J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2016 Aug;42(4):227-230. 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.4.227.
Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. omslips@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2350076
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.4.227
Abstract
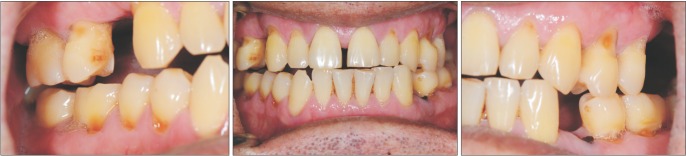
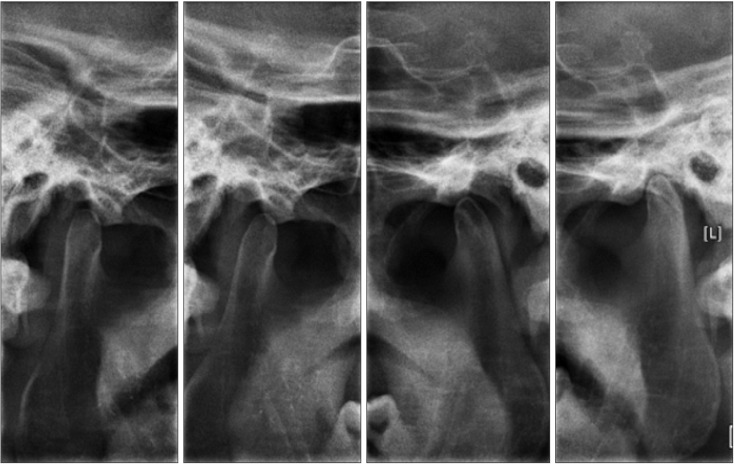
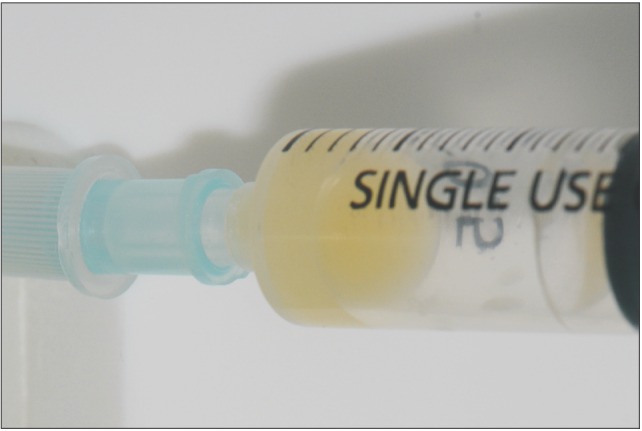
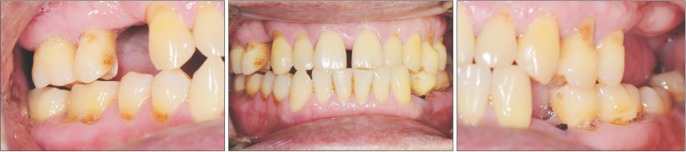
- Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a rare disease. The most common symptoms of this disease are acute malocclusion, limited mouth opening, swelling, and tenderness of affected TMJ. These symptoms are often confused with internal derangement of the articular disc, rheumatoid arthritis, retrodiscitis, or osteoarthritis. Therefore, differential diagnosis by image examination is required. Usually, antimicrobial treatment and surgical drainage by needle aspiration, arthroscopy, or arthrotomy are effective treatment approaches. In this study, a patient who was diagnosed with septic arthritis was treated with arthrocentesis and antibiotics without significant complications. We present a case report with a review of the literature.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cai XY, Yang C, Zhang ZY, Qiu WL, Chen MJ, Zhang SY. Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint: a retrospective review of 40 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:731–738. PMID: 19954877.
Article2. Klüppel LE, Bernabé FB, Primo BT, Stringhini DJ, da Costa DJ, Rebellato NL, et al. Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint. J Craniofac Surg. 2012; 23:1752–1754. PMID: 23147304.
Article3. Parmar J. Case report: septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint in a neonate. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 46:505–506. PMID: 18282642.
Article4. Leighty SM, Spach DH, Myall RW, Burns JL. Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint: review of the literature and report of two cases in children. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993; 22:292–297. PMID: 8245570.
Article5. Bounds GA, Hopkins R, Sugar A. Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint--a problematic diagnosis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1987; 25:61–67. PMID: 2948546.
Article6. Gayle EA, Young SM, McKenna SJ, McNaughton CD. Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint: case reports and review of the literature. J Emerg Med. 2013; 45:674–678. PMID: 23896057.7. Trimble LD, Schoenaers JA, Stoelinga PJ. Acute suppurative arthritis of the temporomandibular joint in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. J Maxillofac Surg. 1983; 11:92–95. PMID: 6575113.
Article8. Sembronio S, Albiero AM, Robiony M, Costa F, Toro C, Politi M. Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint successfully treated with arthroscopic lysis and lavage: case report and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007; 103:e1–e6. PMID: 17095265.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Infection of the temporomandibular joint: a report of three cases
- Arthroscopic Treatment of Septic Arthritis of the Hip in a Child: A Case Report
- Arthroscopic Treatment for Septic Arthritis of the Shoulders in Neonates: A Case Report
- Septic arthritis of the hip joint caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae: a case report
- Arthroscopic Treatment of Septic Arthritis of Acromioclavicular Joint