Korean J Adult Nurs.
2014 Apr;26(2):244-252. 10.7475/kjan.2014.26.2.244.
Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Predicting Factors among Small-sized Company Workers
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate School of Chosun University, Chosun Nursing College, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Kim Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3College of Nursing, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. seon9772@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2351608
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7475/kjan.2014.26.2.244
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was aimed to examine the prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and cardiovascular risk factors among workers at small-sized companies having fewer than 50employees in Korea.
METHODS
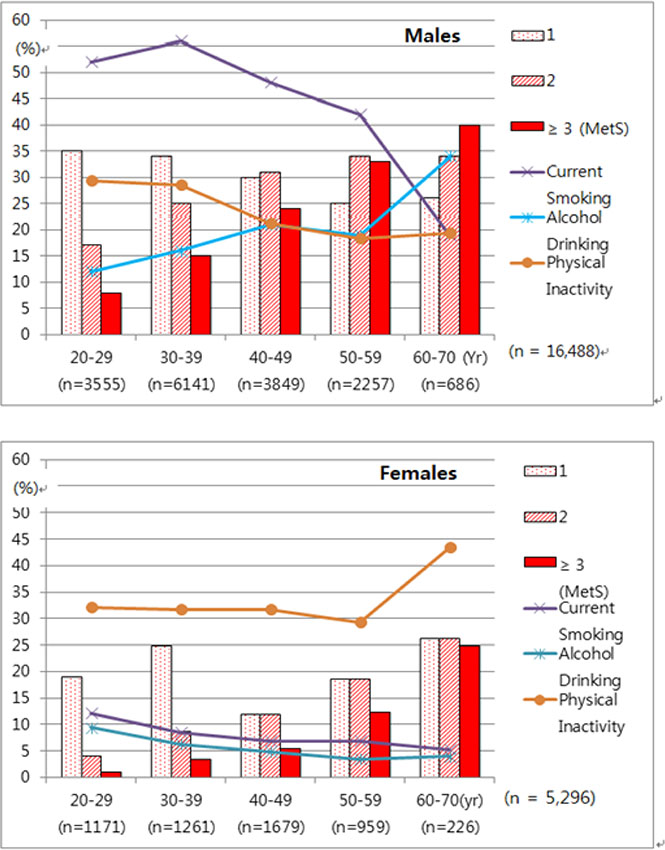
A descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted using a secondary data analysis on workers' health examination data. Data from 21,784 employed workers were analyzed, including 16,488 males (mean age 38.7years)and 5,296 females (mean age 40.5 years). Participants were newly enrolled in annual health check-ups at a professional health clinic from 2009 to 2011. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify age-adjusted gender specific predicting factors of MetS incidence.
RESULTS
The prevalence of MetS was 13.4% in male and 7.7% in female workers. Logistic regression analysis showed that, when age was adjusted for, family history of cardiovascular disease (CVD) was a predicting factor in both male and female workers. For male workers, heavy alcohol drinking and non-manual occupation (office workers/drivers) predicted MetS.
CONCLUSION
Health care providers should screen for MetS periodically in small work places especially for those with a family history of CVD. Educational counseling needs to be given to male workers with sedentary occupations with an aim to reduce heavy drinking and encourage lifestyle modification.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Allen JC, Lewis JB, Tagliaferro AR. Cost-effectiveness of health risk reduction after lifestyle education in the small workplace. Preventing Chronic Disease. 2012; 9:E96. DOI: 10.5888/pcd9.110169.
Article2. Ascaso JF, Millan J, Mateo-Gallego R, Ruiz A, Suarez-Tembra M, Borrallo RM, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease in a hypertriglyceridemic population. European Journal of Internal Medicine. 2011; 22(2):177–181. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2010.12.011.
Article3. Azadbakht L, Mirmiran P, Esmaillzadeh A, Azizi T, Azizi F. Beneficial effects of a dietary approaches to stop hypertension eating plan on features of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28(12):2823–2831. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.28.12.2823.
Article4. Bamia C, Trichopoulou A, Lenas D, Trichopoulos D. Tobacco smoking in relation to body fat mass and distribution in a general population sample. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 2004; 28:1091–1096. DOI: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802697.
Article5. Boyko EJ, de Courten M, Zimmet PZ. Features of the metabolic syndrome predict higher risk of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23(9):1242–1248.6. Davila EP, Florez H, Fleming LE, Lee DJ, Goodman E, Leblanc WG. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US workers. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33(11):2390–2395. DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0681.
Article7. Dunkley AJ, Taub NA, Davies MJ, Stone MA, Khunti K. Is having a familyhistory of type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease a predictive factor for metabolic syndrome? Primary Care Diabetes. 2009; 3(1):49–56. DOI: 10.1016/j.pcd.2009.02.002.8. Gami AS, Witt BJ, Howard DE, Erwin PJ, Gami LA, Somers VK, et al. Metabolic syndrome and risk of incident cardiovascular events and death: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Journal of American College of Cardiology. 2007; 49(4):403–414. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.09.032.9. Giugliano D, Ceriello A, Esposito K. The effects of diet on inflammation emphasis on the metabolic syndrome. Journal of American College of Cardiology. 2006; 48(4):677–685. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.03.052.10. Grundy SM. Metabolic syndrome pandemic. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2008; 28(4):629–636. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.151092.
