Blood Culture Proven Early Onset Sepsis and Late Onset Sepsis in Very-Low-Birth-Weight Infants in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Pediatrics, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kskim@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2351138
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.S1.S67
Abstract
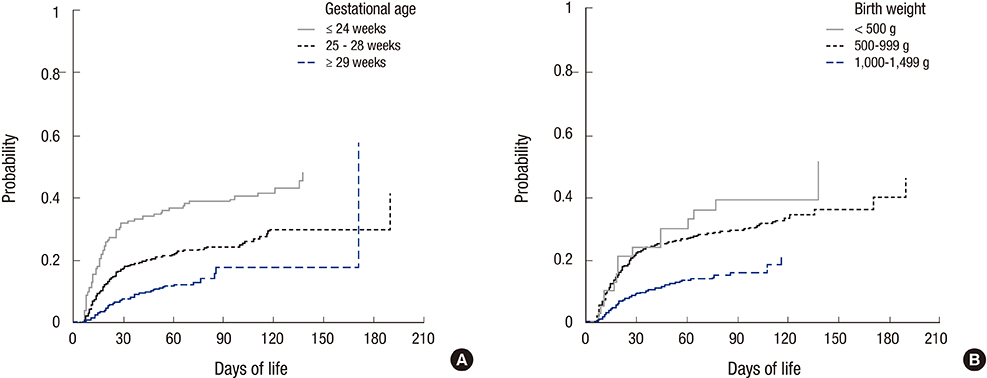
- Neonatal sepsis remains one of the most important causes of death and co-morbidity in very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) infants. The aim of this study was to determine the current incidences of early-onset sepsis (EOS) and late-onset sepsis (LOS), the distribution of pathogens, and the impact of infection on co-morbidities in VLBW infants. We analyzed the data including sepsis episode from 2,386 VLBW infants enrolled in Korean Neonatal Network from January 2013 to June 2014. We defined EOS as a positive blood culture occurring between birth and 7 days of life and LOS after 7 days of life. Sepsis was found in 21.1% of VLBW infants. The risk of sepsis was inversely related to birth weight and gestational age. EOS was found in only 3.6% of VLBW infants, however the mortality rate was as high as 34.1%. EOS was associated with the increased odds for bronchopulmonary dysplasia and intraventricular hemorrhage. The vast majority of EOS was caused by Gram-positive organisms, particularly coagulase-negative staphylococci (30.6%). LOS developed in 19.4% of VLBW infants with a 16.1% mortality rate. Pathogens in LOS were dominated by coagulase-negative staphylococci (38.3%). Twenty-five percent and fifty percent of first LOS episode occurred after 12 days and 20 days from birth, respectively. Younger and smaller VLBW infants showed the earlier occurrence day for the 25% of first LOS episode. This study provides a recent nationwide epidemiology of sepsis in VLBW infants in Korea. Based on this study, successful strategies to reduce infections would improve survival and reduce morbidity.
MeSH Terms
-
Coagulase/metabolism
Databases, Factual
Gestational Age
Gram-Negative Bacteria/isolation & purification
Gram-Positive Bacteria/isolation & purification
Humans
Incidence
Infant, Newborn
*Infant, Very Low Birth Weight
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Republic of Korea/epidemiology
Risk Factors
Sepsis/*epidemiology/microbiology/mortality
Staphylococcus/enzymology/isolation & purification
Coagulase
Figure
Cited by 9 articles
-
Neonatal Outcomes according to the Latent Period from Membrane Rupture to Delivery among Extremely Preterm Infants Exposed to Preterm Premature Rupture of Membrane: a Nationwide Cohort Study
Jae Hyun Park, Jin Gon Bae, Yun Sil Chang
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(14):e93. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e93.Moving Forward to Improve Safety and Quality of Neonatal Intensive Care in Korea
Yun Sil Chang
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(9):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e89.Changes in neonatal outcomes in Korea
So Young Kim
J Korean Med Assoc. 2016;59(7):498-505. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2016.59.7.498.Clinical Characteristics of Early Onset Sepsis in Micropreemie Born at 25 or Less than 25 Weeks of Gestational Age
Shin Ae Yoon, Ji Young Chun, Yo Han Ho, Ji Sook Kim, Hye Soo Yoo, Se In Sung, So Yoon Ahn, Yun Sil Chang, Won Soon Park
Korean J Perinatol. 2016;27(1):53-59. doi: 10.14734/kjp.2016.27.1.53.Staphylococcus capitis Induced Late-onset Sepsis in Very Low Birth Weight Infants
In Kim, Gina Lim, Eun Ha Hwang, Ki Won Oh, Joseph Jeong
Perinatology. 2017;28(4):140-145. doi: 10.14734/PN.2017.28.04.140.The Effect of Macrolide Therapy on Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in
Ureaplasma Positive Very Low Birth Weight Infants
Soohyun Kim, Chae Young Kim, Euiseok Jung, Heeyoung Kim, Woo Sun Song, Byong Sop Lee, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim, Ki-Soo Kim
Perinatology. 2018;29(3):107-113. doi: 10.14734/PN.2018.29.03.107.1차 분만병원 수준에서의 임신 후기 산모의질내 B군 연쇄상 구균 집락 형성의 임상적 특성에 대한 평가
Sumin Oh, Joong Shin Park
J Korean Soc Matern Child Health. 2022;26(1):27-34. doi: 10.21896/jksmch.2022.26.1.27.Restriction of Central Line Insertion and Prophylactic Antibiotics Usage in Moderate and Late Preterm Infants from a Quality Improvement Perspective
Sae Yun Kim, Geun Moo Lee, Eun Sun Kim
Perinatology. 2019;30(2):71-77. doi: 10.14734/PN.2019.30.2.71.Current Status and Issues of Infection Control in the Neonatal Intensive Care Units
Do-Hyun Kim
Korean J Healthc Assoc Infect Control Prev. 2023;28(1):29-35. doi: 10.14192/kjicp.2023.28.1.29.
Reference
-
1. Hornik CP, Fort P, Clark RH, Watt K, Benjamin DK Jr, Smith PB, Manzoni P, Jacqz-Aigrain E, Kaguelidou F, Cohen-Wolkowiez M. Early and late onset sepsis in very-low-birth-weight infants from a large group of neonatal intensive care units. Early Hum Dev. 2012; 88:S69–S74.2. Stoll BJ, Gordon T, Korones SB, Shankaran S, Tyson JE, Bauer CR, Fanaroff AA, Lemons JA, Donovan EF, Oh W, et al. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: a report from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. J Pediatr. 1996; 129:63–71.3. Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, Lemons JA, Donovan EF, Stark AR, Tyson JE, et al. Changes in pathogens causing early-onset sepsis in very-low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:240–247.4. Alshaikh B, Yusuf K, Sauve R. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of very low birth weight infants with neonatal sepsis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Perinatol. 2013; 33:558–564.5. Klinger G, Levy I, Sirota L, Boyko V, Lerner-Geva L, Reichman B. Israel Neonatal Network. Outcome of early-onset sepsis in a national cohort of very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2010; 125:e736–e740.6. Ozkan H, Cetinkaya M, Koksal N, Celebi S, Hacimustafaoglu M. Culture-proven neonatal sepsis in preterm infants in a neonatal intensive care unit over a 7 year period: coagulase-negative Staphylococcus as the predominant pathogen. Pediatr Int. 2014; 56:60–66.7. Wójkowska-Mach J, Borszewska-Kornacka M, Domańska J, Gadzinowski J, Gulczyńska E, Helwich E, Kordek A, Pawlik D, Szczapa J, Klamka J, et al. Early-onset infections of very-low-birth-weight infants in Polish neonatal intensive care units. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012; 31:691–695.8. Vergnano S, Menson E, Kennea N, Embleton N, Russell AB, Watts T, Robinson MJ, Collinson A, Heath PT. Neonatal infections in England: the NeonIN surveillance network. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2011; 96:F9–F14.9. Jeong IS, Jeong JS, Choi EO. Nosocomial infection in a newborn intensive care unit (NICU), South Korea. BMC Infect Dis. 2006; 6:103.10. Shim GH, Kim SD, Kim HS, Kim ES, Lee HJ, Lee JA, Choi CW, Kim EK, Choi EH, Kim BI, et al. Trends in epidemiology of neonatal sepsis in a tertiary center in Korea: a 26-year longitudinal analysis, 1980-2005. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:284–289.11. Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, Lemons JA, Donovan EF, Stark AR, Tyson JE, et al. Late-onset sepsis in very low birth weight neonates: the experience of the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2002; 110:285–291.12. Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978; 92:529–534.13. Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L, Brotherton T. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg. 1978; 187:1–7.14. Ehrenkranz RA, Walsh MC, Vohr BR, Jobe AH, Wright LL, Fanaroff AA, Wrage LA, Poole K. National Institutes of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Validation of the National Institutes of Health consensus definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. 2005; 116:1353–1360.15. Kusuda S, Fujimura M, Sakuma I, Aotani H, Kabe K, Itani Y, Ichiba H, Matsunami K, Nishida H. Neonatal Research Network Japan. Morbidity and mortality of infants with very low birth weight in Japan: center variation. Pediatrics. 2006; 118:e1130–e1138.16. The Canadian Neonatal Network TM. accessed on 2 November 2014. Available at http://www.canadianneonatalnetwork.org/portal.17. Australian & New Zealand Neonatal Network (ANZNN). National Perinatal Epidemiology and Statistics Unit (NPESU). accessed on 2 December 2014. Available at https://npesu.unsw.edu.au/data-collection/australian-new-zealand-neonatal-network-anznn.18. Neonatal Research Network Japan. accessed on 25 January 2015. Available at http:nrn.shiga-med.ac.jp/Englishdefault.htm.19. Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Walsh MC, Hale EC, Newman NS, Schibler K, Carlo WA, et al. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 2010; 126:443–456.20. Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Sánchez PJ, Faix RG, Poindexter BB, Van Meurs KP, Bizzarro MJ, Goldberg RN, Frantz ID 3rd, Hale EC, et al. Early onset neonatal sepsis: the burden of group B Streptococcal and E. coli disease continues. Pediatrics. 2011; 127:817–826.21. Wójkowska-Mach J, Gulczyńska E, Nowiczewski M, Borszewska-Kornacka M, Domańska J, Merritt TA, Helwich E, Kordek A, Pawlik D, Gadzinowski J, et al. Late-onset bloodstream infections of Very-Low-Birth-Weight infants: data from the Polish Neonatology Surveillance Network in 2009-2011. BMC Infect Dis. 2014; 14:339.22. Shah AJ, Mulla SA, Revdiwala SB. Neonatal sepsis: high antibiotic resistance of the bacterial pathogens in a neonatal intensive care unit of a tertiary care hospital. J Clin Neonatol. 2012; 1:72–75.23. Stoll BJ, Hansen N. Infections in VLBW infants: studies from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Semin Perinatol. 2003; 27:293–301.24. Benjamin DK Jr, Stoll BJ, Fanaroff AA, McDonald SA, Oh W, Higgins RD, Duara S, Poole K, Laptook A, Goldberg R, et al. Neonatal candidiasis among extremely low birth weight infants: risk factors, mortality rates, and neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18 to 22 months. Pediatrics. 2006; 117:84–92.25. Rosenthal VD, Lynch P, Jarvis WR, Khader IA, Richtmann R, Jaballah NB, Aygun C, Villamil-Gómez W, Dueñas L, Atencio-Espinoza T, et al. Socioeconomic impact on device-associated infections in limited-resource neonatal intensive care units: findings of the INICC. Infection. 2011; 39:439–450.26. Kim EA. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection in neonates. Neonatal Med. 2013; 20:354–360.27. Makhoul IR, Sujov P, Smolkin T, Lusky A, Reichman B. Israel Neonatal Network. Pathogen-specific early mortality in very low birth weight infants with late-onset sepsis: a national survey. Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 40:218–224.28. Westby Wold SH, Sommerfelt K, Reigstad H, Rønnestad A, Medbo S, Farstad T, Kaaresen PI, Stoen R, Leversen KT, Irgens LM, et al. Neonatal mortality and morbidity in extremely preterm small for gestational age infants: a population based study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2009; 94:F363–F367.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early-Onset Sepsis Due to Listeria Monocytogenes in a Extremely Low Birth Weight Infant
- Analysis of causative microorganisms and choice of antibiotics according to the onset of neonatal sepsis
- Risk Factors for Neonatal Sepsis in Premature Infants Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Changes in Pathogens and Antibiotic Sensitivities in very Low Birth Weight Infants with Neonatal Sepsis
- Platelet count and mean platelet volume in low birth weight infants (< or =2,000 g) with sepsis