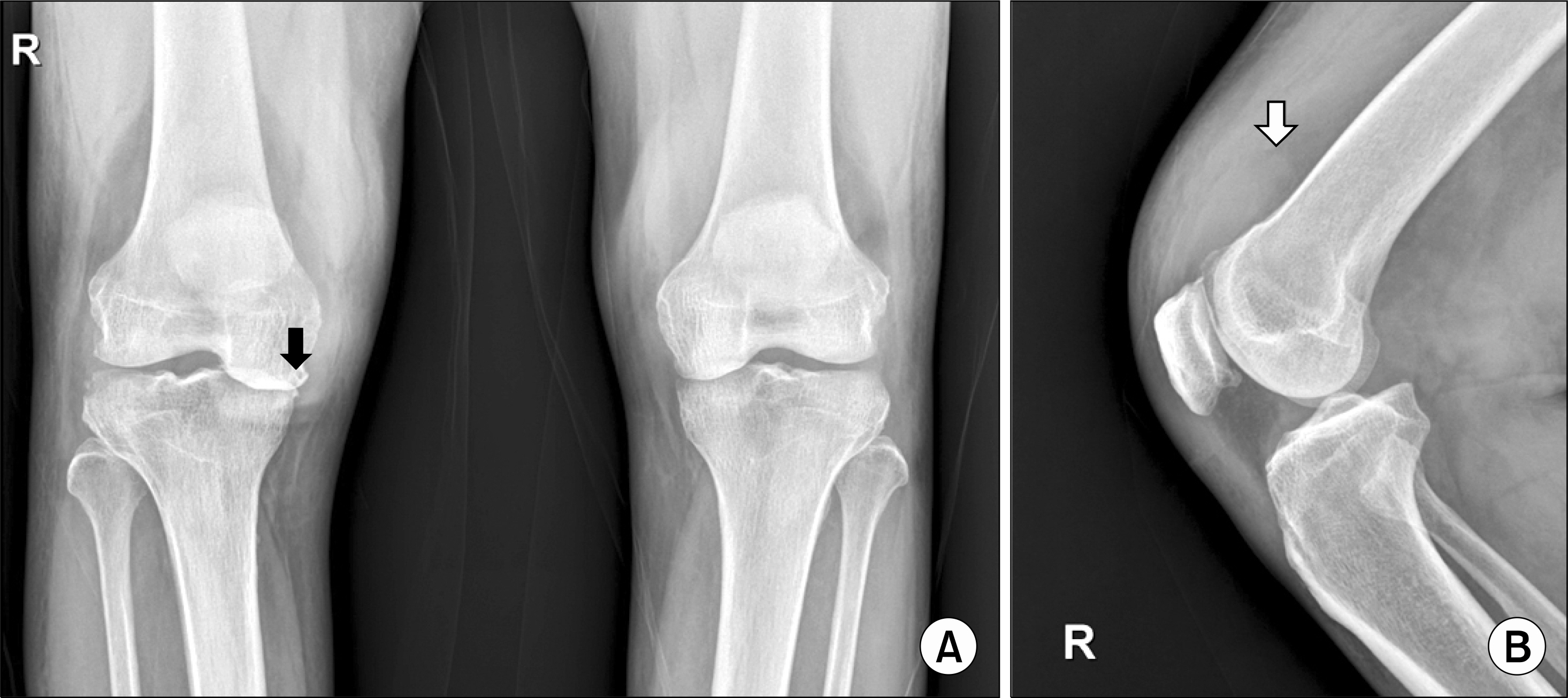
- Intra-articular hyaluronic acid injections for symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis are widely used but can result in complications, such as infectious arthritis. Staphylococcus lugdunensis is a common normal skin flora but can cause severe infectious disease, such as infective endocarditis. We present the first report of infectious arthritis caused by methicillin-sensitive S. lugdunensis after intra-articular hyaluronic acid injection in an immunocompromised patient in Korea.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Frank KL, Reichert EJ, Piper KE, Patel R. In vitro effects of antimicrobial agents on planktonic and biofilm forms of Staphylococcus lugdunensis clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007; 51:888–95.2. Bernardeau C, Bucki B, Lioté F. Acute arthritis after intraarticular hyaluronate injection: onset of effusions without crystal. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001; 60:518–20.
Article3. Shemesh S, Heller S, Salai M, Velkes S. Septic arthritis of the knee following intraarticular injections in elderly patients: report of six patients. Isr Med Assoc J. 2011; 13:757–60.4. Freney J, Brun Y, Bes M, Meugnier H, Grimont F, Grimond PAD, et al. Staphylococcus lugdunensis sp. Nov. and Staphylococcus schleiferi sp. Nov., two species from human clinical specimens. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 1988; 38:168–72.
Article5. Maria M, Manuel R, Clara C, Juan G. Artritis séptica por Staphylococcus lugdunensis. Reumatol Clin. 2009; 5:44–5.6. Klotchko A, Wallace MR, Licitra C, Sieger B. Staphylococcus lugdunensis: an emerging pathogen. South Med J. 2011; 104:509–14.7. Grupper M, Potasman I, Rosner I, Slobodin G, Rozenbaum M. Septic arthritis due to Staphylococcus lugdunensis in a native joint. Rheumatol Int. 2010; 30:1231–3.
Article8. Green SL. Efficacy of oral fleroxacin in bone and joint infections. Am J Med. 1993; 94:174S–6S.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Septic Knee Arthritis Caused by Staphylococcus lugdunensis After Intraarticular Injection Therapy
- Septic Arthritis after Intra-articular Hyaluronic Acid Injections in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: A report of two cases
- A case of bilateral psoas abscesses in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis
- Diagnosis of Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis by 68 Ga‑FAPI PET/CT
- Isolated Staphylococcal Infection of the Sternoclavicular Joint in Healthy Adult - A Case Report -