Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Tumors: How We Do It Safely and Completely
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju 61469, Korea. kjradsss@dreamwiz.com
- 2Center for Aging and Geriatrics, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju 61469, Korea.
- 3Department of Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Surgery, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju 61469, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju 61469, Korea.
- KMID: 2344276
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.6.1226
Abstract
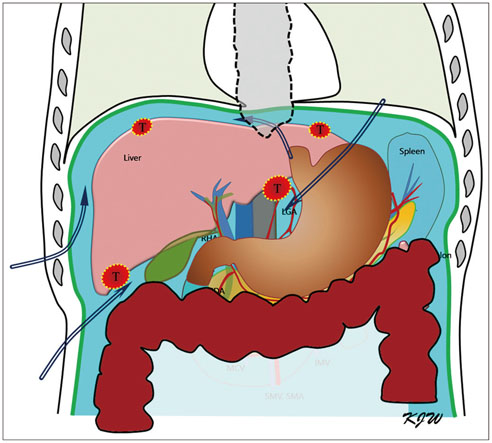
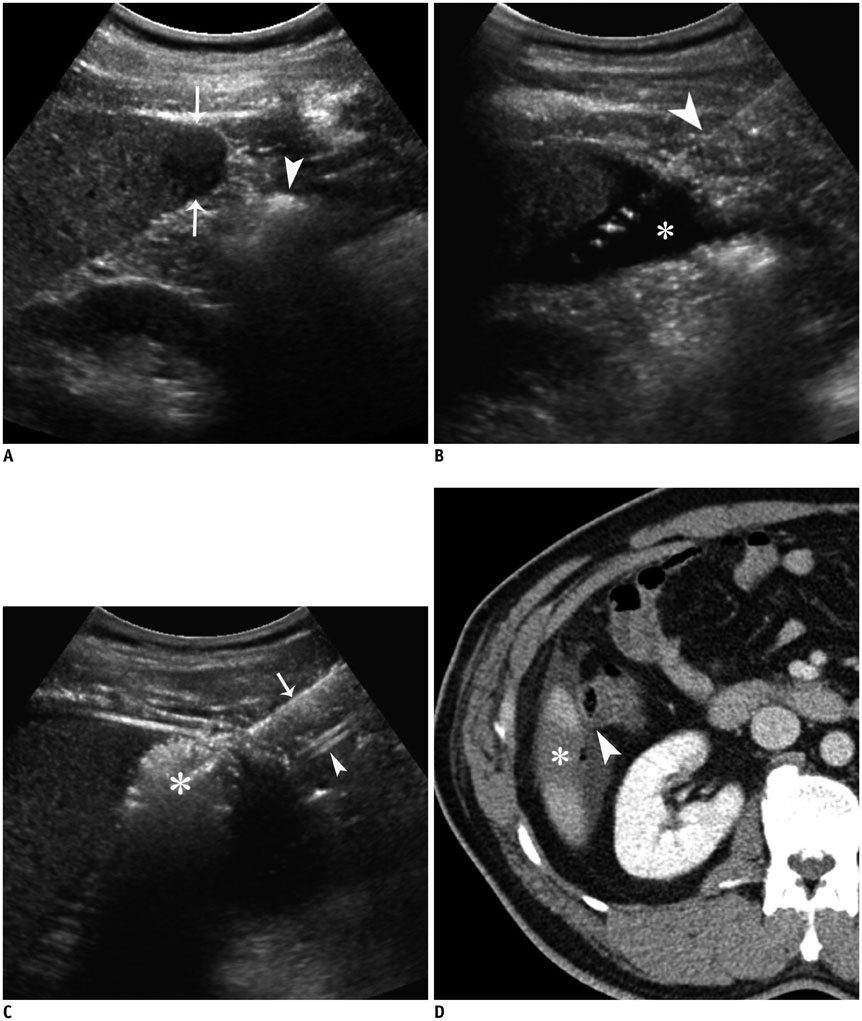
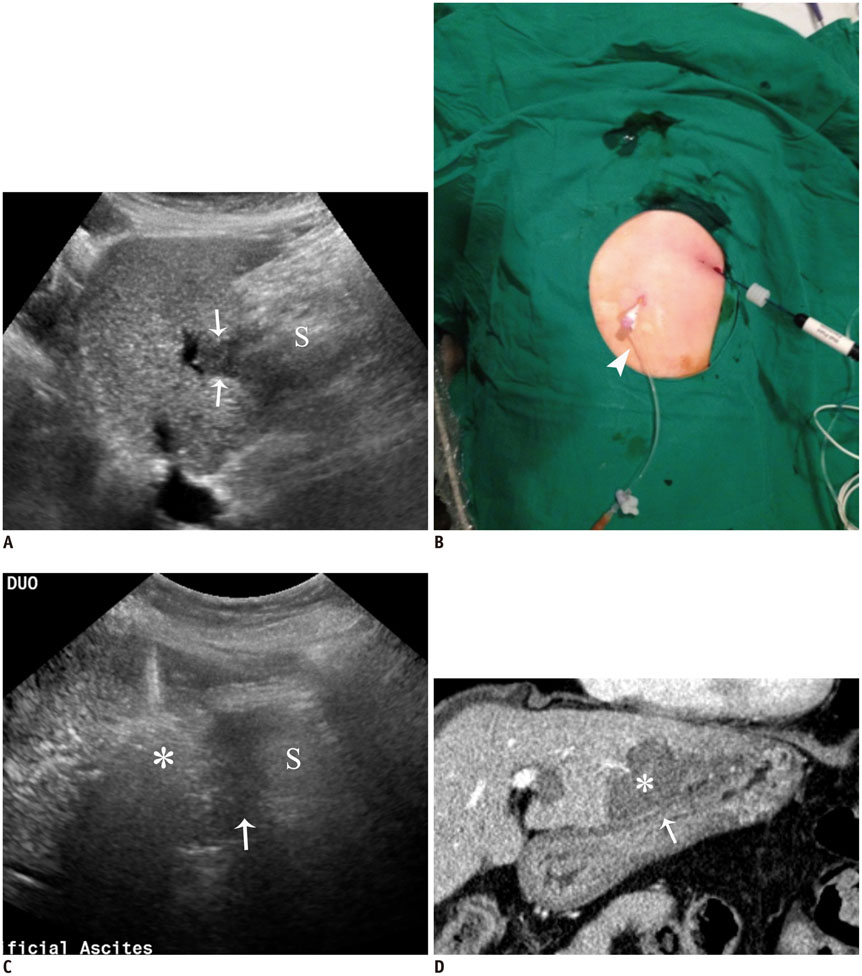
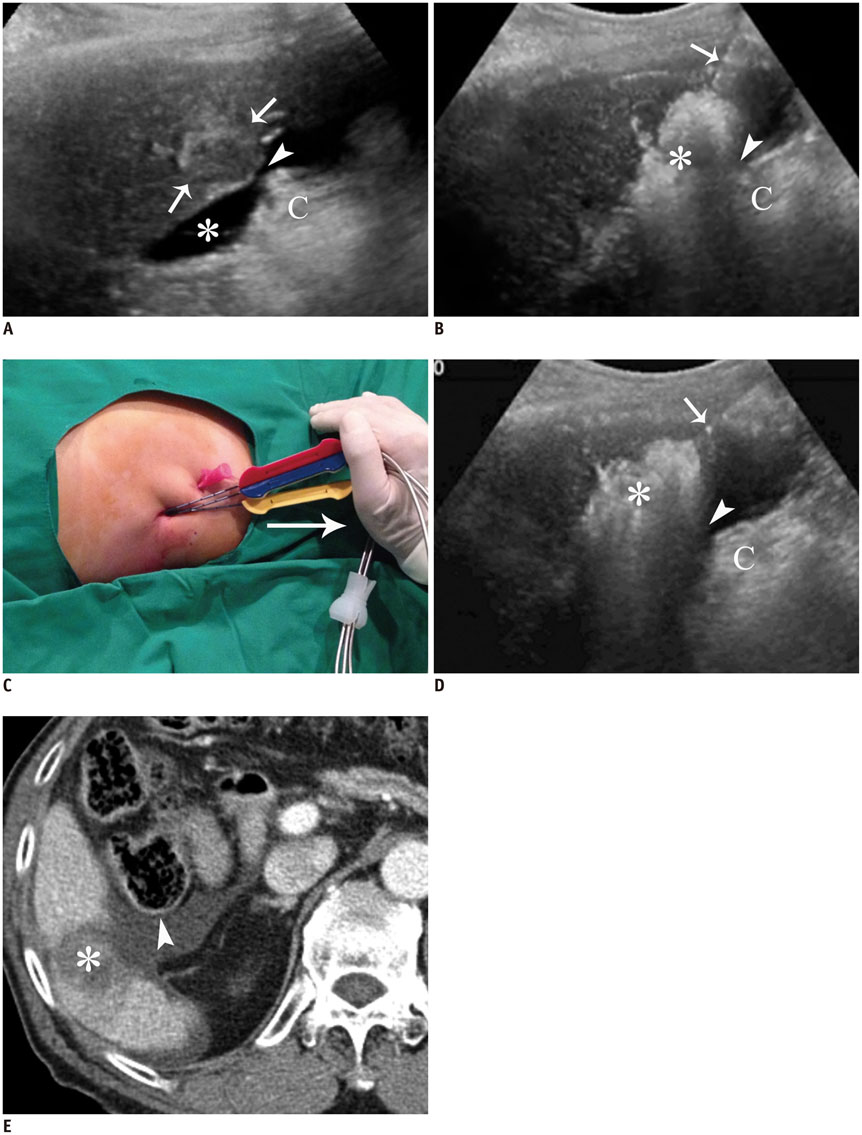
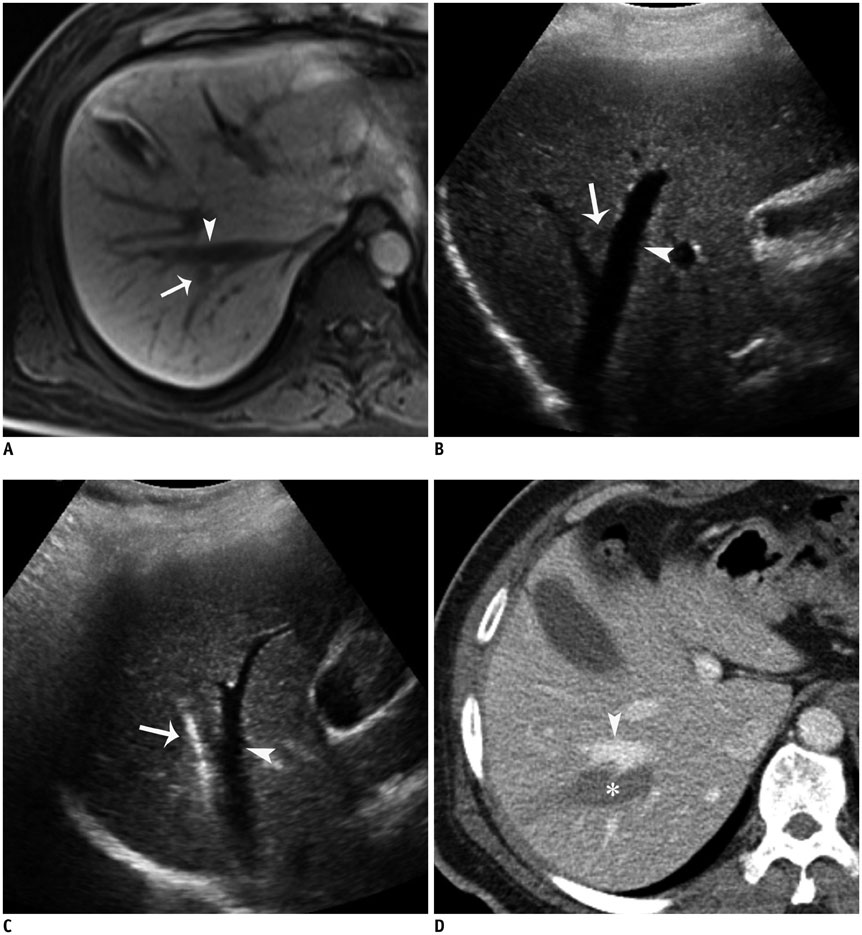
- Ultrasound-guided percutaneous radiofrequency (RF) ablation has become one of the most promising local cancer therapies for both resectable and nonresectable hepatic tumors. Although RF ablation is a safe and effective technique for the treatment of liver tumors, the outcome of treatment can be closely related to the location and shape of the tumors. There may be difficulties with RF ablation of tumors that are adjacent to large vessels or extrahepatic heat-vulnerable organs and tumors in the caudate lobe, possibly resulting in major complications or treatment failure. Thus, a number of strategies have been developed to overcome these challenges, which include artificial ascites, needle track ablation, fusion imaging guidance, parallel targeting, bypass targeting, etc. Operators need to use the right strategy in the right situation to avoid the possibility of complications and incomplete thermal tissue destruction; with the right strategy, RF ablation can be performed successfully, even for hepatic tumors in high-risk locations. This article offers technical strategies that can be used to effectively perform RF ablation as well as to minimize possible complications related to the procedure with representative cases and schematic illustrations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Percutaneous Dual-Switching Monopolar Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Separable Clustered Electrode: A Preliminary Study
Tae Won Choi, Jeong Min Lee, Dong Ho Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Su Jong Yu, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Joon Koo Han
