J Korean Fract Soc.
2016 Jul;29(3):171-177. 10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.171.
Radiologic Assessment of Postoperative Stability in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture Using Lateral Radiograph
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Wonkwang University School of Medicine, Iksan, Korea. osksh@wonkwang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St. Carollo Hospital, Suncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2344089
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.3.171
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to compare the sliding distance of lag screw in patients with unstable femoral intertrochanteric fractures treated with intramedullary fixation using a cephalomedullary nail with a fixed angle between the neck and shaft of the femur in relation to reduction type by lateral radiographs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
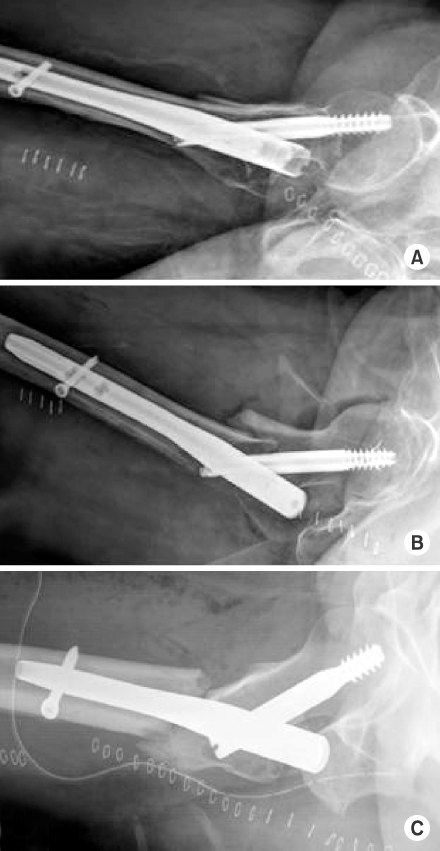
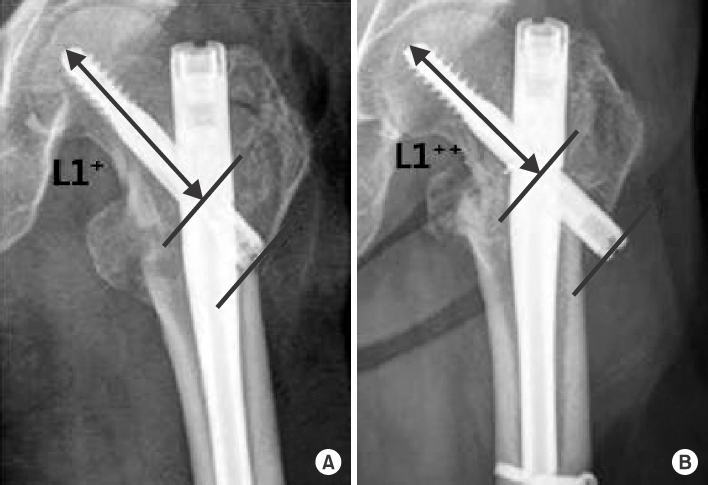
Between January 2009 to October 2013, 86 cases (86 patients) with unstable femoral intertrochanteric fractures were treated with intramedullary fixation using a metal nail with a fixed neck-shaft angle and followed for at least 6 months. We used AO/OTA classification, and all cases were unstable fractures. Twenty cases were 31-A22, 54 cases were 31-A23, and 12 cases were 31-A3. There were 30 men and 56 women. Average patient age was 73.7 years (range, 47-97 years). We classified reduction types into three groups as postoperative lateral radiologic findings. Group 1 showed no displacement, group 2 showed anterior displacement of the femur neck, and group 3 showed posterior displacement of the femur neck. The radiological assessment compared the sliding distance of the lag screw between postoperative X-ray and last follow-up X-ray.
RESULTS
Forty-two cases were in group 1, 22 cases were in group 2, and the other 22 cases were in group 3. There was no significant difference in the patient characteristics of each group. The sliding distances of the lag screw were 4.9±3.2 mm, 4.6±3.6 mm, and 8.5±4.9 mm, respectively, and group 3 showed a significant result (p<0.0001, p=0.024).
