J Korean Fract Soc.
2016 Jul;29(3):221-231. 10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.221.
Surgical Treatment for Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. ossoj@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2344096
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.221
Abstract
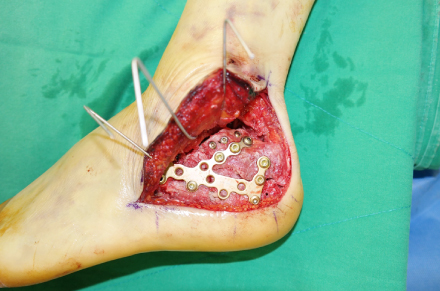
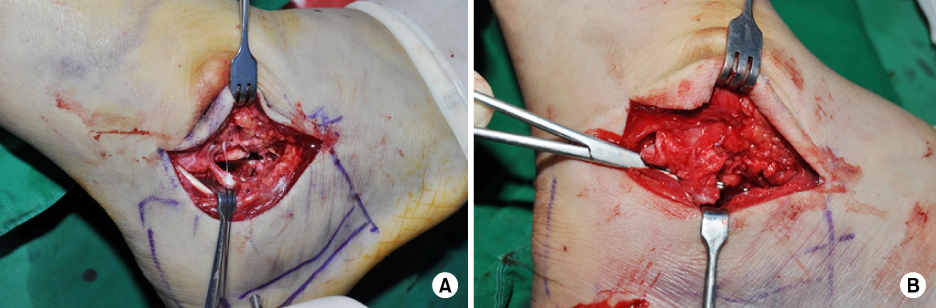
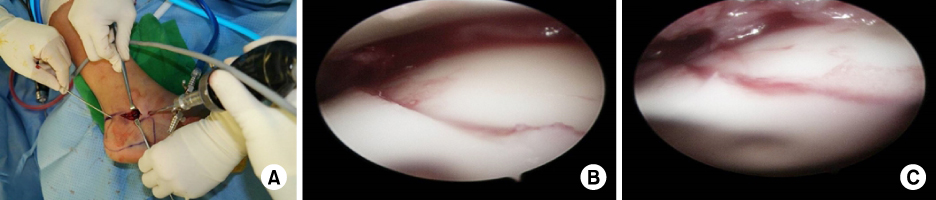
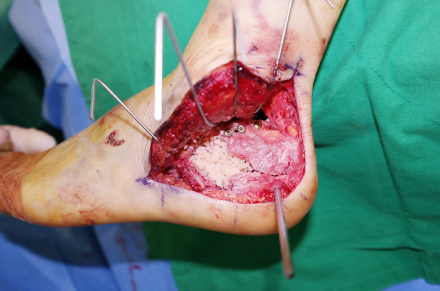
- Calcaneal fractures are the most common type of tarsal fracture, and comminuted and bursting fractures are common due to the anatomic characteristics of the calcaneus. Assessment and treatment of calcaneal fractures has improved significantly over time. Despite advancements in surgical techniques and equipment, these fractures remain difficult to treat. In this review article, the physiopathology, classification, and surgical treatments of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures are updated.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hollawell S. Wound closure technique for lateral extensile approach to intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2008; 98:422–425.
Article2. Sanders R, Vaupel ZM, Erdogan M, Downes K. Operative treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures: long-term (10-20 years) results in 108 fractures using a prognostic CT classification. J Orthop Trauma. 2014; 28:551–563.3. Agren PH, Mukka S, Tullberg T, Wretenberg P, Sayed-Noor AS. Factors affecting long-term treatment results of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures: a post hoc analysis of a prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2014; 28:564–568.4. Makki D, Alnajjar HM, Walkay S, Ramkumar U, Watson AJ, Allen PW. Osteosynthesis of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum: a long-term review of 47 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010; 92:693–700.5. Kurozumi T, Jinno Y, Sato T, Inoue H, Aitani T, Okuda K. Open reduction for intra-articular calcaneal fractures: evaluation using computed tomography. Foot Ankle Int. 2003; 24:942–948.
Article6. Gavlik JM, Rammelt S, Zwipp H. The use of subtalar arthroscopy in open reduction and internal fixation of intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Injury. 2002; 33:63–71.
Article7. Essex-Lopresti P. The mechanism, reduction technique, and results in fractures of the OS calcis. Br J Surg. 1952; 39:395–419.
Article8. Carr JB, Hamilton JJ, Bear LS. Experimental intra-articular calcaneal fractures: anatomic basis for a new classification. Foot Ankle. 1989; 10:81–87.
Article9. Carr JB. Mechanism and pathoanatomy of the intra-articular calcaneal fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (290):36–40.
Article10. Burdeaux BD. Reduction of calcaneal fractures by the McReynolds medial approach technique and its experimental basis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; (177):87–103.
Article11. Maskill JD, Bohay DR, Anderson JG. Calcaneus fractures: a review article. Foot Ankle Clin. 2005; 10:463–489.
Article12. Dhillon MS, Bali K, Prabhakar S. Controversies in calcaneus fracture management: a systematic review of the literature. Musculoskelet Surg. 2011; 95:171–181.
Article13. Soeur R, Remy R. Fractures of the calcaneus with displacement of the thalamic portion. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1975; 57:413–421.
Article14. Zwipp H, Tscherne H, Wülker N, Grote R. Intra-articular fracture of the calcaneus. Classification, assessment and surgical procedures. Unfallchirurg. 1989; 92:117–129.15. Sanders R, Fortin P, DiPasquale T, Walling A. Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (290):87–95.16. Wiley JJ, Profitt A. Fractures of the os calcis in children. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984; (188):131–138.
Article17. Schantz K, Rasmussen F. Good prognosis after calcaneal fracture in childhood. Acta Orthop Scand. 1988; 59:560–563.
Article18. Buckingham R, Jackson M, Atkins R. Calcaneal fractures in adolescents. CT classification and results of operative treatment. Injury. 2003; 34:454–459.19. Pickle A, Benaroch TE, Guy P, Harvey EJ. Clinical outcome of pediatric calcaneal fractures treated with open reduction and internal fixation. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004; 24:178–180.
Article20. Petit CJ, Lee BM, Kasser JR, Kocher MS. Operative treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures in the pediatric population. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007; 27:856–862.
Article21. Lindsay WR, Dewar FP. Fractures of the os calcis. Am J Surg. 1958; 95:555–576.
Article22. Paley D, Hall H. Intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A critical analysis of results and prognostic factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993; 75:342–354.
Article23. Buckley R, Tough S, McCormack R, et al. Operative compared with nonoperative treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84:1733–1744.
Article24. Herscovici D Jr, Widmaier J, Scaduto JM, Sanders RW, Walling A. Operative treatment of calcaneal fractures in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:1260–1264.
Article25. Basile A. Operative versus nonoperative treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures in elderly patients. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2010; 49:25–32.
Article26. Loder RT. The influence of diabetes mellitus on the healing of closed fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (232):210–216.
Article27. Folk JW, Starr AJ, Early JS. Early wound complications of operative treatment of calcaneus fractures: analysis of 190 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1999; 13:369–372.
Article28. Tennent TD, Calder PR, Salisbury RD, Allen PW, Eastwood DM. The operative management of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum: a two-centre study using a defined protocol. Injury. 2001; 32:491–496.
Article29. Rammelt S, Barthel S, Biewener A, Gavlik JM, Zwipp H. Calcaneus fractures. Open reduction and internal fixation. Zentralbl Chir. 2003; 128:517–528.30. Potenza V, Caterini R, Farsetti P, Bisicchia S, Ippolito E. Primary subtalar arthrodesis for the treatment of comminuted intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Injury. 2010; 41:702–706.
Article31. Hüfner T, Geerling J, Gerich T, Zeichen J, Richter M, Krettek C. Open reduction and internal fixation by primary subtalar arthrodesis for intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2007; 19:155–169.
Article32. Huefner T, Thermann H, Geerling J, Pape HC, Pohlemann T. Primary subtalar arthrodesis of calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2001; 22:9–14.
Article33. Rammelt S, Amlang M, Barthel S, Gavlik JM, Zwipp H. Percutaneous treatment of less severe intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468:983–990.
Article34. Palmer I. The mechanism and treatment of fractures of the calcaneus; open reduction with the use of cancellous grafts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1948; 30:2–8.35. Letournel E. Open treatment of acute calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (290):60–67.
Article36. Benirschke SK, Sangeorzan BJ. Extensive intraarticular fractures of the foot. Surgical management of calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (292):128–134.37. Bèzes H, Massart P, Delvaux D, Fourquet JP, Tazi F. The operative treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Indications, technique, and results in 257 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (290):55–59.38. Buckley RE, Meek RN. Comparison of open versus closed reduction of intraarticular calcaneal fractures: a matched cohort in workmen. J Orthop Trauma. 1992; 6:216–222.
Article39. Crosby LA, Fitzgibbons T. Computerized tomography scanning of acute intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A new classification system. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990; 72:852–859.
