Anesth Pain Med.
2016 Jul;11(3):299-306. 10.17085/apm.2016.11.3.299.
Comparison of the streamlined liner of the pharynx airway (SLIPAâ„¢) with the I-gelâ„¢ in paralyzed, anesthetized patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. roman00@naver.com
- KMID: 2344936
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.3.299
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
I-gelâ„¢ and Streamlined Liner of the Pharynx Airway (SLIPAâ„¢) are the second generation supraglottic airway devices characterized by disposability and non-inflatable cuff that provide adequate sealing pressure and easy use. This study was designed to compare oro-pharyngeal leakage pressure of the I-gelâ„¢ with the SLIPAâ„¢.
METHODS
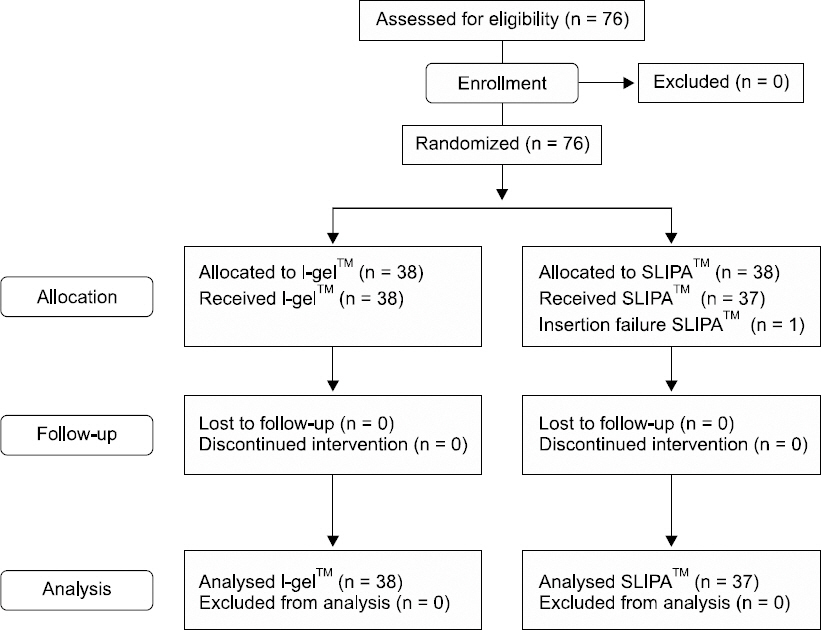
Seventy-eight adult patients were randomly assigned to undergo general anesthesia with either I-gelâ„¢ or SLIPAâ„¢. Hemodynamic changes and Oro-pharyngeal leakage pressure were assessed at one minute after the insertion. The total insertion time, number of attempts, ease of insertion, and presence of blood staining and regurgitation were recorded. After surgery, postoperative sore throat and other complications (dysphonia, dysphagia or paresthesia of tongue) were evaluated.
RESULTS
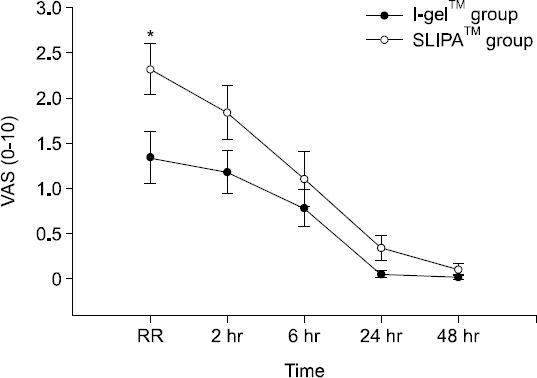
Oro-pharyngeal leakage pressure after device insertion was higher in the SLIPAâ„¢ group than the I-gelâ„¢ group. Insertion time was significantly shorter in the I-gelâ„¢ group than the SLIPAâ„¢ group. Blood staining was presented in 21.1% of the SLIPAâ„¢ group vs. 2.6% of the I-gelâ„¢ group. In the recovery room, postoperative sore throat measured in visual rating scale (VAS) was significantly higher in the SLIPAâ„¢ group than in the I-gelâ„¢ group. Ease of insertion, regurgitation, respiratory index and hemodynamic change after insertion showed no significant differences.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study, the SLIPAâ„¢ devices provided higher oro-pharyngeal leakage pressure than I-gelâ„¢. However, the results verified ease of insertion, and safety of ventilation and hemodynamic changes, without any severe complications in both I-gelâ„¢ and SLIPAâ„¢.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Luba K, Cutter TW. Supraglottic airway devices in the ambulatory setting. Anesthesiol Clin. 2010; 28:295–314. DOI: 10.1016/j.anclin.2010.02.004. PMID: 20488396.
Article2. Hernandez MR, Klock PA Jr, Ovassapian A. Evolution of the extraglottic airway: a review of its history, applications, and practical tips for success. Anesth Analg. 2012; 114:349–68. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31823b6748. PMID: 22178627.3. Lee KH, Lee JY, Park JH, Jung S, Jeon Y, Shin JJ, et al. Clinical performance comparison of I-gel insertion by anesthesiology residents versus novice clinicians. Anesth Pain Med. 2015; 10:312–6. DOI: 10.17085/apm.2015.10.4.312.
Article4. Timmermann A, Bergner UA, Russo SG. Laryngeal mask airway indications: new frontiers for second-generation supraglottic airways. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2015; 28:717–26. DOI: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000262. PMID: 26539790.5. Ramachandran SK, Kumar AM. Supraglottic airway devices. Respir Care. 2014; 59:920–31. DOI: 10.4187/respcare.02976. PMID: 24891199.
Article6. Miller DM, Light D. Laboratory and clinical comparisons of the Streamlined Liner of the Pharynx Airway (SLIPA) with the laryngeal mask airway. Anaesthesia. 2003; 58:136–42. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2044.2003.02962.x.
Article7. Keijzer C, Buitelaar DR, Efthymiou KM, Srámek M, ten Cate J, Ronday M, et al. A comparison of postoperative throat and neck complaints after the use of the i-gel and the La Premiere disposable laryngeal mask: a double-blinded, randomized, controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2009; 109:1092–5. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181b6496a. PMID: 19641052.
Article8. Park PG, Choi GJ, Kim WJ, Yang SY, Shin HY, Kang H, et al. A comparative study among normal saline, water soluble gel and 2% lidocaine gel as a SLIPA lubricant. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014; 66:105–11. DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2014.66.2.105. PMID: 24624267. PMCID: PMC3948436.
Article9. Komasawa N, Nishihara I, Tatsumi S, Minami T. Prewarming of the i-gel facilitates successful insertion and ventilation efficacy with muscle relaxation: a randomized study. J Clin Anesth. 2014; 26:663–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2014.08.009. PMID: 25468575.
Article10. Choi YM, Cha SM, Kang H, Baek CW, Jung YH, Woo YC, et al. The clinical effectiveness of the streamlined liner of pharyngeal airway (SLIPA) compared with the laryngeal mask airway ProSeal during general anesthesia. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010; 58:450–7. DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2010.58.5.450. PMID: 20532053. PMCID: PMC2881520.
Article11. Joly N, Poulin LP, Tanoubi I, Drolet P, Donati F, St-Pierre P. Randomized prospective trial comparing two supraglottic airway devices: i-gel™ and LMA-Supreme™ in paralyzed patients. Can J Anaesth. 2014; 61:794–800. DOI: 10.1007/s12630-014-0198-6. PMID: 25141831.
Article12. Woo YC, Cha SM, Kang H, Baek CW, Jung YH, Kim JY, et al. Less perilaryngeal gas leakage with SLIPA™ than with LMA-ProSeal™ in paralyzed patients. Can J Anaesth. 2011; 58:48–54. DOI: 10.1007/s12630-010-9412-3. PMID: 21042901.13. Keller C, Brimacombe JR, Keller K, Morris R. Comparison of four methods for assessing airway sealing pressure with the laryngeal mask airway in adult patients. Br J Anaesth. 1999; 82:286–7. DOI: 10.1093/bja/82.2.286. PMID: 10365012.
Article14. Lange M, Smul T, Zimmermann P, Kohlenberger R, Roewer N, Kehl F. The effectiveness and patient comfort of the novel streamlined pharynx airway liner (SLIPA) compared with the conventional laryngeal mask airway in ophthalmic surgery. Anesth Analg. 2007; 104:431–4. DOI: 10.1213/01.ane.0000252460.94046.7c. PMID: 17242104.
Article15. Park SK, Choi GJ, Choi YS, Ahn EJ, Kang H. Comparison of the i-gel and the laryngeal mask airway proseal during general anesthesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0119469. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119469. PMID: 25812135. PMCID: PMC4374933.
Article16. Weiler N, Latorre F, Eberle B, Goedecke R, Heinrichs W. Respiratory mechanics, gastric insufflation pressure, and air leakage of the laryngeal mask airway. Anesth Analg. 1997; 84:1025–8. DOI: 10.1097/00000539-199705000-00013. PMID: 9141925.
Article17. Devitt JH, Wenstone R, Noel AG, O’Donnell MP. The laryngeal mask airway and positive-pressure ventilation. Anesthesiology. 1994; 80:550–5. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199403000-00011. PMID: 8141451.
Article18. Siddiqui NT, Khan FH. Haemodynamic response to tracheal intubation via intubating laryngeal mask airway versus direct laryngoscopic tracheal intubation. J Pak Med Assoc. 2007; 57:11–4. PMID: 17319412.19. Kahl M, Eberhart LH, Behnke H, Sänger S, Schwarz U, Vogt S, et al. Stress response to tracheal intubation in patients undergoing coronary artery surgery: direct laryngoscopy versus an intubating laryngeal mask airway. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2004; 18:275–80. DOI: 10.1053/j.jvca.2004.03.005. PMID: 15232805.
Article20. Das B, Mitra S, Jamil SN, Varshney RK. Comparison of three supraglottic devices in anesthetised paralyzed children undergoing elective surgery. Saudi J Anaesth. 2012; 6:224–8. DOI: 10.4103/1658-354X.101212. PMID: 23162394. PMCID: PMC3498659.
Article21. Choi GJ, Kang H, Baek CW, Jung YH, Woo YC, Kim SH, et al. Comparison of streamlined liner of the pharynx airway (SLIPA™) and laryngeal mask airway: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anaesthesia. 2015; 70:613–22. DOI: 10.1111/anae.13035. PMID: 25693455.
Article22. Trivedi V, Batil P. A clinical comparative study of evaluation of proseal LMA v/s I-GEL for ease of insertion and hemodynamic stability;a study of 60 cases. Internet J Anesthesiol. 2011; 27:1–7.23. Rieger A, Brunne B, Hass I, Brummer G, Spies C, Striebel HW, et al. Laryngo-pharyngeal complaints following laryngeal mask airway and endotracheal intubation. J Clin Anesth. 1997; 9:42–7. DOI: 10.1016/S0952-8180(96)00209-7.
Article24. Figueredo E, Vivar-Diago M, Muñoz-Blanco F. Laryngo-pharyngeal complaints after use of the laryngeal mask airway. Can J Anaesth. 1999; 46:220–5. DOI: 10.1007/BF03012599. PMID: 10210044.
Article25. Burgard G, Möllhoff T, Prien T. The effect of laryngeal mask cuff pressure on postoperative sore throat incidence. J Clin Anesth. 1996; 8:198–201. DOI: 10.1016/0952-8180(95)00229-4.
Article26. Joe HB, Kim DH, Chae YJ, Kim JY, Kang M, Park KS. The effect of cuff pressure on postoperative sore throat after Cobra perilaryngeal airway. J Anesth. 2012; 26:225–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00540-011-1293-2. PMID: 22127511. PMCID: PMC3328671.
Article27. Ahn E, Kang H, Choi G, Yang S, Shin H, Baek C, et al. Streamlined Liner of the Pharynx Airway: Randomised comparison of size selection strategies with regard to patient height versus thyroid cartilage width. Hong Kong J Emerg Med. 2015; 22:303–11.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of the clinical effectiveness between the streamlined liner of pharyngeal airway (SLIPA) and the laryngeal mask airway by novice personnel
- The clinical effectiveness of the streamlined liner of pharyngeal airway (SLIPA(TM)) compared with the laryngeal mask airway ProSeal(TM) during general anesthesia
- Comparison of the clinical performance of airway management with the i-gel® and laryngeal mask airway Supreme™ in geriatric patients: a prospective and randomized study
- The Insertion of a Nasogastric Tube with a Nasopharyngeal Airway
- A comparison of i-gelâ„¢ and Laryngeal Mask Airway Supremeâ„¢ during general anesthesia in infants