Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Oct;48(4):1196-1209. 10.4143/crt.2015.189.
Overexpression of Endoplasmic Reticulum Oxidoreductin 1-α (ERO1L) Is Associated with Poor Prognosis of Gastric Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Oncology, Gangnam Severance Cancer Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. chojy@yuhs.ac
- 2Samsung Bioepis Co., Ltd., Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Gangnam Severance Cancer Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, Gangnam Severance Cancer Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2356222
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2015.189
Abstract
- PURPOSE
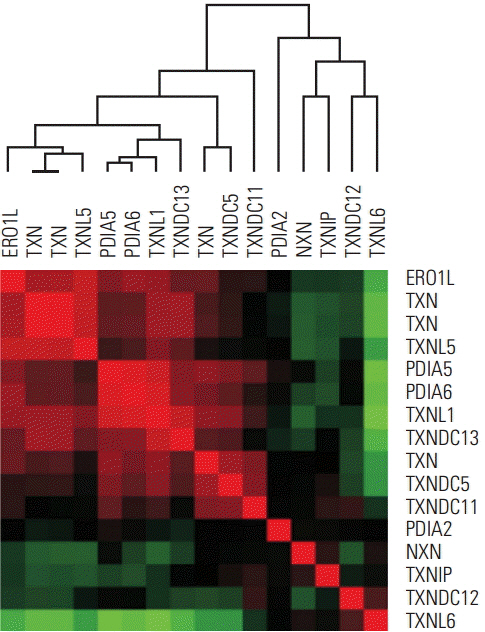
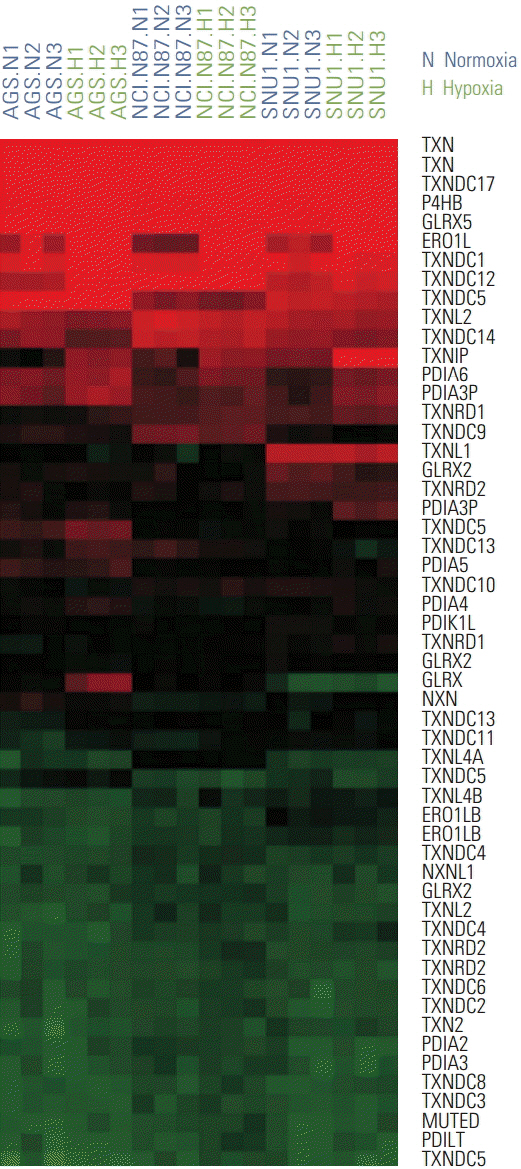
Gastric cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Although surgery is the standard curative treatment for gastric cancer, relapse occurs in a large number of patients, except in the case of early diagnosed gastric cancer. Following previous studies that identified endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin 1-α (ERO1L) as a potential marker for gastric cancer, we investigated the functional role of ERO1L in gastric cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
For validation of microarray data, the mRNA expression level of ERO1L was measured by quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction in 56 independent stage III gastric cancer patients. Immunohistochemical staining was performed to examine the protein expression level of ERO1L in 231 gastric cancer patients. Correlation between gene expression and cancer prognosis was evaluated.
RESULTS
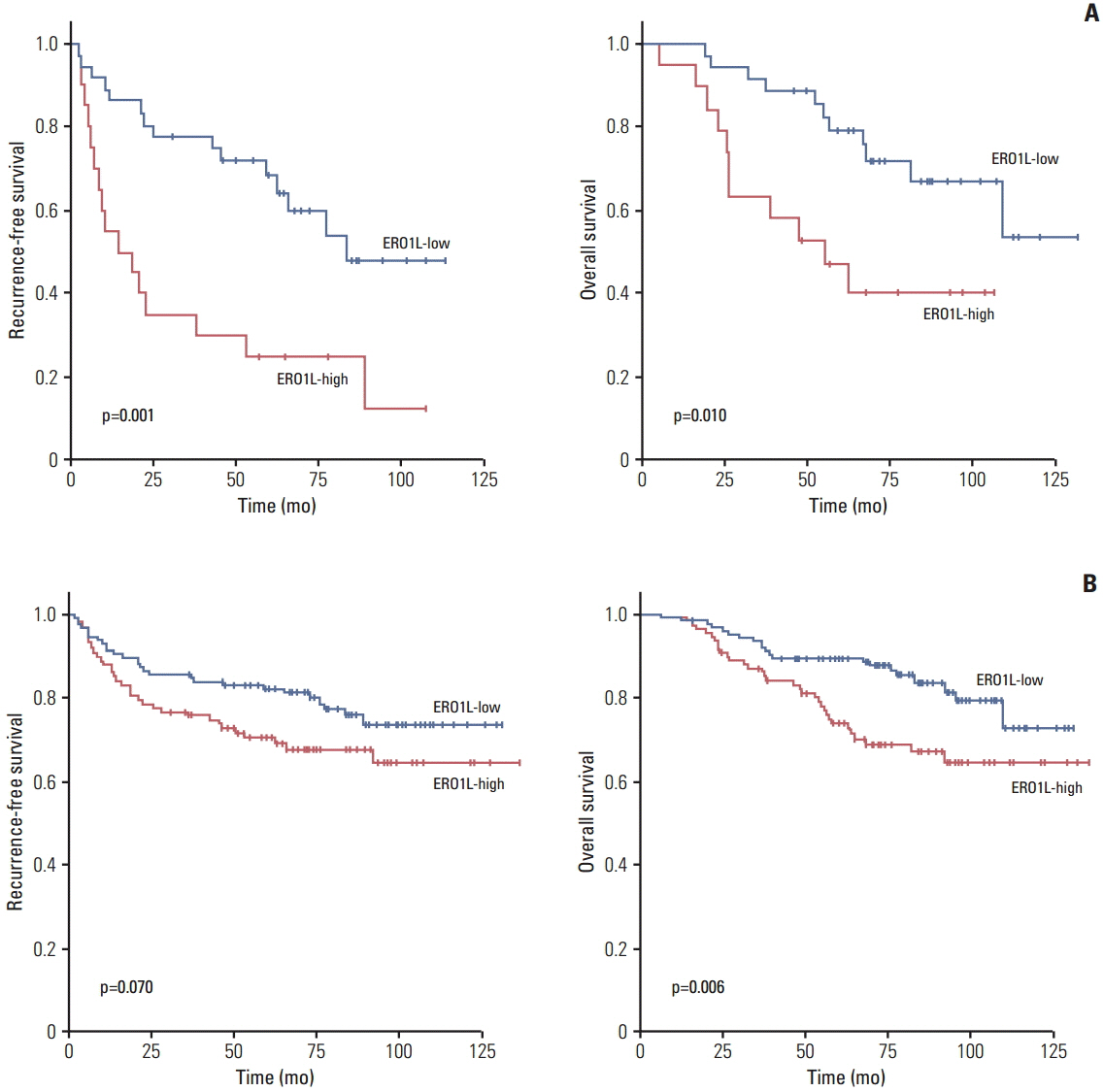
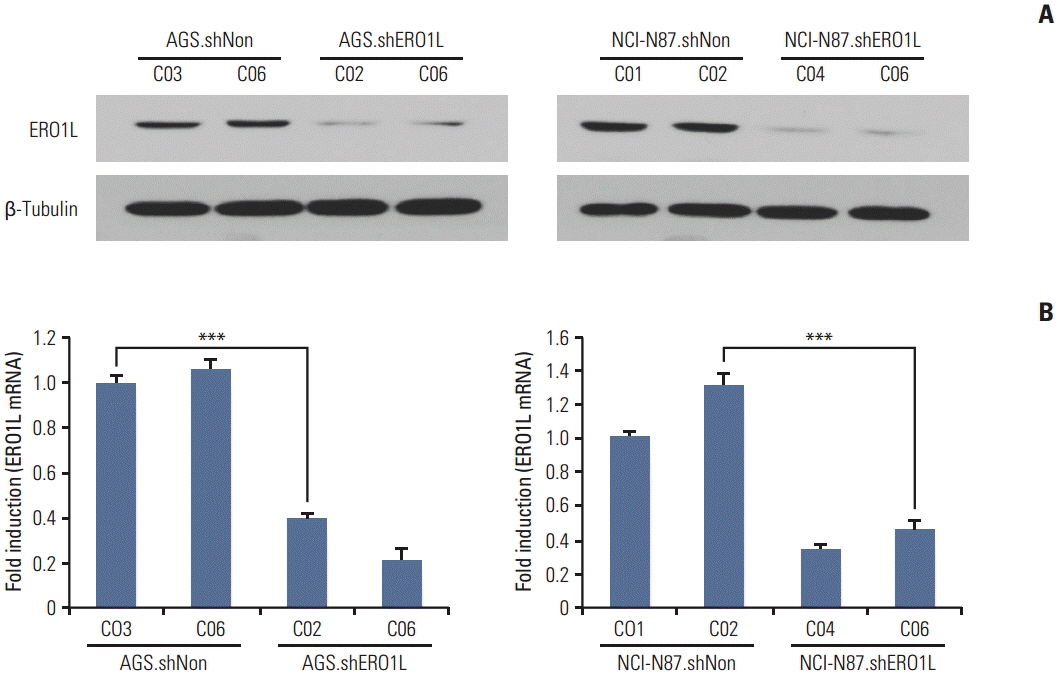
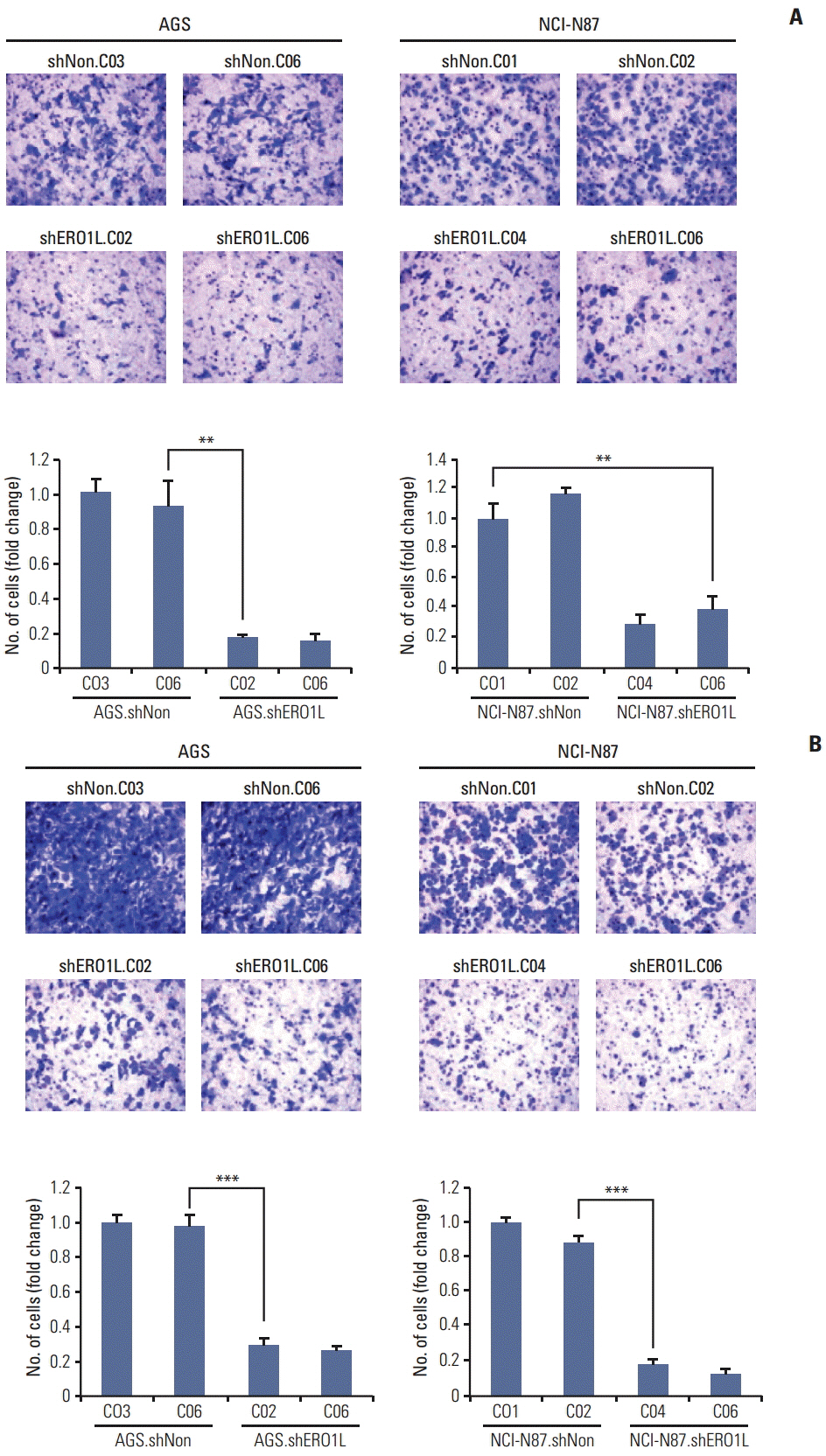
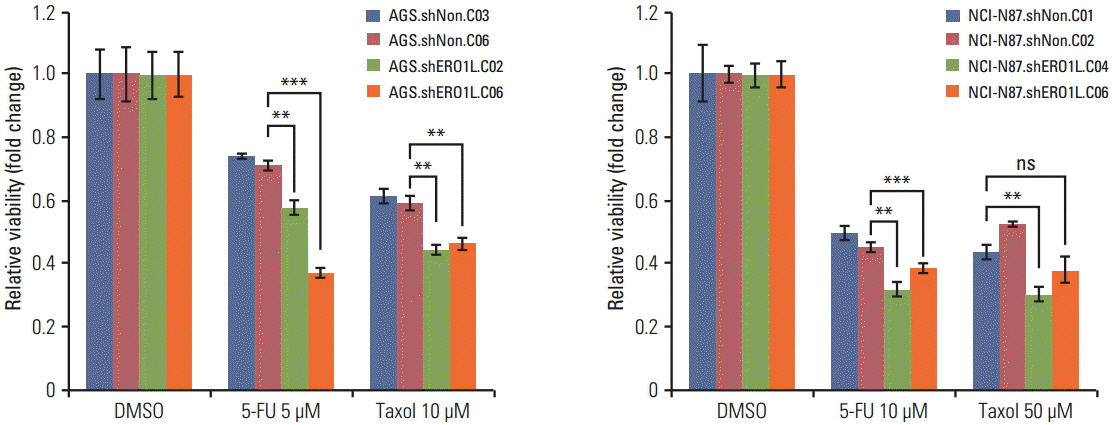
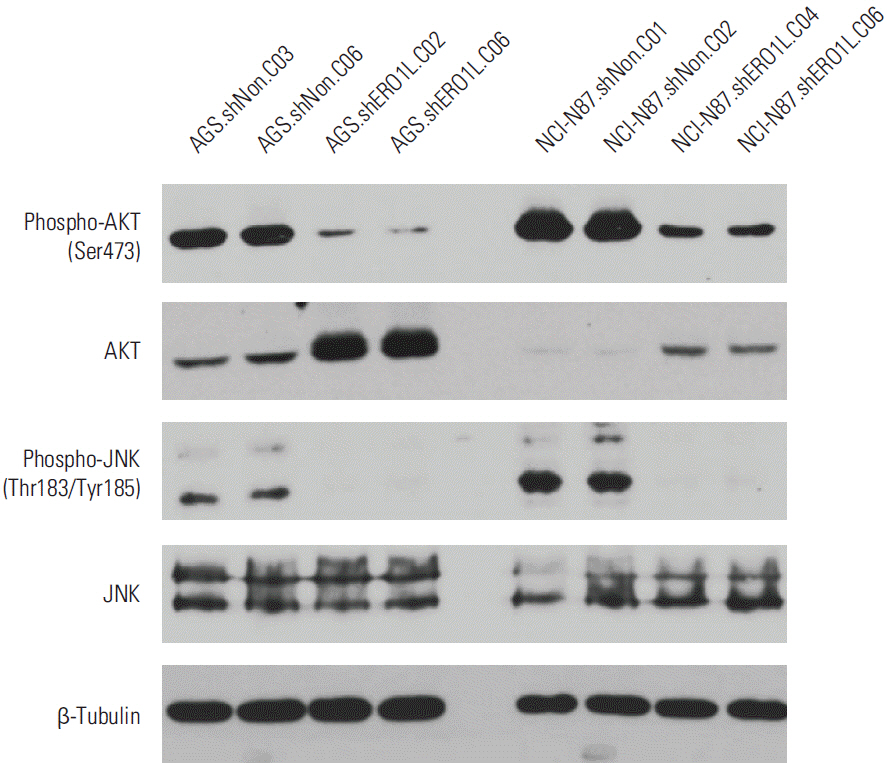
Patients with high ERO1L expression had poorer survival than those with low expression (p < 0.01). Functional assays demonstrated that ERO1L knockdown inhibited cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and chemoresistance. In addition, involvement of inactivation of Akt and JNK signaling in molecular mechanisms of ERO1L inhibition was demonstrated.
CONCLUSION
High expression of ERO1L is associated with poor prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. These results indicate that ERO1L expression may be a clinically promising therapeutic target for prevention of gastric cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Increased Progastrin-Releasing Peptide Expression is Associated with Progression in Gastric Cancer Patients
Li Li, Xiaodong Yin, Hai Meng, Juanyu Hu, Zhengqing Yu, Jianyong Xu
Yonsei Med J. 2020;61(1):15-19. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.1.15.
Reference
-
References
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.
Article2. Lynch HT, Grady W, Suriano G, Huntsman D. Gastric cancer: new genetic developments. J Surg Oncol. 2005; 90:114–33.
Article3. Shah MA, Ajani JA. Gastric cancer: an enigmatic and heterogeneous disease. JAMA. 2010; 303:1753–4.4. Gallo A, Cha C. Updates on esophageal and gastric cancers. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:3237–42.
Article5. Bang YJ, Kim YW, Yang HK, Chung HC, Park YK, Lee KH, et al. Adjuvant capecitabine and oxaliplatin for gastric cancer after D2 gastrectomy (CLASSIC): a phase 3 open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012; 379:315–21.
Article6. Tay ST, Leong SH, Yu K, Aggarwal A, Tan SY, Lee CH, et al. A combined comparative genomic hybridization and expression microarray analysis of gastric cancer reveals novel molecular subtypes. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:3309–16.7. Kim B, Bang S, Lee S, Kim S, Jung Y, Lee C, et al. Expression profiling and subtype-specific expression of stomach cancer. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:8248–55.8. Chen X, Leung SY, Yuen ST, Chu KM, Ji J, Li R, et al. Variation in gene expression patterns in human gastric cancers. Mol Biol Cell. 2003; 14:3208–15.
Article9. Lee HS, Cho SB, Lee HE, Kim MA, Kim JH, Park DJ, et al. Protein expression profiling and molecular classification of gastric cancer by the tissue array method. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:4154–63.
Article10. Tan IB, Ivanova T, Lim KH, Ong CW, Deng N, Lee J, et al. Intrinsic subtypes of gastric cancer, based on gene expression pattern, predict survival and respond differently to chemotherapy. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141:476–85.
Article11. Ooi CH, Ivanova T, Wu J, Lee M, Tan IB, Tao J, et al. Oncogenic pathway combinations predict clinical prognosis in gastric cancer. PLoS Genet. 2009; 5:e1000676.
Article12. Cho JY, Lim JY, Cheong JH, Park YY, Yoon SL, Kim SM, et al. Gene expression signature-based prognostic risk score in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011; 17:1850–7.
Article13. Bristow RG, Hill RP. Hypoxia and metabolism: hypoxia, DNA repair and genetic instability. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008; 8:180–92.14. Benham AM, Cabibbo A, Fassio A, Bulleid N, Sitia R, Braakman I. The CXXCXXC motif determines the folding, structure and stability of human Ero1-Lalpha. EMBO J. 2000; 19:4493–502.
Article15. Gess B, Hofbauer KH, Wenger RH, Lohaus C, Meyer HE, Kurtz A. The cellular oxygen tension regulates expression of the endoplasmic oxidoreductase ERO1-Lalpha. Eur J Biochem. 2003; 270:2228–35.16. May D, Itin A, Gal O, Kalinski H, Feinstein E, Keshet E. Ero1-L alpha plays a key role in a HIF-1-mediated pathway to improve disulfide bond formation and VEGF secretion under hypoxia: implication for cancer. Oncogene. 2005; 24:1011–20.17. Simon R, Lam A, Li MC, Ngan M, Menenzes S, Zhao Y. Analysis of gene expression data using BRB-ArrayTools. Cancer Inform. 2007; 3:11–7.18. Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D. Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95:14863–8.
Article19. Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di Cristofano A, Testa JR. Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: implications for therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res. 2005; 94:29–86.
Article20. Malik SN, Brattain M, Ghosh PM, Troyer DA, Prihoda T, Bedolla R, et al. Immunohistochemical demonstration of phospho-Akt in high Gleason grade prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2002; 8:1168–71.21. Kreisberg JI, Malik SN, Prihoda TJ, Bedolla RG, Troyer DA, Kreisberg S, et al. Phosphorylation of Akt (Ser473) is an excellent predictor of poor clinical outcome in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:5232–6.
Article22. Ali A, Sidorova TS, Matesic DF. Dual modulation of JNK and Akt signaling pathways by chaetoglobosin K in human lung carcinoma and ras-transformed epithelial cells. Invest New Drugs. 2013; 31:525–34.
Article23. Engelberg D. Stress-activated protein kinases-tumor suppressors or tumor initiators? Semin Cancer Biol. 2004; 14:271–82.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Diabetes
- New Insights into the Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Breast Cancer Metastasis
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress and Vascular Complication
- Clinicopathological Features and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients
- Nuclear Receptors Resolve Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress to Improve Hepatic Insulin Resistance