J Korean Soc Radiol.
2016 Sep;75(3):191-197. 10.3348/jksr.2016.75.3.191.
Ultrasonographic and Clinical Findings of Inguinal Hernia Containing the Ovary or Omentum in Girls
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. chaijw@gmail.com
- KMID: 2349324
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.3.191
Abstract
- PURPOSE
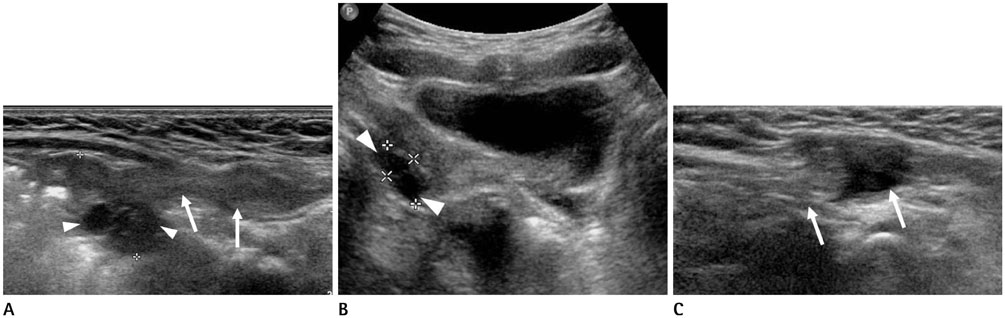
To characterize the ultrasonographic and clinical findings of inguinal hernia containing the ovary or omentum in girls.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We studied 46 girls (49 cases) who were diagnosed with inguinal hernia on ultrasonography between March 2009 and December 2015. The ultrasonographic findings were retrospectively analyzed with respect to location, age at detection, contents of hernia, diameter of the canal of Nuck, and incidence of reducibility, incarceration and strangulation. The clinical findings included the number of cases that underwent operation, contents of hernia discovered during operation, and duration between ultrasonographic diagnosis and operation. The two groups in which inguinal hernia contained the ovary and omentum were statistically compared.
RESULTS
Of the 49 cases, the contents of hernia were the ovary or tube in 14 cases, omentum in 32 cases, and bowel in 3 cases. The ovarian herniation group was significantly younger (10.1 months vs. 4.9 years, p < 0.001), had a lower incidence of reducibility (n = 3 vs. n = 29, p < 0.001), higher incidence of incarceration (n = 4 vs. n = 0, p = 0.006), and a shorter duration between ultrasonographic diagnosis and operation (5.7 days vs. 55.8 days, p = 0.032) than the omental herniation group.
CONCLUSION
The ovarian herniation group was younger, had a lower incidence of reducibility, higher incidence of incarceration, and a shorter duration between ultrasonographic diagnosis and operation.
MeSH Terms
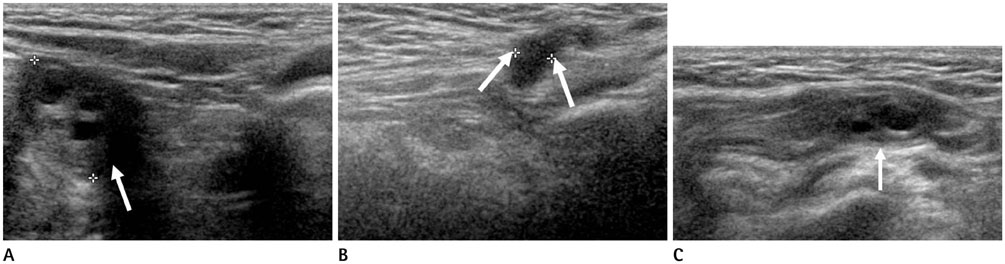
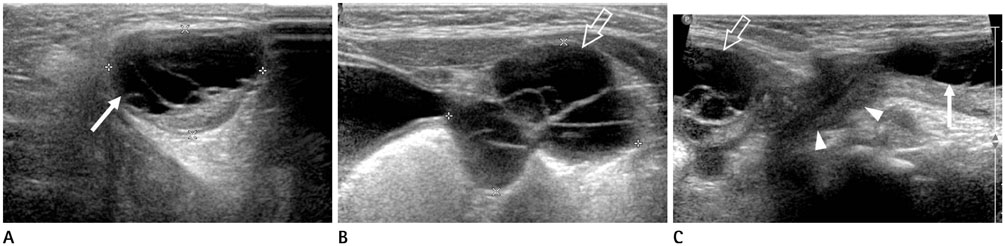
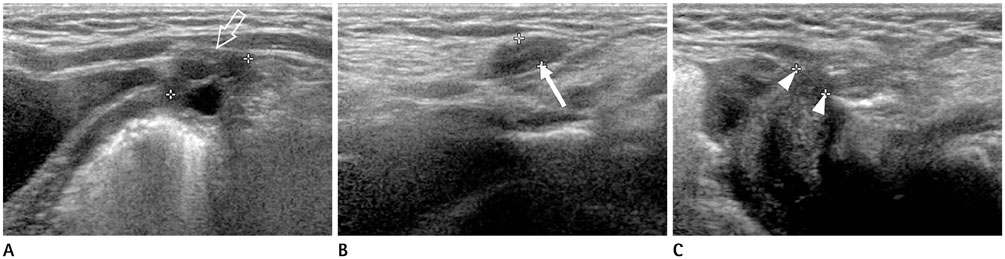
