Yonsei Med J.
2015 Nov;56(6):1686-1693. 10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1686.
Hemodynamic Significance of Internal Carotid or Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis Detected on Magnetic Resonance Angiography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea. paengjc@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Sciences, WCU Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Nuclear Medicine, The Medical City, Pasig City, Philippines.
- 5Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2345901
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.6.1686
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We evaluated hemodynamic significance of stenosis on magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) using acetazolamide perfusion single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Of 171 patients, stenosis in internal carotid artery (ICA) and middle cerebral artery (MCA) (ICA-MCA) on MRA and cerebrovascular reserve (CVR) of MCA territory on SPECT was measured using quantification and a 3-grade system. Stenosis and CVR grades were compared with each other, and their prognostic value for subsequent stroke was evaluated.
RESULTS
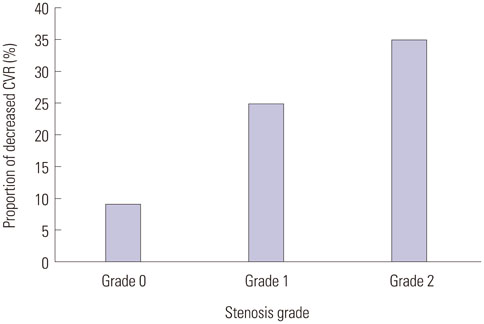
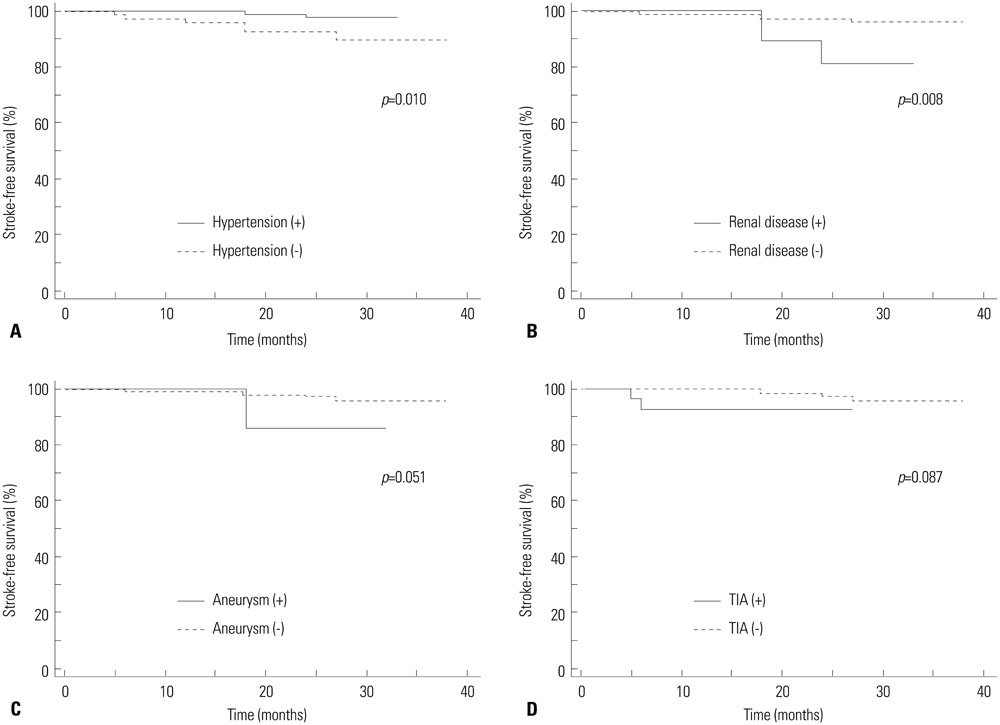
Of 342 ICA-MCA, 151 (44%) presented stenosis on MRA; grade 1 in 69 (20%) and grade 2 in 82 (24%) cases. Decreased CVR was observed in 9% of grade 0 stenosis, 25% of grade 1, and 35% of grade 2. The average CVR of grade 0 was significantly different from grade 1 (p<0.001) and grade 2 stenosis (p=0.007). In quantitative analysis, average CVR index was -0.56+/-7.91 in grade 0, -1.81+/-6.66 in grade 1 and -1.18+/-5.88 in grade 2 stenosis. Agreement between stenosis and CVR grades was fair in patients with lateralizing and non-lateralizing symptoms (kappa=0.230 and 0.346). Of the factors tested, both MRA and CVR were not significant prognostic factors (p=0.104 and 0.988, respectively), whereas hypertension and renal disease were significant factors (p<0.05, respectively).