Article40. Crosby LA, Fitzgibbons TC. Open reduction and internal fixation of type II intra-articular calcaneus fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 1996; 17:253–258.
Article41. Leung KS, Yuen KM, Chan WS. Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum. Mediumterm results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993; 75:196–201.
Article42. Sanders R. Displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 82:225–250.
Article43. Thordarson DB, Latteier M. Open reduction and internal fixation of calcaneal fractures with a low profile titanium calcaneal perimeter plate. Foot Ankle Int. 2003; 24:217–221.
Article44. Zwipp H, Tscherne H, Thermann H, Weber T. Osteosynthesis of displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus Results in 123 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (290):76–86.45. Harvey EJ, Grujic L, Early JS, Benirschke SK, Sangeorzan BJ. Morbidity associated with ORIF of intra-articular calcaneus fractures using a lateral approach. Foot Ankle Int. 2001; 22:868–873.
Article46. Rammelt S, Zwipp H. Calcaneus fractures: facts, controversies and recent developments. Injury. 2004; 35:443–461.
Article47. Borrelli J Jr, Lashgari C. Vascularity of the lateral calcaneal flap: a cadaveric injection study. J Orthop Trauma. 1999; 13:73–77.
Article48. Femino JE, Vaseenon T, Levin DA, Yian EH. Modification of the sinus tarsi approach for open reduction and plate fixation of intra-articular calcaneus fractures: the limits of proximal extension based upon the vascular anatomy of the lateral calcaneal artery. Iowa Orthop J. 2010; 30:161–167.49. Laughlin RT, Carson JG, Calhoun JH. Displaced intra-articular calcaneus fractures treated with the Galveston plate. Foot Ankle Int. 1996; 17:71–78.
Article50. Ebraheim NA, Elgafy H, Sabry FF, Freih M, Abou-Chakra IS. Sinus tarsi approach with trans-articular fixation for displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. Foot Ankle Int. 2000; 21:105–113.
Article51. Geel CW, Flemister AS Jr. Standardized treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures using an oblique lateral incision and no bone graft. J Trauma. 2001; 50:1083–1089.
Article52. Gupta A, Ghalambor N, Nihal A, Trepman E. The modified Palmer lateral approach for calcaneal fractures: wound healing and postoperative computed tomographic evaluation of fracture reduction. Foot Ankle Int. 2003; 24:744–753.
Article53. Hospodar P, Guzman C, Johnson P, Uhl R. Treatment of displaced calcaneus fractures using a minimally invasive sinus tarsi approach. Orthopedics. 2008; 31:1112.54. Kikuchi C, Charlton TP, Thordarson DB. Limited sinus tarsi approach for intra-articular calcaneus fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 34:1689–1694.
Article55. Kline AJ, Anderson RB, Davis WH, Jones CP, Cohen BE. Minimally invasive technique versus an extensile lateral approach for intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2013; 34:773–780.
Article56. Mostafa MF, El-Adl G, Hassanin EY, Abdellatif MS. Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2010; 5:87–95.
Article57. Nosewicz T, Knupp M, Barg A, et al. Mini-open sinus tarsi approach with percutaneous screw fixation of displaced calcaneal fractures: a prospective computed tomography-based study. Foot Ankle Int. 2012; 33:925–933.
Article58. Schepers T. The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review. Int Orthop. 2011; 35:697–703.
Article59. Weber M, Lehmann O, Sägesser D, Krause F. Limited open reduction and internal fixation of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008; 90:1608–1616.
Article60. Sato T, Shiota N, Tetsunaga T, Kim BS. The sinus tarsi approach for the treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2013; 17:257–263.61. Palmersheim K, Hines B, Olsen BL. Calcaneal fractures: update on current treatments. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2012; 29:205–220.
Article62. Yeo JH, Cho HJ, Lee KB. Comparison of two surgical approaches for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: sinus tarsi versus extensile lateral approach. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16:63.
Article63. Nelson JD, McIff TE, Moodie PG, Iverson JL, Horton GA. Biomechanical stability of intramedullary technique for fixation of joint depressed calcaneus fracture. Foot Ankle Int. 2010; 31:229–235.
Article64. Zwipp H, Paša L, Žilka L, Amlang M, Rammelt S, Pompach M. Introduction of a new locking nail for treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2016; 30:e88–e92.
Article65. Park IH, Song KW, Shin SI, Lee JY, Kim TG, Park RS. Displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture treated surgically with limited posterior incision. Foot Ankle Int. 2000; 21:195–205.
Article66. Della Rocca GJ, Nork SE, Barei DP, Taitsman LA, Benirschke SK. Fractures of the sustentaculum tali: injury characteristics and surgical technique for reduction. Foot Ankle Int. 2009; 30:1037–1041.
Article67. Guerado E, Bertrand ML, Cano JR. Management of calcaneal fractures: what have we learnt over the years? Injury. 2012; 43:1640–1650.68. Carr JB. Surgical treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a review of small incision approaches. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:109–117.69. Johnson EE, Gebhardt JS. Surgical management of calcaneal fractures using bilateral incisions and minimal internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (290):117–124.
Article70. Stephenson JR. Surgical treatment of displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus. A combined lateraland medial approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (290):68–75.71. Kissel CG, Husain ZS, Cottom JM, Scott RT, Vest J. Early clinical and radiographic outcomes after treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures using delta-frame external fixator construct. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011; 50:135–140.
Article72. Talarico LM, Vito GR, Zyryanov SY. Management of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures by using external ring fixation, minimally invasive open reduction, and early weightbearing. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2004; 43:43–50.
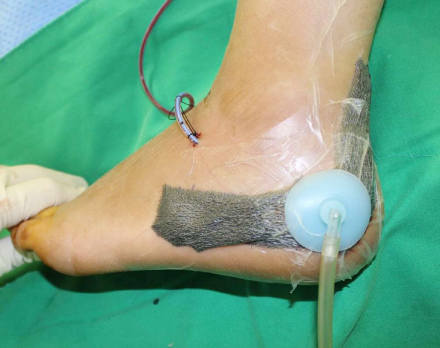
Article73. Gupta AK, Gluck GS, Parekh SG. Balloon reduction of displaced calcaneus fractures: surgical technique and case series. Foot Ankle Int. 2011; 32:205–210.
Article74. Rammelt S, Gavlik JM, Barthel S, Zwipp H. The value of subtalar arthroscopy in the management of intra-articular calcaneus fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2002; 23:906–916.
Article75. Schuberth JM, Cobb MD, Talarico RH. Minimally invasive arthroscopic-assisted reduction with percutaneous fixation in the management of intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a review of 24 cases. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2009; 48:315–322.
Article76. Atesok K, Finkelstein J, Khoury A, et al. The use of intraoperative three-dimensional imaging (ISO-C-3D) in fixation of intraarticular fractures. Injury. 2007; 38:1163–1169.
Article77. Kendoff D, Citak M, Gardner M, et al. Three-dimensional fluoroscopy for evaluation of articular reduction and screw placement in calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28:1165–1171.
Article78. Richter M, Geerling J, Zech S, Goesling T, Krettek C. Intraoperative three-dimensional imaging with a motorized mobile C-arm (SIREMOBIL ISO-C-3D) in foot and ankle trauma care: a preliminary report. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:259–266.
Article79. Rübberdt A, Hofbauer VR, Herbort M, Löhrer L, Ochman S, Raschke MJ. 3D navigated osteosynthesis of calcaneal fractures. Open and minimally invasive techniques. Unfallchirurg. 2009; 112:15–22.80. Longino D, Buckley RE. Bone graft in the operative treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures: is it helpful? J Orthop Trauma. 2001; 15:280–286.
Article81. Sohn HM, Ha SH, Lee JY, Jo SH, Yang H. Intra-articular calcaneal fractures treated with open reduction and internal fixation: a comparative study between groups with and without bone graft. J Korean Fract Soc. 2010; 23:180–186.
Article82. Nie WZ, Sun L, Yang MQ, Tan YC, Zhu HF. Comparison between mini-traumatic bone-grafting and non-bonegrafting in percutaneous K-wire fixation to treat the calcaneal fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009; 22:1–3.83. DeCarbo WT, Hyer CF. Negative-pressure wound therapy applied to high-risk surgical incisions. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2010; 49:299–300.
Article84. Stannard JP, Robinson JT, Anderson ER, McGwin G Jr, Volgas DA, Alonso JE. Negative pressure wound therapy to treat hematomas and surgical incisions following high-energy trauma. J Trauma. 2006; 60:1301–1306.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Management of Displaced Intra-articular Calcaneal Fracture
- Surgical Treatment of Displaced Intra-articular Calcaneal Fractures: Minimum of 2-year Follow-up
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation with AO Calcaneal Plate for Displaced Intra-articular Calcaneal Fracture
- The Significance of Calcaneal Posterior Tuberosity Fragment Reduction When Treated with Open Reduction in Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
- The Comparison of Radiographic Parameters and Clinical Results after Operative Treatment of Displaced Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures