J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2016 Sep;18(3):291-295. 10.7461/jcen.2016.18.3.291.
Onyx Embolization of Intracranial Pial Arteriovenous Fistula
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. fhjhcho@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2355657
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2016.18.3.291
Abstract
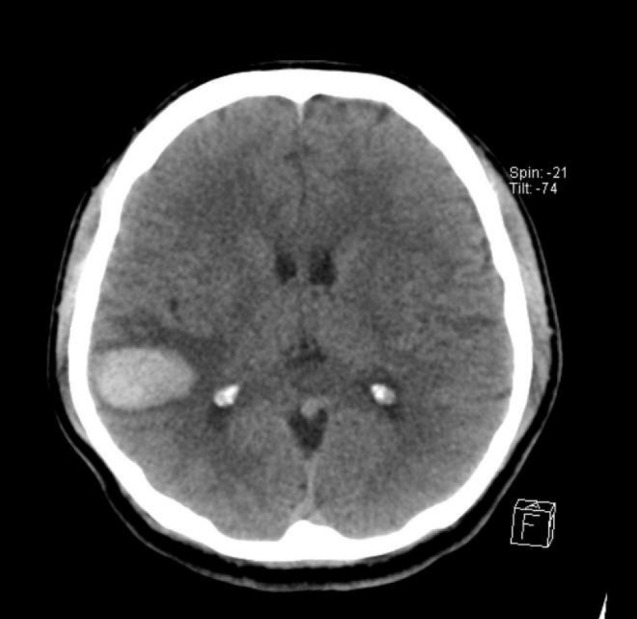
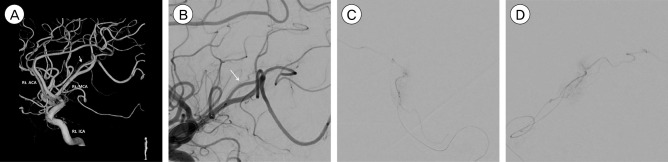
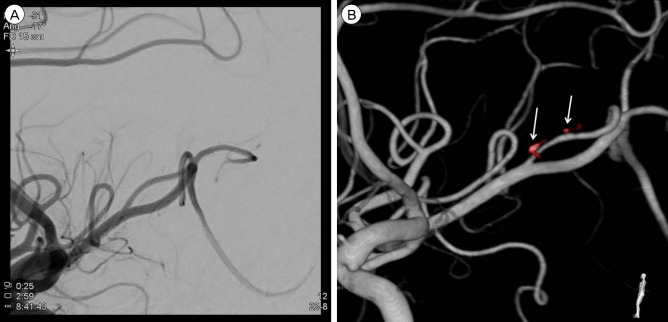
- Intracranial pial arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) are rare cerebrovascular lesions consisting of one or more arterial connections to a single venous channel without an intervening nidus. Because of the location and high flow dynamics of these lesions, neurosurgeons may have a difficulty deciding between endovascular treatment and open surgical treatment. We report on a patient who underwent endovascular treatment with liquid embolic agent. A 50-year-old man with a decreased mental state and a tonic seizure event was brought to our hospital. Computed tomography (CT) of the brain showed a subcortical hematoma in the right temporoparietal lobe. On three-dimensional cerebral artery CT, there was no evidence of definite cerebrovascular abnormality. Cerebral angiography showed a pial AVF supplied by the right middle cerebral artery with early drainage into the right superior cerebral vein. The patient was treated with Onyx embolization for definitive closure of the fistula. The patient was transferred to the department of rehabilitation medicine two weeks later with grade 4 left hemiparesis. The application of advanced equipment, such as the latest angiography and endovascular tools, will facilitate the correct diagnosis and delicate treatment of pial AVF.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Almeida GM, Shibata MK. Hemispheric arteriovenous fistulae with giant venous dilation. Childs Nerv Syst. 1990; 6. 6(4):216–219. PMID: 2383876.
Article2. Alurkar A, Karanam LS, Nayak S, Ghanta RK. Intracranial pial arteriovenous fistulae: diagnosis and treatment techniques in pediatric patients with review of literature. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2016; 1. 6:2. PMID: 26958432.
Article3. Aoki N, Sakai T, Oikawa A. Intracranial arteriovenous fistula manifesting as progressive neurological deterioration in an infant: case report. Neurosurgery. 1991; 4. 28(4):619–622. discussion 622-3. PMID: 2034363.
Article4. Barnwell SL, Ciricillo SF, Halbach VV, Edwards MS, Cogen PH. Intracerebral arteriovenous fistulas associated with intraparenchymal varix in childhood: case reports. Neurosurgery. 1990; 1. 26(1):122–125. PMID: 2294462.
Article5. Carrillo R, Carreira LM, Prada J, Rosas C, Egas G. Giant aneurysm arising from a single arteriovenous fistula in a child. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1984; 5. 60(5):1085–1088. PMID: 6716144.6. Garcia-Monaco R, De Victor D, Mann C, Hannedouche A, Terbrugge K, Lasjaunias P. Congestive cardiac manifestations from cerebrocranial arteriovenous shunts. Endovascular management in 30 children. Childs Nerv Syst. 1991; 2. 7(1):48–52. PMID: 2054809.7. García-Mónaco R, Taylor W, Rodesch G, Alvarez H, Burrows P, Coubes P, et al. Pial arteriovenous fistula in children as presenting manifestation of Rendu-Osler-Weber disease. Neuroradiology. 1995; 1. 37(1):60–64. PMID: 7708192.
Article8. Giller CA, Batjer HH, Purdy P, Walker B, Mathews D. Interdisciplinary evaluation of cerebral hemodynamics in the treatment of arteriovenous fistulae associated with giant varices. Neurosurgery. 1994; 10. 35(4):778–782. discussion 782-4. PMID: 7808630.
Article9. Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Hieshima GB, Hardin CW, Dowd CF, Barnwell SL. Transarterial occlusion of solitary intracerebral arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1989; Jul-Aug. 10(4):747–752. PMID: 2505503.10. Hoh BL, Putman CM, Budzik RF, Ogilvy CS. Surgical and endovascular flow disconnection of intracranial pial single-channel arteriovenous fistulae. Neurosurgery. 2001; 12. 49(6):1351–1363. discussion 1363-4. PMID: 11846934.
Article11. Kikuchi K, Kowada M, Sasajima H. Vascular malformations of the brain in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber disease). Surg Neurol. 1994; 5. 41(5):374–380. PMID: 8009411.
Article12. Krings T, Ozanne A, Chng SM, Alvarez H, Rodesch G, Lasjaunias PL. Neurovascular phenotypes in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia patients according to age. Review of 50 consecutive patients aged 1 day-60 years. Neuroradiology. 2005; 10. 47(10):711–720. PMID: 16136265.13. Lasjaunias P, Manelfe C, Chiu M. Angiographic architecture of intracranial vascular malformations and fistulas--pretherapeutic aspects. Neurosurg Rev. 1986; 9(4):253–263. PMID: 3614684.14. Lv X, Li Y, Jiang C, Wu Z. Endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 4. 30(4):851–856. PMID: 19147710.
Article15. Nelson PK, Niimi Y, Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A. Endovascular embolization of congenital intracranial pial arteriovenous fistulas. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 1992; 2(2):309–317.16. Newman CB, Hu YC, McDougall CG, Albuquerque FC. Balloon-assisted Onyx embolization of cerebral single-channel pial arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2011; 6. 7(6):637–642. PMID: 21631202.
Article17. Nomura S, Ishikawa O, Tanaka K, Otani R, Miura K, Maeda K. Pial arteriovenous fistula caused by trauma: a case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2015; 55(11):856–858. PMID: 26458846.
Article18. Tomlinson FH, Rüfenacht DA, Sundt TM Jr, Nichols DA, Fode NC. Arteriovenous fistulas of the brain and the spinal cord. J Neurosurg. 1993; 7. 79(1):16–27. PMID: 8315463.
Article19. Vinuela F, Drake CG, Fox AJ, Pelz DM. Giant intracranial varices secondary to high-flow arteriovenous fistulae. J Neurosurg. 1987; 2. 66(2):198–203. PMID: 3806202.20. Viñuela F, Fox AJ, Kan S, Drake CG. Balloon occlusion of a spontaneous fistula of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1983; 2. 58(2):287–290. PMID: 6848692.21. Wang YC, Wong HF, Yeh YS. Intracranial pial arteriovenous fistulas with single-vein drainage. Report of three cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 2004; 2. 100(2 Suppl Pediatrics):201–205. PMID: 14758951.22. Weon YC, Yoshida Y, Sachet M, Mahadevan J, Alvarez H, Rodesch G, et al. Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) in children: review of 41 cases with 63 non choroidal single-hole AVFs. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005; 1. 147(1):17–31. discussion 31. PMID: 15614467.
Article23. Yang WH, Lu MS, Cheng YK, Wang TC. Pial arteriovenous fistula: a review of literature. Br J Neurosurg. 2011; 10. 25(5):580–585. PMID: 21501060.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful Treatment of Intracranial Small Pial Single-Channel Arteriovenous Fistula Using N-butyl Cyanoacrylate: Report of 2 Cases
- Coil Embolization of High-flow Pial Arteriovenous Fistula and Management of Hyperperfusion Syndrome: a Case Report
- Embolization of Cerebral Pial Arteriovenous Fistula Under Balloon-assisted Flow Control Using NBCA: a Case Report
- Congenital Intracranial Pial Arteriovenous Fistula Complicated with Congestive Heart Failure in Neonate: A Case Report
- Intracranial Pial Arteriovenous Fistula Presenting as Brain Hemorrhage in Newborn Infants