Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2016 Sep;20(3):152-157. 10.13104/imri.2016.20.3.152.
Safety Management for MR-Guided Interventions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Dr. Berezin Medical Center, Saint-Petersburg, Russia. mc@ldc.ru
- KMID: 2354795
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.3.152
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Operating room management is the serious and complex task for hospital managers and the common approach is to develop relevant standard operational procedures. From patient and staff safety perspective, operating room management should be well-studied and hospital should identify and address any potential risks. Simultaneous usage of different imaging and less-invasive treatment technologies demands strong management control.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
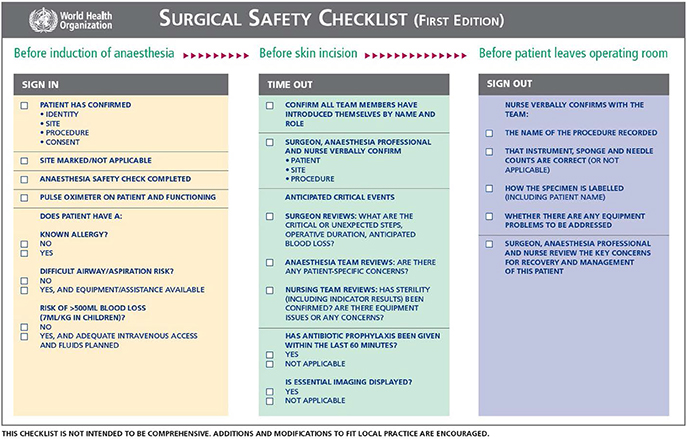
We have formed the multidisciplinary expert panel (surgeons, anesthesiologists, radiologists, healthcare managers etc.) for hybrid theater management standard operational procedure development. On the first stage the general concept of hybrid room design and patient routing was developed. The second stage included the technical details discussion. For patient safety improvement we modified the Surgical Safety Check-list in accordance with potential MRI-related safety challenges and concerns.
RESULTS
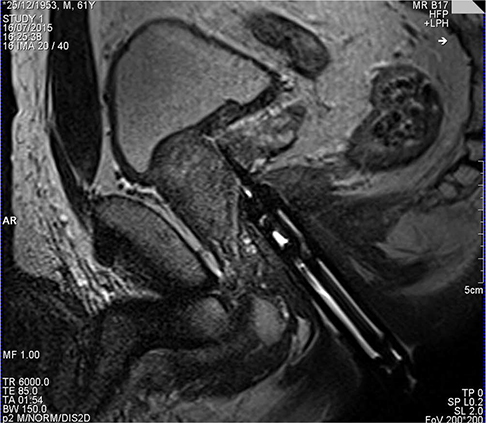
WHO Surgical Safety Checklist is a simple and easy-to use tool which includes three blocks of question (grouped by the surgery process). We have developed two additional blocks of questions for the intraoperative magnetic resonance investigation. It is very important to have a special detailed routing with a strong control of ferromagnetic devices and anesthesiology care.
CONCLUSION
High-energy MRI (1.5-3.0T) is characterized by potential influence on patient and staff safety in case of hybrid surgery. It is obvious to have a strong managerial control of ferromagnetic devices and anesthesiology care. Surgical Safety Checklist is the validated tool for improving patient safety. Modification and customization of this check-list potentially provides the opportunity for surgery processes improving.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sivathasan N, Rakowski KR, Robertson BF, Vijayarajan L. The World Health Organization's 'Surgical Safety Checklist': should evidence-based initiatives be enforced in hospital policy? JRSM Short Rep. 2010; 1:40.2. Conley DM, Singer SJ, Edmondson L, Berry WR, Gawande AA. Effective surgical safety checklist implementation. J Am Coll Surg. 2011; 212:873–879.3. Haynes AB, Weiser TG, Berry WR, et al. A surgical safety checklist to reduce morbidity and mortality in a global population. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:491–499.4. de Vries EN, Prins HA, Crolla RM, et al. Effect of a comprehensive surgical safety system on patient outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1928–1937.5. Neily J, Mills PD, Young-Xu Y, et al. Association between implementation of a medical team training program and surgical mortality. JAMA. 2010; 304:1693–1700.6. Li G, Su H, Cole GA, et al. Robotic system for MRI-guided stereotactic neurosurgery. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2015; 62:1077–1088.7. Yu N, Gassert R, Riener R. Mutual interferences and design principles for mechatronic devices in magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2011; 6:473–488.8. White MJ, Thornton JS, Hawkes DJ, et al. Design, operation, and safety of single-room interventional MRI suites: practical experience from two centers. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015; 41:34–43.9. Porteous J. Intraoperative MRI: the challenges of providing a safe environment for patients and personnel. 201. ORNAC J. 2014; 32:12–14. 16–19. 22 passim10. Henrichs B, Walsh RP. Intraoperative MRI for neurosurgical and general surgical interventions. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2014; 27:448–452.11. http://www.who.int/patientsafety/safesurgery/ss_checklist/en/. Published 2008. Accessed September 28, 2016.12. Helmreich RL. On error management: lessons from aviation. BMJ. 2000; 320:781–785.13. Soroka VV, Andreichuk KA, Kechaeva EI, Postnov AA, Kagachev PN. Hybrid operating room: a new horizon in cardiovascular surgery. Angiol Sosud Khir. 2011; 17:93–101.14. Childs S, Bruch P. Successful management of risk in the hybrid OR. AORN J. 2015; 101:223–234. quiz 235-227.15. Hemingway M, Kilfoyle M. Safety planning for intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. AORN J. 2013; 98:508–524.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided vascular interventions: An overview of current and emerging techniques
- Ultrasound-guided genitourinary interventions: principles and techniques
- Factors Influencing the Implementation of Anticancer Drug Safety Management Guidelines for Nurses
- Essential Clinical Tips about Ultrasound Guided Cervical Intervention
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Management of Pancreatic Fluid Collections: Update and Review of the Literature