Article11. Hwang CK, Koh SB, Chang SJ, Park CY, Cha BS, Hyun SJ, et al. Occupational stress in relation to cerebrovascular and cardiovascular disease: Longitudinal analysis from the NSDSOS project. Korean Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2007; 19(2):105–114.
Article12. Hwang WJ, Hong OS. Work-related cardiovascular disease risk factors using a socioecological approach: implications for practice and research. European Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing. 2012; 11(1):114–126.
Article13. Hwang WJ, Hong OS, Kim MJ. Factors associated with blue-collar workers' risk perception of cardiovascular disease. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing. 2012; 42:1095–1104.
Article14. Isomaa B, Almgren P, Tuomi T, Forsen B, Lahti K, Nissen M, et al. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2001; 24(4):683–689. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.24.4.683.
Article15. Jekarl J, Kim KK, Lee JT. Structural relationship between drinker's characteristics, work environment, and alcohol problems among employee. Health and Social Science. 2010; 28:5–31.16. Kanjilal S, Gregg EW, Cheng YJ, Zhang P, Nelson DE, Mensah G, et al. Socioeconomic status and trends in disparities in 4 major risk factors for cardiovascular disease among US adults, 1971-2002. Archives of internal medicine. 2006; 166(21):2348–2355.
Article17. Kim HC, Kim DJ. Causes of different estimates of the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korea. The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine. 2011; 26:440–448.
Article18. Kim YH, Park RJ, Park WJ, Kim MB, Moon JD. Predictors of metabolic syndrome among shipyard workers and its prevalence. Korean Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 2009; 21:209–217.
Article19. Kim DS, Kang SK. Work-related cerebro-cardiovascular diseases in Korea. Journal of Korean Medical Science. 2010; 25:S105–S111.
Article20. Klein BE, Klein R, Lee KE. Components of the metabolic syndrome and risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes in Beaver Dam. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:1790–1794.
Article21. Korea Ministry Employment and Labor. Occupational safety and health act Article 16. 2013. Retrieved April 30, 2013. from http://www.moel.go.kr/english/topic/laborlaw_view.jsp?idx=264&tab=Occupational.22. Korea National Statistical Office. The cause of death in 2011. 2011. Retrieved April 30, 2013. from http://www.index.go.kr/egams/stts/jsp/potal/stts/PO_STTS_IdxMain.jsp?idx_cd=1012&bbs=INDX_001&clas_div=C&rootKey=1.48.23. Korea Occupational Safety and Health Agency. 2009 Annual report of health examination for employees. 2009. Retrieved April 30, 2013. from http://www.kosha.or.kr/www/boardView.do?contentId=338572&menuId=557&boardType=A2.24. Lee WY, Jung CH, Park JS, Rhee EJ, Kim SW. Effects of smoking, alcohol, exercise, education, and family history on the metabolic syndrome as defined by the ATP III. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2005; 67:70–77.
Article25. Myong JP, Kim HR, Jung-Choi K, Baker D, Choi B. Disparities of metabolic syndrome prevalence by age, gender, and occupation among Korean adult workers. Industrial Health. 2012; 50:115–122.
Article26. National Cholesterol Education Program. Third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Final Report. Circulation. 2002; 106:3143–3421.27. Obunai K, Jani S, Dangas GD. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality of the metabolic syndrome. Medical Clinics of North America. 2007; 91(6):1169–1184.
Article28. Park HS, Oh SW, Cho SI, Choi WH, Kim YS. The metabolic syndrome and associated lifestyle factors among South Korean adults. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2004; 33:328–336.
Article29. Real JT, Romero P, Martinez-Hervas S, Pedro T, Carmena R, Ascaso JF. Role of atherogenic dyslipidemia in the development of metabolic syndrome. Medicina Clinica (Barc). 2006; 127:321–324.30. Sanchez-Chaparro MA, Calvo-Bonacho E, Gonzalez-Quintela A, Fernandez-Labandera C, Cabrera M, Sainz JC, et al. Occupation-related differences in the prevalence of metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31(9):1884–1885.31. Shiwaku K, Nogi A, Kitajima K, Anuurad E, Enkhmaa B, Yamasaki M. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome using the modified ATP III definitions for workers in Japan, Korea and Mongolia. Journal of Occupational Health. 2005; 47:126–135.
Article32. Yoon YS, Oh SW, Baik HW, Park HS, Kim WY. Alcohol consumption and the metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: The 1998 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2004; 80(1):217–224.
Article33. Yoon J, Yi K, Oh J, Lee S. The relationship between metabolic syndrome and Korean cardiocerebrovascular risk assessment: For male researchers in a workplace. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health. 2007; 40:397–403.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Metabolic Syndrome and Associated Risk Factors Among Male Workers in an Electronics Manufacturing Company
- Effects of Sleep Duration and Quality on Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Metabolic Syndrome Components in Korean Blue-collar Workers
- Health Disparities among Korean Workers by Enterprise Size: Using Korean Labor and Income Panel Study (17th)
- Predictors of Metabolic Syndrome Among Shipyard Workers and its Prevalence
- Influence of Occupational Type and Lifestyle Risk Factors on Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome among Male Workers: A Retrospective Cohort Study