Nutr Res Pract.
2016 Jun;10(3):352-358. 10.4162/nrp.2016.10.3.352.
Health Blief Model-based intervention to improve nutritional behavior among elderly women
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Public Health, Health and Paramedical Faculty, 5714783734, Nazlou Campus, Urmia, Iran. Jamileh.Amirzadeh@gmail.com
- 2Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, Uneversiti Putra Malaysia (UPM), 43400, Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia.
- 3Faculty of Nursing and Midwifery, Ilam University of Medical Sciences, Pazhuhesh Blvd., Ilam, Iran.
- KMID: 2342139
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2016.10.3.352
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
Nutrition is a determinant factor of health in elderly people. Independent living in elderly people can be maintained or enhanced by improvement of nutritional behavior. Hence, the present study was conducted to determine the impact of Health Belief Model (HBM)-based intervention on the nutritional behavior of elderly women.
SUBJECTS/METHODS
Cluster-random sampling was used to assess the sample of this clinical trial study. The participants of this study attended a 12-week nutrition education program consisting of two (2) sessions per week. There was also a follow-up for another three (3) months. Smart PLS 3.5 and SPSS 19 were used for structural equation modeling, determination of model fitness, and hypotheses testing.
RESULTS
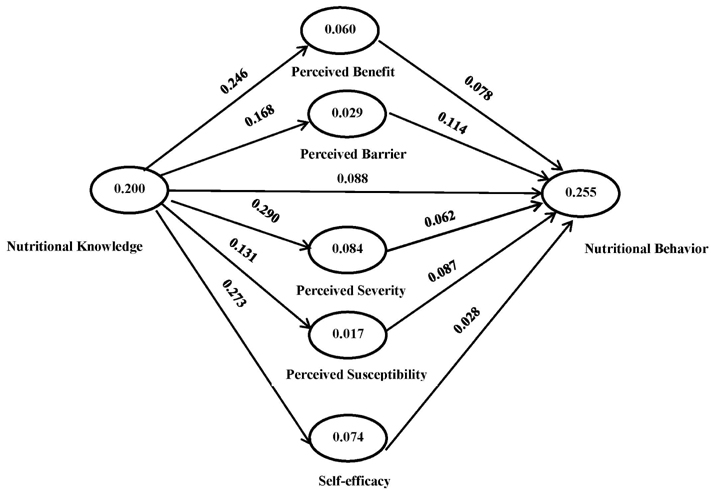
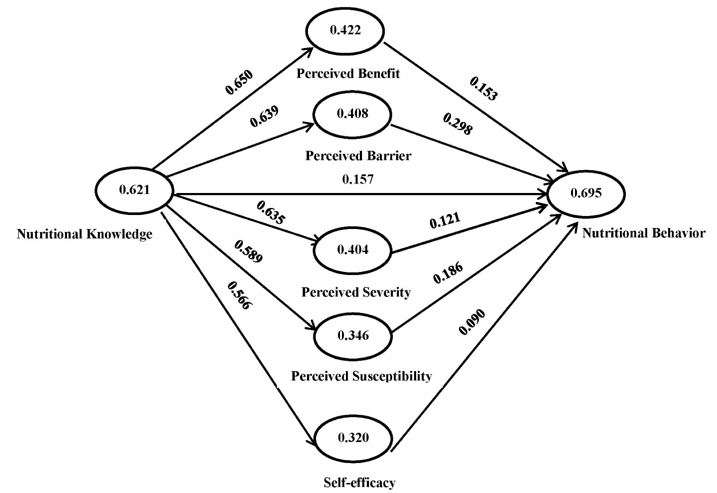
The findings indicate that intervention had a significant effect on knowledge improvement as well as the behavior of elderly women. The model explained 5 to 70% of the variance in nutritional behavior. In addition, nutritional behavior was positively affected by the HBM constructs comprised of perceived susceptibility, self-efficacy, perceived benefits, and barriers after the intervention program.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study show that HBM-based educational intervention has a significant effect in improving nutritional knowledge and behavior among elderly women.
Figure
Reference
-
1. McCutcheon M, Pruchno R. Introducing the international spotlight. Gerontologist. 2011; 51:423–424.
Article2. Forsyth DR, Chia YC. How should Malaysia respond to its ageing society? Med J Malaysia. 2009; 64:46–50.3. Thanakwang K, Ingersoll-Dayton B, Soonthorndhada K. The relationships among family, friends, and psychological well-being for Thai elderly. Aging Ment Health. 2012; 16:993–1003.
Article4. Haron SA, Sharpe DL, Masud J, Abdel-Ghany M. Health divide: economic and demographic factors associated with self-reported health among older Malaysians. J Fam Econ Issues. 2010; 31:328–337.
Article5. Duque S, Freitas P, Silvestre J, Fernandes L, Pinto M, Sousa A, Batalha V, Campos L. Prognostic factors of elderly patients admitted in a medical intermediate care unit. Eur Geriatr Med. 2011; 2:327–331.
Article6. Goetzel RZ, Shechter D, Ozminkowski RJ, Stapleton DC, Lapin PJ, McGinnis JM, Gordon CR, Breslow L. Can health promotion programs save medicare money? Clin Interv Aging. 2007; 2:117–122.
Article7. Oliveira MR, Fogaça KC, Leandro-Merhi VA. Nutritional status and functional capacity of hospitalized elderly. Nutr J. 2009; 8:54.
Article8. Knoops KT, de Groot LC, Kromhout D, Perrin AE, Moreiras-Varela O, Menotti A, van Staveren WA. Mediterranean diet, lifestyle factors, and 10-year mortality in elderly European men and women: the HALE project. JAMA. 2004; 292:1433–1439.
Article9. Sahyoun NR, Pratt CA, Anderson A. Evaluation of nutrition education interventions for older adults: a proposed framework. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004; 104:58–69.
Article10. Baranowski T, Cullen KW, Nicklas T, Thompson D, Baranowski J. Are current health behavioral change models helpful in guiding prevention of weight gain efforts? Obes Res. 2003; 11:23S–43S.
Article11. Becker MH, Maiman LA, Kirscht JP, Haefner DP, Drachman RH. The Health Belief Model and prediction of dietary compliance: a field experiment. J Health Soc Behav. 1977; 18:348–366.
Article12. Ceber E, Turk M, Ciceklioglu M. The effects of an educational program on knowledge of breast cancer, early detection practices and health beliefs of nurses and midwives. J Clin Nurs. 2010; 19:2363–2371.
Article13. Dobe M. Health promotion for prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases: unfinished agenda. Indian J Public Health. 2012; 56:180–186.
Article14. Moore Q, Johnson A. Best Practices for Using Health Education to Change Behavior. Houston (TX): The James A. Baker III Institute for Public Policy of Rice Universit;2015.15. Baghianimoghadam MH, Shogafard G, Sanati HR, Baghianimoghadam B, Mazloomy SS, Askarshahi M. Application of the health belief model in promotion of self-care in heart failure patients. Acta Med Iran. 2013; 51:52–58.16. Orji R, Vassileva J, Mandryk R. Towards an effective health interventions design: an extension of the health belief model. Online J Public Health Inform. 2012; 4:pii: ojphi.v4i3.4321.
Article17. Saeidlou SN, Merdol TK, Mikaili P, Bektaş Y. Assessment of the nutritional status of elderly people living at nursing homes in Northwest Iran. Int J Acad Res. 2011; 3:463–472.18. Wojszel ZB. Determinants of nutritional status of older people in long-term care settings on the example of the nursing home in Białystok. Adv Med Sci. 2006; 51:168–173.19. Saletti A, Lindgren EY, Johansson L, Cederholm T. Nutritional status according to mini nutritional assessment in an institutionalized elderly population in Sweden. Gerontology. 2000; 46:139–145.
Article20. Henseler J, Sarstedt M. Goodness-of-fit indices for partial least squares path modeling. Comput Stat. 2013; 28:565–580.
Article21. Wong KK. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) techniques using SmartPLS. Mark Bull. 2013; 24:1–32.22. Hulland J. Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: a review of four recent studies. Strateg Manage J. 1999; 20:195–204.
Article23. Champion VL, Skinner CS. The health belief model. In : Glanz K, Rimer BK, Viswanath K, editors. Health Behavior and Health Education: Theory, Research, and Practice. 4th ed. San Francisco (CA): Jossey-Bass;2008. p. 45–65.24. Rousset S, Droit-Volet S, Boirie Y. Change in protein intake in elderly French people living at home after a nutritional information program targeting protein consumption. J Am Diet Assoc. 2006; 106:253–261.
Article25. Young K, Bunn F, Trivedi D, Dickinson A. Nutritional education for community dwelling older people: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Int J Nurs Stud. 2011; 48:751–780.
Article26. Kim HS, June KJ, Song R. Effects of nutrition education and exercise programs on perceived dietary behaviors, food intake and serum lipid profiles in elderly Korean women living in residential homes. Asian Nurs Res (Korean Soc Nurs Sci). 2007; 1:35–47.
Article27. Torshizi L, Anoosheh M, Ghofranipour F, Ahmadi F, Houshyar-rad A. The effect of education based on Health Belief Model on preventive factors of osteoporosis among postmenopausal women. Iran J Nurs. 2009; 22:71–82.28. Bayat F, Shojaeezadeh D, Baikpour M, Heshmat R, Baikpour M, Hosseini M. The effects of education based on extended health belief model in type 2 diabetic patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2013; 12:45.
Article29. Sharifirad G, Entezari MH, Kamran A, Azadbakht L. The effectiveness of nutritional education on the knowledge of diabetic patients using the Health Belief Model. J Res Med Sci. 2009; 14:1–6.30. Khabazian A, Rezaei N. The effect of education on the nutritional knowledge, attitude and practice in diabetic patients. Tolue Behdasht. 2003; 2:57.31. Aghamolayee T, Eftekhar H, Mohammad K. The application of Health Belief Model in changing the behavior in diabetic patients. Payesh. 2005; 4:263–269.32. Swaim RA, Barner JC, Brown CM. The relationship of calcium intake and exercise to osteoporosis health beliefs in postmenopausal women. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2008; 4:153–163.
Article33. Rejeski WJ, Brubaker PH, Goff DC Jr, Bearon LB, McClelland JW, Perri MG, Ambrosius WT. Translating weight loss and physical activity programs into the community to preserve mobility in older, obese adults in poor cardiovascular health. Arch Intern Med. 2011; 171:880–886.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erratum: Health Blief Model-based intervention to improve nutritional behavior among elderly women
- A Study on Health Concern, Self-rated Health, Health Status, and Health Promotion Behavior of Elderly Women in Urban Area
- Validation of a Path Model on Elderly Women's Yangsaeng (Yangsaeng; traditional oriental health promotion)
- Development and Effect of a Behavior Program for Reducing Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Unmarried Women
- Evaluation of the nutrient quotient for the elderly (NQ-E) using congregate meal services according to their oral health conditions