J Korean Fract Soc.
2016 Jul;29(3):178-184. 10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.178.
Orthogonal Locking Compression Plate Fixation for Distal Humeral Intraarticular Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. osd11@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2344090
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.178
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To investigate the surgical outcomes of orthogonal locking compression plate fixation for distal humeral intraarticular fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
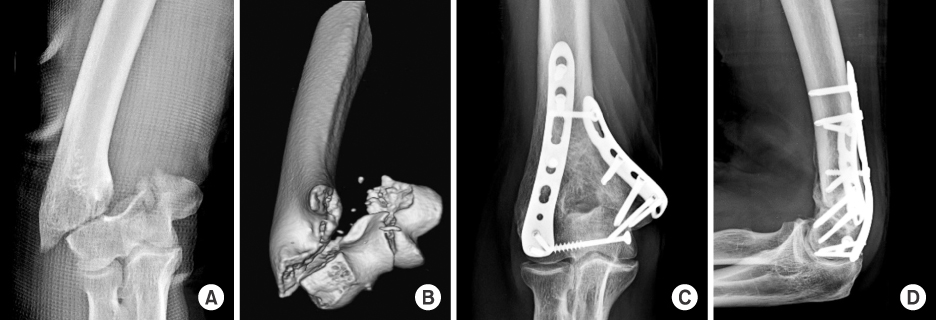
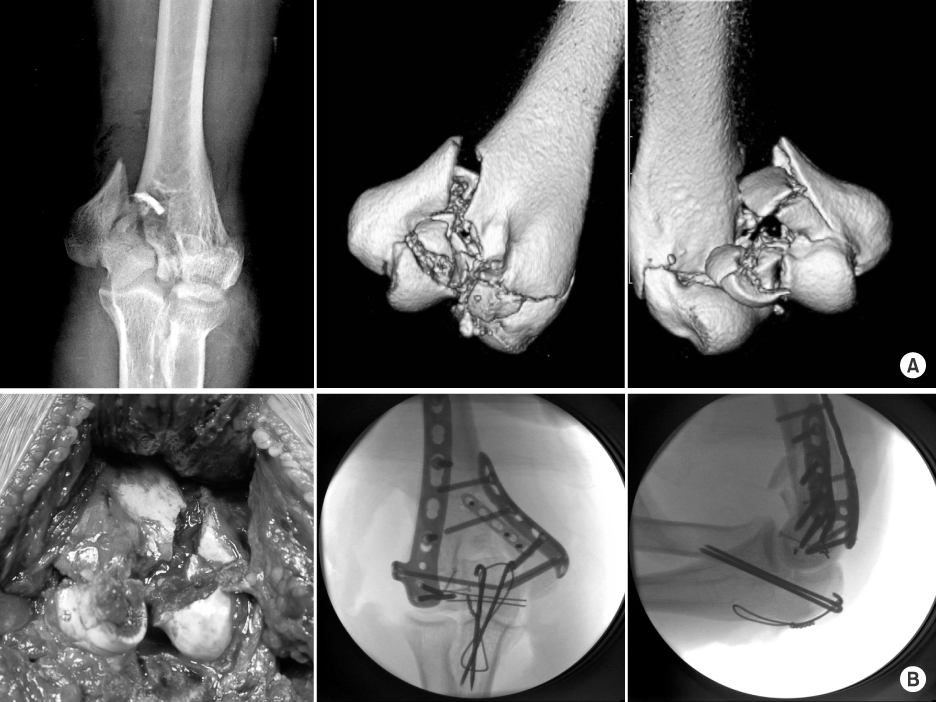
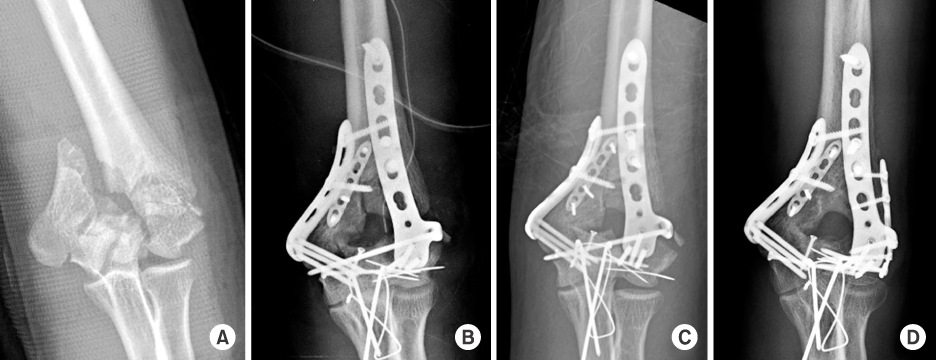
This study included 18 patients presenting a distal humeral intraarticular fracture who were treated with orthogonal locking compression plate fixation. According to the AO/OTA classification, there were eight C2 and ten C3 fractures. We evaluated radiologic outcomes, clinical results with range of motion, operation-related complications, and functional score by Mayo elbow performance score (MEPS).
RESULTS
The a verage u nion t ime was 3.5 months, and there was no c ase of r eduction l oss of a rticular f racture at t he last follow-up. Additional surgical procedures were needed in the three cases of C3 fractures. There was one case of heterotrophic ossification and one case of K-wire irritation. The average range of motion of elbow joint was 7° to 122°, and functional results were graded as 14 excellent, three good, and one fair by MEPS.
CONCLUSION
Anatomical reduction and internal fixation with orthogonal locking compression plate could provide satisfactory surgical outcomes for the treatment of distal humeral intraarticular fracture.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Galano GJ, Ahmad CS, Levine WN. Current treatment strategies for bicolumnar distal humerus fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010; 18:20–30.
Article2. Bégué T. Articular fractures of the distal humerus. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014; 100:S55–S63.
Article3. Davies MB, Stanley D. A clinically applicable fracture classification for distal humeral fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006; 15:602–608.
Article4. O'Driscoll SW. Supracondylar fractures of the elbow: open reduction, internal fixation. Hand Clin. 2004; 20:465–474.5. O'Driscoll SW. Optimizing stability in distal humeral fracture fixation. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005; 14:186S–194S.6. Korner J, Diederichs G, Arzdorf M, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of methods of distal humerus fracture fixation using locking compression plates versus conventional reconstruction plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:286–293.
Article7. Wilkinson JM, Stanley D. Posterior surgical approaches to the elbow: a comparative anatomic study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2001; 10:380–382.
Article8. Bucholz RW, Hackman JD, Court-Brown C. Rockwood and green's fractures in Adults. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2006. p. 1059–1064.9. Kaiser T, Brunner A, Hohendorff B, Ulmar B, Babst R. Treatment of supra- and intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus with the LCP Distal Humerus Plate: a 2-year follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20:206–212.
Article10. Charissoux JL, Mabit C, Fourastier J, et al. Comminuted intra-articular fractures of the distal humerus in elderly patients. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 2008; 94:S36–S62.11. Pajarinen J, Björkenheim JM. Operative treatment of type C intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus: results after a mean follow-up of 2 years in a series of 18 patients. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002; 11:48–52.
Article12. Hoppenfeld S, deBoer P, Buckley R. Surgical exposures in orthopedics. The anatomic approach. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Ed;2009.13. Imatani J, Morito Y, Hashizume H, Inoue H. Internal fixation for coronal shear fracture of the distal end of the humerus by the anterolateral approach. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2001; 10:554–556.
Article14. Faber KJ. Coronal shear fractures of the distal humerus: the capitellum and trochlea. Hand Clin. 2004; 20:455–464.
Article15. Sen MK, Sama N, Helfet DL. Open reduction and internal fixation of coronal fractures of the capitellum. J Hand Surg Am. 2007; 32:1462–1465.
Article16. Vennettilli M, Athwal GS. Parallel versus orthogonal plating for distal humerus fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2012; 37:819–820.
Article17. Ruan HJ, Liu JJ, Fan CY, Jiang J, Zeng BF. Incidence, management, and prognosis of early ulnar nerve dysfunction in type C fractures of distal humerus. J Trauma. 2009; 67:1397–1401.
Article18. Chen RC, Harris DJ, Leduc S, Borrelli JJ Jr, Tornetta P 3rd, Ricci WM. Is ulnar nerve transposition beneficial during open reduction internal fixation of distal humerus fractures? J Orthop Trauma. 2010; 24:391–394.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Failure of Distal Locking Screws in an Intraarticular Distal Radius Fracture Treated with Volar Locking Plate Fixation
- Orthogonal versus Parallel Plating for Distal Humeral Fractures
- Ulnar Nerve Injury Caused by the Incomplete Insertion of a Screw Head after Internal Fixation with Dual Locking Plates in AO/OTA Type C2 Distal Humerus Fractures
- Comparison of Radiologic and Clinical Results between Locking Compression Plate and Unlocked Plate in Proximal Humerus Fractures
- Treatment of Femur Supracondylar Fracture with Locking Compression Plate