Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2017 Jan;9(1):35-42. 10.4168/aair.2017.9.1.35.
Oral Food Desensitization in Children With IgE-Mediated Cow's Milk Allergy: Immunological Changes Underlying Desensitization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Instituto de Investigación en Ciencias de la Alimentación (CIAL) (CSIC-UAM), Madrid, Spain. e.molina@csic.es
- 2Servicio de alergologÃa, Hospital Infanta SofÃa, San Sebastián de los Reyes, Madrid, Spain.
- KMID: 2355892
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2017.9.1.35
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy to induce clinical desensitization to cow's milk (CM) of an oral immunotherapy (OIT) protocol in a pediatric population with cow's milk allergy (CMA). In addition, the immune responses against β-casein, of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from CMA patients, before and after the protocol were evaluated and compared to a nonallergic population.
METHODS
A group of 20 children with IgE-mediated CMA and 15 nonallergic children were recruited. Allergic subjects underwent an OIT protocol based on weekly doses of commercial semi-skimmed ultra-high temperature treated (UHT) CM, followed by a maintenance phase. Immune profiles and changes in all subjects were investigated by measuring Th1, Th2, and Treg cytokines, transcription factors, and specific IgE and IgG4 levels.
RESULTS
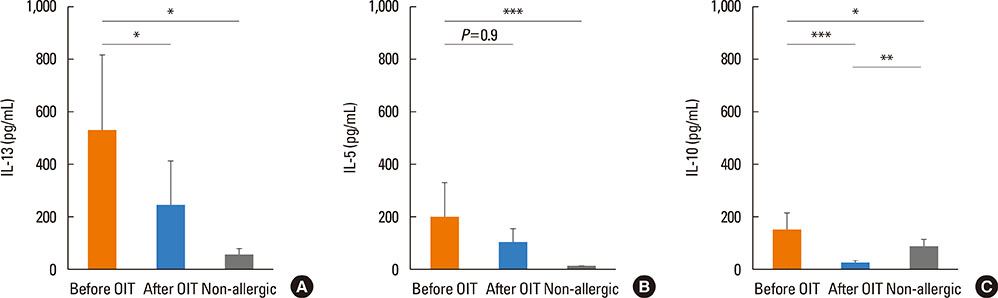
The CM-OIT protocol enabled to desensitize 70% of the allergic patients. Successful OIT was accompanied by significant increases in casein-specific IgG4 levels, together with a reduction in the concentration of antigen-specific IgE and in IL-5, IL-13, and IL-10 production by β-casein-stimulated PBMCs. Baseline significant differences observed between allergic and nonallergic children in IL-13 and IL-5 levels were no longer found once the protocol had finished.
CONCLUSIONS
The OIT protocol was safe and effective in inducing milk desensitization in 70% of the children with CMA, leading to alterations in their immune profiles toward a nonallergic phenotype.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Allergen-Specific Immunotherapies for Food Allergy
Elizabeth Feuille, Anna Nowak-Wegrzyn
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018;10(3):189-206. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.3.189.
Reference
-
1. Skripak JM, Matsui EC, Mudd K, Wood RA. The natural history of IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:1172–1177.2. Vanto T, Helppilä S, Juntunen-Backman K, Kalimo K, Klemola T, Korpela R, et al. Prediction of the development of tolerance to milk in children with cow's milk hypersensitivity. J Pediatr. 2004; 144:218–222.3. Høst A, Halken S, Jacobsen HP, Christensen AE, Herskind AM, Plesner K. Clinical course of cow's milk protein allergy/intolerance and atopic diseases in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2002; 13:Suppl 15. 23–28.4. Santos A, Dias A, Pinheiro JA. Predictive factors for the persistence of cow's milk allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010; 21:1127–1134.5. Bock SA, Muñoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Fatalities due to anaphylactic reactions to foods. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 107:191–193.6. Bock SA, Muñoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA. Further fatalities caused by anaphylactic reactions to food, 2001-2006. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:1016–1018.7. Lieberman JA, Sicherer SH. Quality of life in food allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 11:236–242.8. Wood RA. Food-specific immunotherapy: past, present, and future. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:336–337.9. Martorell Calatayud C, Muriel García A, Martorell Aragonés A, De La Hoz Caballer B. Safety and efficacy profile and immunological changes associated with oral immunotherapy for IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy in children: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2014; 24:298–307.10. Brożek JL, Terracciano L, Hsu J, Kreis J, Compalati E, Santesso N, et al. Oral immunotherapy for IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012; 42:363–374.11. Pajno GB. Oral desensitization for milk allergy in children: state of the art. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 11:560–564.12. Sopo SM, Onesimo R, Giorgio V, Fundarò C. Specific oral tolerance induction (SOTI) in pediatric age: clinical research or just routine practice? Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2010; 21:e446–e449.13. Keet CA, Seopaul S, Knorr S, Narisety S, Skripak J, Wood RA. Long-term follow-up of oral immunotherapy for cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 132:737–739.e6.14. Savilahti EM, Kuitunen M, Savilahti E, Mäkelä MJ. Specific antibodies in oral immunotherapy for cow's milk allergy: kinetics and prediction of clinical outcome. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2014; 164:32–39.15. Pajno GB, Caminiti L, Salzano G, Crisafulli G, Aversa T, Messina MF, et al. Comparison between two maintenance feeding regimens after successful cow's milk oral desensitization. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2013; 24:376–381.16. Lee JH, Kim WS, Kim H, Hahn YS. Increased cow's milk protein-specific IgG4 levels after oral desensitization in 7- to 12-month-old infants. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013; 111:523–528.17. Skripak JM, Nash SD, Rowley H, Brereton NH, Oh S, Hamilton RG, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of milk oral immunotherapy for cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 122:1154–1160.18. Longo G, Barbi E, Berti I, Meneghetti R, Pittalis A, Ronfani L, et al. Specific oral tolerance induction in children with very severe cow's milk-induced reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:343–347.19. García-Ara C, Pedrosa M, Belver MT, Martín-Muñoz MF, Quirce S, Boyano-Martínez T. Efficacy and safety of oral desensitization in children with cow's milk allergy according to their serum specific IgE level. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2013; 110:290–294.20. Pajno GB, Caminiti L, Ruggeri P, De Luca R, Vita D, La Rosa M, et al. Oral immunotherapy for cow's milk allergy with a weekly up-dosing regimen: a randomized single-blind controlled study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010; 105:376–381.21. Bedoret D, Singh AK, Shaw V, Hoyte EG, Hamilton R, DeKruyff RH, et al. Changes in antigen-specific T-cell number and function during oral desensitization in cow's milk allergy enabled with omalizumab. Mucosal Immunol. 2012; 5:267–276.22. Clark AT, Ewan PW. Food allergy in childhood. Arch Dis Child. 2003; 88:79–81.23. González Jiménez D, Larrea Tamayo E, Díaz Martin JJ, Molinos Norniella C, Pérez Solis D, Menéndez Arias C, et al. Eficacia y seguridad de una pauta rush de inducción de tolerancia oral en pacientes con alergia a proteínas de leche de vaca: evolución clínica e inmunológica). An Pediatr (Barc). 2013; 79:346–351.24. Vázquez-Ortiz M, Alvaro-Lozano M, Alsina L, Garcia-Paba MB, Piquer-Gibert M, Giner-Muñoz MT, et al. Safety and predictors of adverse events during oral immunotherapy for milk allergy: severity of reaction at oral challenge, specific IgE and prick test. Clin Exp Allergy. 2013; 43:92–102.25. Meglio P, Bartone E, Plantamura M, Arabito E, Giampietro PG. A protocol for oral desensitization in children with IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy. Allergy. 2004; 59:980–987.26. Alonso-Lebrero E, Fuentes V, Zapatero L, Pérez-Bustamante S, Pineda F, Martinez-Molero MI. Goat's milk allergies in children following specific oral tolerance induction to cow's milk. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2008; 36:180–181.27. Tripodi S, Comberiati P, Di Rienzo Businco A, Bianchi A, Bondanini F, Sargentini V, et al. Severe anaphylaxis to sheep's milk cheese in a child desensitized to cow's milk through specific oral tolerance induction. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 45:56–60.28. Rodríguez del Río P, Sánchez-García S, Escudero C, Pastor-Vargas C, Sánchez Hernández JJ, Pérez-Rangel I, et al. Allergy to goat's and sheep's milk in a population of cow's milk-allergic children treated with oral immunotherapy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2012; 23:128–132.29. Sánchez-García S, Rodríguez del Río P, Escudero C, García-Fernández C, Ramirez A, Ibáñez MD. Efficacy of oral immunotherapy protocol for specific oral tolerance induction in children with cow's milk allergy. Isr Med Assoc J. 2012; 14:43–47.30. Zapatero L, Alonso E, Fuentes V, Martínez MI. Oral desensitization in children with cow's milk allergy. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2008; 18:389–396.31. Staden U, Rolinck-Werninghaus C, Brewe F, Wahn U, Niggemann B, Beyer K. Specific oral tolerance induction in food allergy in children: efficacy and clinical patterns of reaction. Allergy. 2007; 62:1261–1269.32. Perezábad L, Reche M, Valbuena T, López-Fandiño R, Molina E, López-Expósito I. Clinical efficacy and immunological changes subjacent to egg oral immunotherapy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015; 114:504–509.33. Meglio P, Giampietro PG, Carello R, Gabriele I, Avitabile S, Galli E. Oral food desensitization in children with IgE-mediated hen's egg allergy: a new protocol with raw hen's egg. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2013; 24:75–83.34. Narisety SD, Skripak JM, Steele P, Hamilton RG, Matsui EC, Burks AW, et al. Open-label maintenance after milk oral immunotherapy for IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:610–612.35. Wood RA, Sicherer SH, Vickery BP, Jones SM, Liu AH, Fleischer DM, et al. The natural history of milk allergy in an observational cohort. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131:805–812.36. Elizur A, Rajuan N, Goldberg MR, Leshno M, Cohen A, Katz Y. Natural course and risk factors for persistence of IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy. J Pediatr. 2012; 161:482–487.e1.37. Fiocchi A, Terracciano L, Bouygue GR, Veglia F, Sarratud T, Martelli A, et al. Incremental prognostic factors associated with cow's milk allergy outcomes in infant and child referrals: the Milan Cow's Milk Allergy Cohort study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008; 101:166–173.38. Meglio P, Giampietro PG, Gianni S, Galli E. Oral desensitization in children with immunoglobulin E-mediated cow's milk allergy--follow-up at 4 yr and 8 months. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2008; 19:412–419.39. Savilahti EM, Rantanen V, Lin JS, Karinen S, Saarinen KM, Goldis M, et al. Early recovery from cow's milk allergy is associated with decreasing IgE and increasing IgG4 binding to cow's milk epitopes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:1315–1321.e9.40. Alvaro M, Giner MT, Vázquez M, Lozano J, Domínguez O, Piquer M, et al. Specific oral desensitization in children with IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy. Evolution in one year. Eur J Pediatr. 2012; 171:1389–1395.41. Tsuge I, Kondo Y, Tokuda R, Kakami M, Kawamura M, Nakajima Y, et al. Allergen-specific helper T cell response in patients with cow's milk allergy: simultaneous analysis of proliferation and cytokine production by carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester dilution assay. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006; 36:1538–1545.42. Tiemessen MM, Van Ieperen-Van Dijk AG, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA, Garssen J, Knol EF, Van Hoffen E. Cow's milk-specific T-cell reactivity of children with and without persistent cow's milk allergy: key role for IL-10. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:932–939.43. Michaud B, Aroulandom J, Baiz N, Amat F, Gouvis-Echraghi R, Candon S, et al. Casein-specific IL-4- and IL-13-secreting T cells: a tool to implement diagnosis of cow's milk allergy. Allergy. 2014; 69:1473–1480.44. Shek LP, Bardina L, Castro R, Sampson HA, Beyer K. Humoral and cellular responses to cow milk proteins in patients with milk-induced IgE-mediated and non-IgE-mediated disorders. Allergy. 2005; 60:912–919.45. Sletten GB, Halvorsen R, Egaas E, Halstensen TS. Memory T cell proliferation in cow's milk allergy after CD25+ regulatory T cell removal suggests a role for casein-specific cellular immunity in IgE-mediated but not in non-IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2007; 142:190–198.46. Vickery BP, Pons L, Kulis M, Steele P, Jones SM, Burks AW. Individualized IgE-based dosing of egg oral immunotherapy and the development of tolerance. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010; 105:444–450.47. Jones SM, Pons L, Roberts JL, Scurlock AM, Perry TT, Kulis M, et al. Clinical efficacy and immune regulation with peanut oral immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:292–300.48. Akdis CA, Blesken T, Akdis M, Wüthrich B, Blaser K. Role of interleukin 10 in specific immunotherapy. J Clin Invest. 1998; 102:98–106.49. Shreffler WG, Wanich N, Moloney M, Nowak-Wegrzyn A, Sampson HA. Association of allergen-specific regulatory T cells with the onset of clinical tolerance to milk protein. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:43–52.e7.50. Varshney P, Jones SM, Scurlock AM, Perry TT, Kemper A, Steele P, et al. A randomized controlled study of peanut oral immunotherapy: clinical desensitization and modulation of the allergic response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:654–660.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Butter Tolerance in Children Allergic to Cow's Milk
- Clinical applications of drug desensitization in the Asia-Pacific region
- A Case of Cow's Milk Allergy with Atopic Dermatitis
- The Diagnosis of Food Allergy in a Pediatric Gastroenterology: Focusing on Non-IgE-mediated Allergic Diseases
- Cow mild allergy in infant who neonatal onset