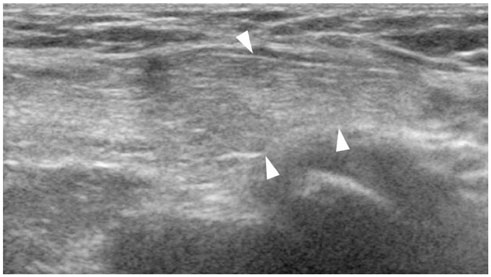
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hyun PM, Jung AY, Lee Y, Yang I, Yang DH, Hwang JY. CT and US findings of ovarian torsion within an incarcerated inguinal hernia. Emerg Radiol. 2015; 22:91–94.2. Choi KE, An SY, Kim KA, Ko SY, Lee YK, Shin SM, et al. Characteristics and clinical course of ovarian hernias in infants. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2008; 15:80–83.3. Huang CS, Luo CC, Chao HC, Chu SM, Yu YJ, Yen JB. The presentation of asymptomatic palpable movable mass in female inguinal hernia. Eur J Pediatr. 2003; 162:493–495.4. Munden M, McEniff N, Mulvihill D. Sonographic investigation of female infants with inguinal masses. Clin Radiol. 1995; 50:696–698.5. Fowler CL. Sliding indirect hernia containing both ovaries. J Pediatr Surg. 2005; 40:e13–e14.6. Boley SJ, Cahn D, Lauer T, Weinberg G, Kleinhaus S. The irreducible ovary: a true emergency. J Pediatr Surg. 1991; 26:1035–1038.7. Kim YK, Lee SW. Sonographic findings of inguinal herniation of the ovary. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2003; 49:211–215.8. Laing FC, Townsend BA, Rodriguez JR. Ovary-containing hernia in a premature infant: sonographic diagnosis. J Ultrasound Med. 2007; 26:985–987.9. Yang DM, Kim HC, Kim SW, Lim SJ, Park SJ, Lim JW. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of ovary-containing hernias of the canal of Nuck. Ultrasonography. 2014; 33:178–183.10. Kapur P, Caty MG, Glick PL. Pediatric hernias and hydroceles. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1998; 45:773–789.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incarcerated Inguinal Hernia in Children
- Inguinal hernia of ovary and fallopian tube in adult woman
- Sonographic Findings of Inguinal Herniation of the Ovary
- Indirect Inguinal Hernia Containing the Uterus, Both Ovaries, and Fallopian Tubes in an Infant: A Case Report
- Ultrasonographic diagnosis of ovary-containing hernias of the canal of Nuck