CONCLUSION
In cases treated with intramedullary fixation using a cephalomedullary nail with a fixed neck-shaft angle, appropriate reduction with a lateral radiograph before screw fixation is needed to prevent excessive lag screw sliding.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chung YK, Hwang JH, Kim HK. The treatment of peritrochanteric fracture of femur with proximal femoral nail: comparative study with dynamic hip screw. J Korean Hip Soc. 2007; 19:167–175.
Article2. Bridle SH, Patel AD, Bircher M, Calvert PT. Fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. A randomised prospective comparison of the gamma nail and the dynamdynamic hip screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991; 73:330–334.3. Chang WS, Zuckerman JD, Kummer FJ, Frankel VH. Biomechanical evaluation of anatomic reduction versus medial displacement osteotomy in unstable intertrochanteric fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; (225):141–146.
Article4. Haidukewych GJ, Israel TA, Berry DJ. Reverse obliquity fractures of the intertrochanteric region of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001; 83:643–650.
Article5. Chang SM, Zhang YQ, Ma Z, Li Q, Dargel J, Eysel P. Fracture reduction with positive medial cortical support: a key element in stability reconstruction for the unstable pertrochanteric hip fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015; 135:811–818.
Article6. Chevalley F, Gamba D. Gamma nailing of pertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures: clinical results of a series of 63 consecutive cases. J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11:412–415.
Article7. Hardy DC, Descamps PY, Krallis P, et al. Use of an intramedullary hip-screw compared with a compression hip-screw with a plate for intertrochanteric femoral fractures A prospective, randomized study of one hundred patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80:618–630.
Article8. Harrington P, Nihal A, Singhania AK, Howell FR. Intramedullary hip screw versus sliding hip screw for unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures in the elderly. Injury. 2002; 33:23–28.
Article9. Kwun KW, Kim SK, Lee SW, Youn KH. Treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur: Comparison of the gamma nail and the dynamic hip screw. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1993; 28:1666–1673.
Article10. Park MS, Kim GN. Intertrochanteric fractures of the femur treated with sliding hip compression screw and gamma nail: mechanical failure after internal fixation. J Korean Hip Soc. 2000; 12:102–111.11. Radford PJ, Needoff M, Webb JK. A prospective randomised comparison of the dynamic hip screw and the gamma locking nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1993; 75:789–793.
Article12. Fracture and dislocation compendium. Orthopaedic trauma association committee for coding and classification. J Orthop Trauma. 1996; 10:Suppl 1. v–ix. 1–154.13. Tsukada S, Okumura G, Matsueda M. Postoperative stability on lateral radiographs in the surgical treatment of pertrochanteric hip fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012; 132:839–846.
Article14. Evans EM. Trochanteric fractures: a review of 110 cases treated by nail-plate fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1951; 33:192–204.15. Evans EM. Trochanteric fractures: a review of 110 cases treated by nail-plate fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1951; 33:192–204.16. Clawson DK. Trochanteric fractures treated by the sliding screw plate fixation method. J Trauma. 1964; 4:737–752.
Article17. Kyle RF, Gustilo RB, Premer RF. Analysis of six hundred and twenty-two intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979; 61:216–221.
Article18. Davis TR, Sher JL, Horsman A, Simpson M, Porter BB, Checketts RG. Intertrochanteric femoral fractures Mechanical failure after internal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990; 72:26–31.
Article19. Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM, Keggi JM. The value of the tip-apex distance in predicting failure of fixation of peritrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:1058–1064.
Article20. Ebbinghaus S, Mjöberg B. Posterior angulation in trochanteric fractures detected with roentgen stereophotogrammetry. Ups J Med Sci. 1991; 96:235–237.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment using Reduction of Lateral and Posterior Displacement in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of the Elderly
- The Effects of Bone Graft in the Treatment of Osteoporotic Unstable Intertrochanteric Fracture of the Femur
- Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture with the AO/ASIF Proximal Femoral Nail (PFN)
- The Biomechanical Study on the Stability of the Knowles Pinning in the Intertrochanteric Fracture of the Femur
- Effect of Unreduced Lesser Trochanteric Fracture on Stability in Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur