J Korean Soc Radiol.
2016 Nov;75(5):415-418. 10.3348/jksr.2016.75.5.415.
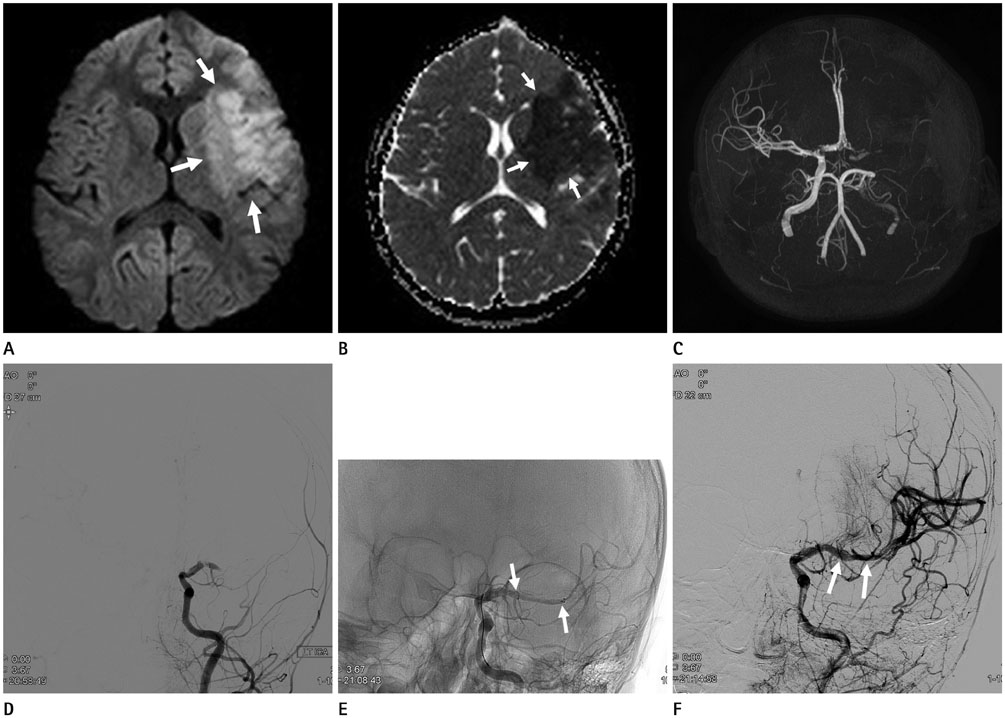
Acute Ischemic Stroke in a 6-Year-Old Boy, Treated with Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. musuki.lee@gmail.com
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2355998
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.5.415
Abstract
- Pediatric acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is a relatively rare disease with an annual estimated incidence of 2.4-13 per 100000 children. However, pediatric AIS can lead to significant morbidity and mortality. Stroke in children differs from that in adults with respect to etiology, clinical presentation, or management. Therapeutic options for adult AIS are intravenous tissue plasminogen activator, intra-arterial pharmacological thrombolysis, and mechanical thrombectomy. However, management strategies for pediatric AIS, extrapolated largely from those of adult AIS, remain controversial. In this article, we present our experience in a boy with AIS, who was successfully treated with mechanical thrombectomy, by utilizing the Solitaire FR revascularization device.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Giroud M, Lemesle M, Gouyon JB, Nivelon JL, Milan C, Dumas R. Cerebrovascular disease in children under 16 years of age in the city of Dijon, France: a study of incidence and clinical features from 1985 to 1993. J Clin Epidemiol. 1995; 48:1343–1348.2. deVeber GA, MacGregor D, Curtis R, Mayank S. Neurologic outcome in survivors of childhood arterial ischemic stroke and sinovenous thrombosis. J Child Neurol. 2000; 15:316–324.3. Tsze DS, Valente JH. Pediatric stroke: a review. Emerg Med Int. 2011; 2011:734506.4. Ellis MJ, Amlie-Lefond C, Orbach DB. Endovascular therapy in children with acute ischemic stroke: review and recommendations. Neurology. 2012; 79:13 Suppl 1. S158–S164.5. Friedman N. Pediatric stroke: past, present and future. Adv Pediatr. 2009; 56:271–299.6. Huded V, Kamath V, Chauhan B, de Souza R, Nair R, Sapare A, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy using solitaire in a 6-year-old child. J Vasc Interv Neurol. 2015; 8:13–16.7. Lanni G, Catalucci A, Conti L, Di Sibio A, Paonessa A, Gallucci M. Pediatric stroke: clinical findings and radiological approach. Stroke Res Treat. 2011; 2011:172168.8. Carlin TM, Chanmugam A. Stroke in children. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2002; 20:671–685.9. Sainz de la Maza S, De Felipe A, Matute MC, Fandiño E, Méndez JC, Morillo P, et al. Acute ischemic stroke in a 12-year-old successfully treated with mechanical thrombectomy. J Child Neurol. 2014; 29:269–273.10. Amlie-Lefond C, Chan AK, Kirton A, deVeber G, Hovinga CA, Ichord R, et al. Thrombolysis in acute childhood stroke: design and challenges of the thrombolysis in pediatric stroke clinical trial. Neuroepidemiology. 2009; 32:279–286.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Mechanical Thrombectomy in a 2-Year-Old Male Through a 4-French Guide Catheter
- Forced Arterial Suction Thrombectomy Using Distal Access Catheter in Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Mechanical Thrombectomy for Large Vessel Occlusion via the Transbrachial Approach: Case Series
- Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Delayed Development of Symptomatic Arterial Stenosis after a Mechanical Thrombectomy for an Acute Embolic Occlusion of the Middle Cerebral Artery