CONCLUSION
A considerable proportion of ICA-MCA stenosis detected on MRA does not cause CVR impairment despite a fair correlation between them. Thus, hemodynamic state needs to be assessed for evaluating significance of stenosis, particularly in asymptomatic patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
*Acetazolamide
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Brain/blood supply/radionuclide imaging
Carotid Artery, Internal/physiopathology/radionuclide imaging
Carotid Stenosis/physiopathology/*radionuclide imaging
*Cerebrovascular Circulation
Constriction, Pathologic
Diuretics
Female
*Hemodynamics
Humans
Hypertension/physiopathology
Iodine Radioisotopes
*Magnetic Resonance Angiography
Male
Middle Aged
*Radiopharmaceuticals
Tomography, Emission-Computed, Single-Photon/*methods
Acetazolamide
Diuretics
Iodine Radioisotopes
Radiopharmaceuticals
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhang Y, Wu S, Jia Z, Zhou Y, Liu X, Wang W, et al. The relationship of asymptomatic intracranial artery stenosis and Framingham stroke risk profile in a Northern Chinese industrial city. Neurol Res. 2012; 34:359–365.2. Yang F, Liu L, Li M, Li M, Yin Q, Guo R, et al. Pattern of cerebrovascular atherosclerotic stenosis in older Chinese patients with stroke. J Clin Neurosci. 2013; 20:979–983.
Article3. Silvestrini M, Vernieri F, Pasqualetti P, Matteis M, Passarelli F, Troisi E, et al. Impaired cerebral vasoreactivity and risk of stroke in patients with asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. JAMA. 2000; 283:2122–2127.
Article4. Gao T, Yu W, Liu C. Mechanisms of ischemic stroke in patients with intracranial atherosclerosis: a high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. Exp Ther Med. 2014; 7:1415–1419.
Article5. Kumar G, Kalita J, Kumar B, Bansal V, Jain SK, Misra U. Magnetic resonance angiography findings in patients with ischemic stroke from North India. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010; 19:146–152.
Article6. Bash S, Villablanca JP, Jahan R, Duckwiler G, Tillis M, Kidwell C, et al. Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusive disease: evaluation with CT angiography, MR angiography, and digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:1012–1021.7. Lutsep HL, Clark WM. Association of intracranial stenosis with cortical symptoms or signs. Neurology. 2000; 55:716–718.
Article8. Man BL, Fu YP, Chan YY, Lam W, Hui CF, Leung WH, et al. Use of magnetic resonance angiography to predict long-term outcomes of ischemic stroke patients with concurrent stenoses in Hong Kong. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2009; 28:112–118.
Article9. Lee K, Kim H, Heo JH, Bae HJ, Koh IS, Chang S. Application of magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance angiography as diagnostic measures for the first attack of suspected cerebrovascular diseases in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2011; 52:727–733.
Article10. Park SA, Park HI, Kim D, Yang CY, Zhang LQ. The prediction of gross motor outcome using cerebrovascular reserve measured by acetazolamide-challenged SPECT. NeuroRehabilitation. 2012; 30:359–367.
Article11. Kuroda S, Houkin K, Kamiyama H, Mitsumori K, Iwasaki Y, Abe H. Long-term prognosis of medically treated patients with internal carotid or middle cerebral artery occlusion: can acetazolamide test predict it. Stroke. 2001; 32:2110–2116.
Article12. Marchal G, Bouvard G, Iglesias S, Sebastien B, Benali K, Defer G, et al. Predictive value of (99m)Tc-HMPAO-SPECT for neurological Outcome/Recovery at the acute stage of stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2000; 10:8–17.
Article13. Kim JM, Jung KH, Sohn CH, Moon J, Han MH, Roh JK. Middle cerebral artery plaque and prediction of the infarction pattern. Arch Neurol. 2012; 69:1470–1475.
Article14. Moore WS, Barnett HJ, Beebe HG, Bernstein EF, Brener BJ, Brott T, et al. Guidelines for carotid endarterectomy. A multidisciplinary consensus statement from the Ad Hoc Committee, American Heart Association. Circulation. 1995; 91:566–579.15. Nederkoorn PJ, van der Graaf Y, Eikelboom BC, van der Lugt A, Bartels LW, Mali WP. Time-of-flight MR angiography of carotid artery stenosis: does a flow void represent severe stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1779–1784.16. U-King-Im JM, Trivedi RA, Cross JJ, Higgins NJ, Hollingworth W, Graves M, et al. Measuring carotid stenosis on contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography: diagnostic performance and reproducibility of 3 different methods. Stroke. 2004; 35:2083–2088.
Article17. So Y, Lee HY, Kim SK, Lee JS, Wang KC, Cho BK, et al. Prediction of the clinical outcome of pediatric moyamoya disease with postoperative basal/acetazolamide stress brain perfusion SPECT after revascularization surgery. Stroke. 2005; 36:1485–1489.
Article18. Lee HY, Paeng JC, Lee DS, Lee JS, Oh CW, Cho MJ, et al. Efficacy assessment of cerebral arterial bypass surgery using statistical parametric mapping and probabilistic brain atlas on basal/acetazolamide brain perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med. 2004; 45:202–206.19. Raoult H, Bannier E, Maurel P, Neyton C, Ferré JC, Schmitt P, et al. Hemodynamic quantification in brain arteriovenous malformations with time-resolved spin-labeled magnetic resonance angiography. Stroke. 2014; 45:2461–2464.
Article20. Kimura K, Iguchi Y, Shibazaki K, Aoki J, Uemura J. Early recanalization rate of major occluded brain arteries after intravenous tissue plasminogen activator therapy using serial magnetic resonance angiography studies. Eur Neurol. 2009; 62:287–292.
Article21. Schellinger PD, Richter G, Kohrmann M, Dorfler A. Noninvasive angiography (magnetic resonance and computed tomography) in the diagnosis of ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Techniques and clinical applications. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007; 24:Suppl 1. 16–23.
Article22. Deus-Silva L, Bonilha L, Damasceno BP, Costa AL, Yasuda CL, Costa FF, et al. Brain Perfusion Impairment in Neurologically Asymptomatic Adult Patients with Sickle-Cell Disease Shown by Voxel-Based Analysis of SPECT Images. Front Neurol. 2013; 4:207.
Article23. Oikawa K, Ogasawara K, Saito H, Yoshida K, Saura H, Sato Y, et al. Combined measurement of cerebral and cerebellar blood flow on preoperative brain perfusion SPECT imaging predicts development of new cerebral ischemic events after endarterectomy for symptomatic unilateral cervical carotid stenosis. Clin Nucl Med. 2013; 38:957–961.
Article24. Volkan-Salanci B, Lay Ergün E, Genc Sel Ç, Yalnizoğlu D, Turanli G. The role of brain perfusion SPECT in Moyamoya disease. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2012; 31:216–218.
Article25. Saura H, Ogasawara K, Suzuki T, Kuroda H, Yamashita T, Kobayashi M, et al. Effect of combination therapy with the angiotensin receptor blocker losartan plus hydrochlorothiazide on brain perfusion in patients with both hypertension and cerebral hemodynamic impairment due to symptomatic chronic major cerebral artery steno-occlusive disease: a SPECT study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012; 33:354–361.
Article26. Gupta A, Chazen JL, Hartman M, Delgado D, Anumula N, Shao H, et al. Cerebrovascular reserve and stroke risk in patients with carotid stenosis or occlusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2012; 43:2884–2891.
Article27. Chen J, Liu J, Xu WH, Xu R, Hou B, Cui LY, et al. Impaired dynamic cerebral autoregulation and cerebrovascular reactivity in middle cerebral artery stenosis. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e88232.
Article28. Kanber B, Hartshorne TC, Horsfield MA, Naylor AR, Robinson TG, Ramnarine KV. Wall motion in the stenotic carotid artery: association with greyscale plaque characteristics, the degree of stenosis and cerebrovascular symptoms. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2013; 11:37.
Article29. Liu M, Zhou L. Cerebrovascular reserve may be a more accurate predictor of stroke than degree of ICA or MCA stenosis. Med Sci Monit. 2014; 20:2082–2087.
Article30. Kuroda S, Shiga T, Ishikawa T, Houkin K, Narita T, Katoh C, et al. Reduced blood flow and preserved vasoreactivity characterize oxygen hypometabolism due to incomplete infarction in occlusive carotid artery diseases. J Nucl Med. 2004; 45:943–949.31. Lee KJ, Jung KH, Byun JI, Kim JM, Roh JK. Infarct pattern and clinical outcome in acute ischemic stroke following middle cerebral artery occlusion. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014; 38:31–38.
Article32. Itrat A, Ahmed B, Khan M, Muhammad M, Thaver D, Khowaja Z, et al. Risk factor profiles of South Asians with cerebrovascular disease. Int J Stroke. 2011; 6:346–348.
Article33. Tripepi G, Mattace-Raso F, Rapisarda F, Stancanelli B, Malatino L, Witteman J, et al. Traditional and nontraditional risk factors as predictors of cerebrovascular events in patients with end stage renal disease. J Hypertens. 2010; 28:2468–2474.
Article34. Hokari M, Isobe M, Imai T, Chiba Y, Iwamoto N, Isu T. The impact of atherosclerotic factors on cerebral aneurysm is location dependent: aneurysms in stroke patients and healthy controls. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014; 23:2301–2307.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Infraoptic Anterior Cerebral Artery Arising from Contralateral Internal Carotid Artery: Case Report
- Delayed Cerebral Hyperperfusion Syndrome after Carotid Artery Stenting: the Finding of Multimodal MRI
- Estimation of Occluded Sites and Flow Dynamics in Internal Carotid Artery Obstruction Using Routine Cerebral Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Transcranial Doppler
- Bilateral Agenesis of the Internal Carotid Artery: Case Report
- Carotid Doppler Ultrasound in Patients with Stenosis of the Intracranial Internal Carotid Artery