Korean J Radiol. 2017;18(5):799-808. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2017.18.5.799.Prediction of Local Tumor Progression after Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Assessment of Ablative Margin Using Pre-RFA MRI and Post-RFA CT Registration
Jeong Hee Yoon, Jeong Min Lee, Ernst Klotz, Hyunsik Woo, Mi Hye Yu, Ijin Joo, Eun Sun Lee, Joon Koo Han
Korean J Radiol. 2018;19(6):1053-1065. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.6.1053.Usefulness of Virtual Expiratory CT Images to Compensate for Respiratory Liver Motion in Ultrasound/CT Image Fusion: A Prospective Study in Patients with Focal Hepatic Lesions
Tae Wook Kang, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ik Cha, Hyun Jung Park, Jun Sung Park, Won-Chul Bang, Seon Woo Kim
Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(2):225-235. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0320.Impact of Energy and Access Methods on Extrahepatic Tumor Spreading and the Ablation Zone: An
Ex vivo Experiment Using a Subcapsular Tumor Model
Jin Sil Kim, Youngsun Ko, Hyeyoung Kwon, Minjeong Kim, Jeong Kyong Lee
Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(4):580-588. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2018.0564.
Reference
-
1. Kim YS, Lim HK, Rhim H, Lee MW, Choi D, Lee WJ, et al. Ten-year outcomes of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation as first-line therapy of early hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis of prognostic factors. J Hepatol. 2013; 58:89–97.2. Shiina S, Tateishi R, Arano T, Uchino K, Enooku K, Nakagawa H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: 10-year outcome and prognostic factors. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:569–577. quiz 578.3. Giannini EG, Farinati F, Del Poggio P, Rapaccini GL, Di Nolfo MA, Benvegnù L, et al. Ten-year outcome of radiofrequency thermal ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: an Italian experience. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:1588–1589. author reply 1590.4. Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012; 379:1245–1255.5. Livraghi T, Meloni F, DiStasi M, Rolle E, Solbiati L, Tinelli C, et al. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology. 2008; 47:82–89.6. Thanos L, Mylona S, Galani P, Pomoni M, Pomoni A, Koskinas I. Overcoming the heat-sink phenomenon: successful radiofrequency thermal ablation of liver tumors in contact with blood vessels. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2008; 14:51–56.7. Rhim H, Yoon KH, Lee JM, Cho Y, Cho JS, Kim SH, et al. Major complications after radio-frequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: spectrum of imaging findings. Radiographics. 2003; 23:123–134. discussion 134-136.8. Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni MF, Gazelle GS, Halpern EF, Goldberg SN. Treatment of focal liver tumors with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: complications encountered in a multicenter study. Radiology. 2003; 226:441–451.9. Mendiratta-Lala M, Brook OR, Midkiff BD, Brennan DD, Thornton E, Faintuch S, et al. Quality initiatives: strategies for anticipating and reducing complications and treatment failures in hepatic radiofrequency ablation. Radiographics. 2010; 30:1107–1122.10. Shibata T, Isoda H, Hirokawa Y, Arizono S, Shimada K, Togashi K. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: is radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization more effective than radiofrequency ablation alone for treatment? Radiology. 2009; 252:905–913.11. Kitamoto M, Nakanishi T, Kira S, Kawaguchi M, Nakashio R, Suemori S, et al. The assessment of proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunohistochemical staining in small hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship to histologic characteristics and prognosis. Cancer. 1993; 72:1859–1865.12. Kim JW, Shin SS, Kim JK, Choi SK, Heo SH, Lim HS, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of single hepatocellular carcinoma of 2 to 5 cm in diameter: comparison with surgical resection. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:626–635.13. Goldberg SN, Bonn J, Dodd G, Dupuy D, Geschwind JH, Hicks M, et al. Society of Interventional Radiology Interventional Oncology Task Force: interventional oncology research vision statement and critical assessment of the state of research affairs. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005; 16:1287–1294.14. Kim YS, Lee WJ, Rhim H, Lim HK, Choi D, Lee JY. The minimal ablative margin of radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma (> 2 and < 5 cm) needed to prevent local tumor progression: 3D quantitative assessment using CT image fusion. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:758–765.15. Nakazawa T, Kokubu S, Shibuya A, Ono K, Watanabe M, Hidaka H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation between local tumor progression after ablation and ablative margin. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:480–488.16. Song I, Rhim H, Lim HK, Kim YS, Choi D. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm and gastrointestinal tracts with the use of artificial ascites: safety and technical efficacy in 143 patients. Eur Radiol. 2009; 19:2630–2640.17. Rhim H, Lim HK, Kim YS, Choi D. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with artificial ascites for hepatocellular carcinoma in the hepatic dome: initial experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:91–98.18. Kang TW, Lee MW, Hye MJ, Song KD, Lim S, Rhim H, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumours: factors affecting technical failure of artificial ascites formation using an angiosheath. Clin Radiol. 2014; 69:1249–1258.19. Koda M, Ueki M, Maeda Y, Mimura K, Okamoto K, Matsunaga Y, et al. Percutaneous sonographically guided radiofrequency ablation with artificial pleural effusion for hepatocellular carcinoma located under the diaphragm. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183:583–588.20. Minami Y, Kudo M, Kawasaki T, Chung H, Ogawa C, Inoue T, et al. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation with artificial pleural effusion for hepatocellular carcinoma in the hepatic dome. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:1066–1070.21. Kim YJ, Lee MW, Park HS. Small hepatocellular carcinomas: ultrasonography guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Abdom Imaging. 2013; 38:98–111.22. Teratani T, Yoshida H, Shiina S, Obi S, Sato S, Tateishi R, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in so-called high-risk locations. Hepatology. 2006; 43:1101–1108.23. Kwon HJ, Kim PN, Byun JH, Kim KW, Won HJ, Shin YM, et al. Various complications of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatic tumors: radiologic findings and technical tips. Acta Radiol. 2014; 55:1082–1092.24. Akahane M, Koga H, Kato N, Yamada H, Uozumi K, Tateishi R, et al. Complications of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepato-cellular carcinoma: imaging spectrum and management. Radiographics. 2005; 25:Suppl 1. S57–S68.25. McGhana JP, Dodd GD 3rd. Radiofrequency ablation of the liver: current status. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001; 176:3–16.26. Liu N, Gao J, Liu Y, Li T, Feng K, Ma K, et al. Determining a minimal safe distance to prevent thermal injury to intrahepatic bile ducts in radiofrequency ablation of the liver: a study in dogs. Int J Hyperthermia. 2012; 28:210–217.27. Ogawa T, Kawamoto H, Kobayashi Y, Nakamura S, Miyatake H, Harada R, et al. Prevention of biliary complication in radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma-Cooling effect by endoscopic nasobiliary drainage tube. Eur J Radiol. 2010; 73:385–390.28. Kong WT, Zhang WW, Qiu YD, Zhou T, Qiu JL, Zhang W, et al. Major complications after radiofrequency ablation for liver tumors: analysis of 255 patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:2651–2656.29. Jaskolka JD, Asch MR, Kachura JR, Ho CS, Ossip M, Wong F, et al. Needle tract seeding after radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005; 16:485–491.30. Livraghi T, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Solbiati L. Risk of tumour seeding after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg. 2005; 92:856–858.31. Llovet JM, Vilana R, Brú C, Bianchi L, Salmeron JM, Boix L, et al. Increased risk of tumor seeding after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for single hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2001; 33:1124–1129.32. Rhim H, Goldberg SN, Dodd GD 3rd, Solbiati L, Lim HK, Tonolini M, et al. Essential techniques for successful radiofrequency thermal ablation of malignant hepatic tumors. Radiographics. 2001; 21 Spec No:S17–S35. discussion S36-S39.33. Seror O, Haddar D, N'Kontchou G, Ajavon Y, Trinchet JC, Beaugrand M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver tumors in the caudate lobe. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2005; 16:981–990.34. Lu DS, Raman SS, Limanond P, Aziz D, Economou J, Busuttil R, et al. Influence of large peritumoral vessels on outcome of radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14:1267–1274.35. Cha DI, Lee MW, Rhim H, Choi D, Kim YS, Lim HK. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of percutaneous ethanol injection with or without combined radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinomas in high risk locations. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:240–247.36. Lee MW, Rhim H, Cha DI, Kim YJ, Choi D, Kim YS, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: fusion imaging guidance for management of lesions with poor conspicuity at conventional sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 198:1438–1444.37. Kunishi Y, Numata K, Morimoto M, Okada M, Kaneko T, Maeda S, et al. Efficacy of fusion imaging combining sonography and hepatobiliary phase MRI with Gd-EOB-DTPA to detect small hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 198:106–114.38. Rajesh S, Mukund A, Arora A, Jain D, Sarin SK. Contrast-enhanced US-guided radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013; 24:1235–1240.39. Kim AY, Lee MW, Rhim H, Cha DI, Choi D, Kim YS, et al. Pretreatment evaluation with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas with poor conspicuity on conventional ultrasonography. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:754–763.40. Lu DS, Yu NC, Raman SS, Limanond P, Lassman C, Murray K, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: treatment success as defined by histologic examination of the explanted liver. Radiology. 2005; 234:954–960.41. Kang TW, Lim HK, Lee MW, Kim YS, Choi D, Rhim H. Perivascular versus nonperivascular small HCC treated with percutaneous RF ablation: retrospective comparison of long-term therapeutic outcomes. Radiology. 2014; 270:888–899.42. Kim JH, Won HJ, Shin YM, Kim SH, Yoon HK, Sung KB, et al. Medium-sized (3.1-5.0 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma: transarterial chemoembolization plus radiofrequency ablation versus radiofrequency ablation alone. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011; 18:1624–1629.43. Yoon JH, Lee JM, Hwang EJ, Hwang IP, Baek J, Han JK, et al. Monopolar radiofrequency ablation using a dual-switching system and a separable clustered electrode: evaluation of the in vivo efficiency. Korean J Radiol. 2014; 15:235–244.44. Yoon JH, Lee JM, Han JK, Choi BI. Dual switching monopolar radiofrequency ablation using a separable clustered electrode: comparison with consecutive and switching monopolar modes in ex vivo bovine livers. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:403–411.45. Lee ES, Lee JM, Kim KW, Lee IJ, Han JK, Choi BI. Evaluation of the in vivo efficiency and safety of hepatic radiofrequency ablation using a 15-G Octopus® in pig liver. Korean J Radiol. 2013; 14:194–201.46. Woo S, Lee JM, Yoon JH, Joo I, Kim SH, Lee JY, et al. Small- and medium-sized hepatocellular carcinomas: monopolar radiofrequency ablation with a multiple-electrode switching system-mid-term results. Radiology. 2013; 268:589–600.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recent developments in endoscopic ultrasound-guided ablation treatment
- Completely Ablated Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Percutaneous Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided ablation of pancreatic cystic lesions
- Ultrasound (US)-Guided Ablation of Thyroid Nodules
- Small Bowel Perforation after Percutaneous Ultrasound-guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma