J Korean Med Sci.
2015 Nov;30(Suppl 2):S167-S177. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.S2.S167.
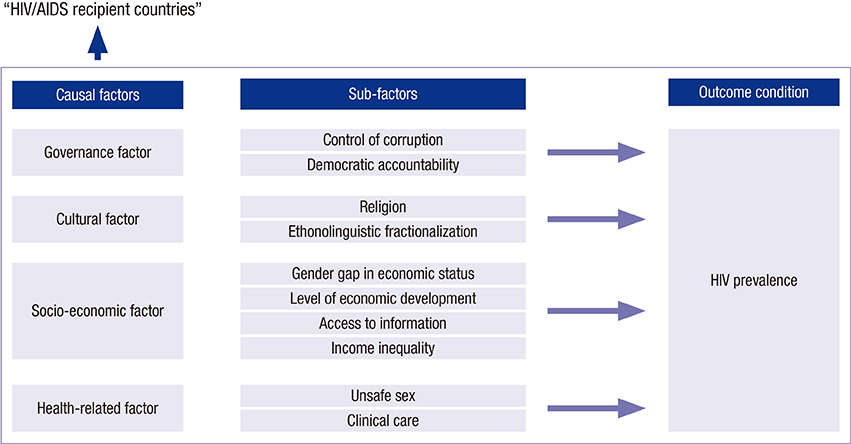
Factor Configurations with Governance as Conditions for Low HIV/AIDS Prevalence in HIV/AIDS Recipient Countries: Fuzzy-set Analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1JW Lee Center for Global Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Graduate School of Public Health, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. bmyang@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Public Administration, College of Social Sciences, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2351155
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.S2.S167
Abstract
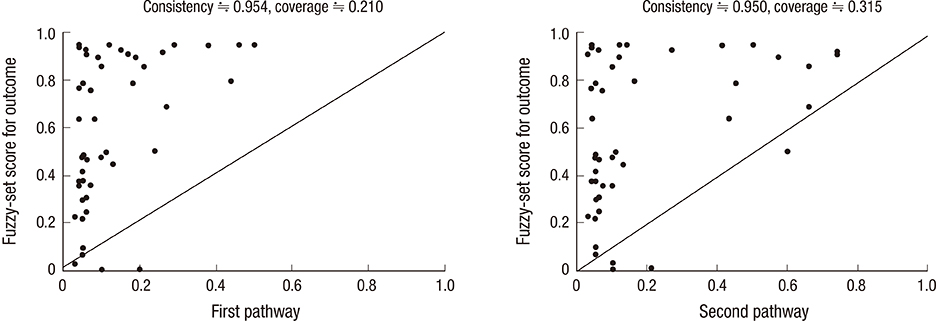
- This paper aims to investigate whether good governance of a recipient country is a necessary condition and what combinations of factors including governance factor are sufficient for low prevalence of HIV/AIDS in HIV/AIDS aid recipient countries during the period of 2002-2010. For this, Fuzzy-set Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) was used. Nine potential attributes for a causal configuration for low HIV/AIDS prevalence were identified through a review of previous studies. For each factor, full membership, full non-membership, and crossover point were specified using both author's knowledge and statistical information of the variables. Calibration and conversion to a fuzzy-set score were conducted using Fs/QCA 2.0 and probabilistic tests for necessary and sufficiency were performed by STATA 11. The result suggested that governance is the necessary condition for low prevalence of HIV/AIDS in a recipient country. From sufficiency test, two pathways were resulted. The low level of governance can lead to low level of HIV/AIDS prevalence when it is combined with other favorable factors, especially, low economic inequality, high economic development and high health expenditure. However, strengthening governance is a more practical measure to keep low prevalence of HIV/AIDS because it is hard to achieve both economic development and economic quality. This study highlights that a comprehensive policy measure is the key for achieving low prevalence of HIV/AIDS in recipient country.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome/*epidemiology/prevention & control
Computer Simulation
Developing Countries/*economics/statistics & numerical data
Economic Development/statistics & numerical data
Fraud/economics/*statistics & numerical data
Fuzzy Logic
HIV Infections/*epidemiology/prevention & control
Humans
Models, Statistical
Prevalence
Risk Factors
Socioeconomic Factors
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bassolé L. Dose Governance matter in the fight against HIV/AIDS epidemic? Evidence from cross-country analysis. African Development Bank;2010.2. Bor J. The political economy of AIDS leadership in developing countries: an exploratory analysis. Soc Sci Med. 2007; 64:1585–1599.3. UNAIDS. Monitoring and evaluation of HIV prevention programmes for most-at-risk populations: a framework for monitoring and evaluation HIV prevention programmes for most-at-risk populations. Geneva: Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS;2006.4. Parkhurst JO, Lush L. The political environment of HIV: lessons from a comparison of Uganda and South Africa. Soc Sci Med. 2004; 59:1913–1924.5. Davis C. Economy and corruption fuelling HIV in Zimbabwe: YMCA African alliance, April. 5th. 2011. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at: http://www.africaymca.org/economy-and-corruption-fuelling-hiv-in-zimbabwe/.6. DelaCruz JJ. The economic impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic across countries: factors explaining the spread of the disease. Saarbrücken: VDM Publishing;2010.7. Gupta GR. Gender, sexuality, and HIV/AIDS: the what, the why, and the how. Can HIV AIDS Policy Law Rev. 2000; 5:86–93.8. Méda N, Ndoye I, M’Boup S, Wade A, Ndiaye S, Niang C, Sarr F, Diop I, Caraël M. Low and stable HIV infection rates in Senegal: natural course of the epidemic or evidence for success of prevention? AIDS. 1999; 13:1397–1405.9. Oliveira-Cruz V, Kowalski J, McPake B. Viewpoint: the Brazilian HIV/AIDS 'success story'-- can others do it? Trop Med Int Health. 2004; 9:292–297.10. Ragin CC. Redesigning social inquiry: fuzzy sets and beyond. Chicago: University of Chicago Press;2008.11. Shleifer A, Vishny RW. Corruption. Quart J Econ. 1993; 108:599–617.12. Seedat F. The reminder of corruption in HIV & AIDS prevention and treatment: clarifying the facts. Consultancy Africa Intelligence Web. 2011. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at: http://www.consultancyafrica.com/index.php?option= com_content&view=article&id=750:the-reminder-of-corruption-in-hiv-a-aids-prevention-and-treatment-clarifying-the-facts-&catid=61:hiv-aids-discussion-papers&Itemid=268.13. Talyer L, Dickinson C. The link between corruption and HIV/AIDS. Global corruption Report. Germany: Transparency International;2006. Original source : Statement by CSO at the fourth ordinary African Union Summit of Heads of States, January 2005, Nigeria.14. Sen A. Development as freedom. New York: Random House Inc;1999.15. Hsu NL. Building dynamic democratic governance and HIV-resilient societies. Int Soc Sci J. 2005; 57:699–713.16. Patterson D. Political commitment, governance, and HIV/AIDS. Can HIV AIDS Policy Law Rev. 2001; 6:39–45.17. Strand P, Matlosa K, Strode A, Chirambo K. HIV/AIDS and democratic governance in South Africa: illustrating the impact on electoral processes. Pretoria: IDASA;2005.18. De Waal A. The links between HIV/AIDS and democratic governance in Africa. [London]: Justice Africa;2004.19. IRIN. SOUTH AFRICA: HIV/AIDS threatens to undermine democracy. 2004. Johannesburg: 2004. April. 9. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at: http://www.irinnews.org/report/36852/south-africa-hiv-aids-threatens-to-undermine-democracy.20. Burnside C, Dollar D. Aid, policies, and growth: revisiting the evidence: World Bank Policy Research Paper Number O-2834. 2004.21. Putzel J. Institutionalising an emergency response: HIV/AIDS and governance in Uganda and Senegal. London: London School of Economy and Political Science, Department for Internat. Development;2003.22. Lewis M. Governance and corruption in public health care systems: Working Paper No 78. Washington, DC: Center for Global Development;2006.23. Gray PB. HIV and Islam: is HIV prevalence lower among Muslims? Soc Sci Med. 2004; 58:1751–1756.24. Alesina A, Devleeschauwer A, Easterly W, Kurlat S, Wacziarg R. Fractionalization. J Econ Growth. 2003; 8:155–194.25. Hughes BB. Measuring Global Values: The Ranking of 162 Countries. By Michael J. Sullivan III. 1991 New York: Greenwood Press, xvi, 423 pp. J Asian Stud. 1992; 51:373–374.26. Over M. The effects of societal variables on urban rates of HIV infection in developing countries: an exploratory analysis, in confronting AIDS: evidence from the developing world. Brussels and Washington: European Commission and World Bank;1998. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at : http://www.cgdev.org/doc/expert%20pages/Mead%20Over%20Effects%20of%20societal%20variables%20on%20urban%20rates%20of%20HIV%20infection%201998.pdf.27. Temah CT. Socio-economic inequalities and HIV/AIDS Epidemic: Evidence from Sub-Saharan Africa. In Conférence AIDSIMPACT 2008. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at: http://www.africametrics.org/documents/conference08/day1/session2/tsafacktema.pdf.28. Kawachi I, Kennedy BP. The health of nations: why inequality is harmful to your health. New York: New Press;2002.29. Holmqvist G. HIV and Income Inequality: If there is a link, what does it tell us?. Working Paper No 54. International Policy Centre for Inclusive Growth;2009.30. Filmer D, Pritchett L. Child mortality and public spending on health: how much does money matter? Policy Research Working Paper No 1864. Washington, DC: World Bank Development Research Group;1997.31. Sang JY. Study on influencing factors of fertility rate: fs/QCA analysis of OECD members. Daejeon: Social Welfare, Graduate school of Chung Nam University;2010. Dissertation.32. Wagemann C, Schneider CQ. Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA) and ruzzy-sets: agenda for a research approach and a data analysis technique. Comp Sociol. 2010; 9:376–396.33. Yemelyanau M. Inequality in Belarus from 1995 to 2007. BEROC and CERGE-EI, Working paper series 001. 2009.34. World Bank. International finance corporation country assistance strategy for the Republic of Bellarus: Report No 40742-BY 200. Washington, DC: International Bank for Reconstruction and Development;2007.35. Freedom House. Nation in transit. 2005. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at: http://www.freedomhouse.org/report/nations-transit/2005/belarus#.U6ADtU09JZQ.36. Carasciuc L. Corruption and Quality of Governance: the case of Moldova. Transparency Inernational;2001.37. European Commission. The EU's neighbouring economies managing policies in a challenging global environment. Occasional Papers 160. Brussels: European Commission, Directorate-General for Economic and Financial Affairs;2013.38. World Bank. IDA at work. MOLDOVA: HIV/AIDS treatment improves;2009. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at: http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/EXTABOUTUS/IDA/0,,print:Y~isCURL:Y~contentMDK:22311261~menuPK:4754051~pagePK:51236175~piPK:437394~theSitePK:73154,00.html.39. Andres AR, Ramlogan-Dobson C. Is corruption really bad for inequality? Evidence from Latin America. J Devel Stud. 2011; 47:959–976.40. Ministry of foreign affairs of Netherlands. Equity, accountability and effectiveness in decentralization policies in Bolivia. 2012. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at: http://www.delog.org/cms/upload/pdf-account/IOB_Study_370-Decentralization_Bolivia_-_Equity_Accountability_and_effectiveness_in_decentralization_policies_in_Bolivia.pdf.41. Freedom house. Costa Rica. 2013. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at: http://www.freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world/2013/costa-rica#.U3XQyE09KdI.42. World Health Organization. Costa Rica. 2005. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at: http://www.who.int/hiv/HIVCP_CRI.pdf.43. NY Times. Costa Rica's wrong turn. 2014. accessed on 30 September 2015. Available at: http://www.nytimes.com/2014/02/01/opinion/costa-ricas-wrong-turn.html?_r=0.44. Gupta S, Davoodi H, Tiongson E. Corruption and the provision of health care and education services. Ann Econ Finance. 2014; 15:759–798.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of HIV/AIDS in HIV-infected Koreans
- The 2013 Clinical Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of HIV/AIDS in HIV-Infected Koreans
- Experience of the Use of Three Screening Kits, Enzygnost Anti-HIV1/2 Plus, ABBOTT TESTPACK HIV- 1/HIV-2 & SERODIA. HIV- 1/2 for the Detection of Antibodies to HIV
- Current Status of the Estimation on the Number of People Who Living with HIV and the Rate of Undiagnosed Cases
- Prediction of HIV and AIDS Incidence Using a Back-calculation Model in Korea