J Korean Med Assoc.
2011 Jan;54(1):12-21.
Breast reconstruction using pedicled transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous (TRAM) flap
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jinsupp@amc.seoul.kr
Abstract
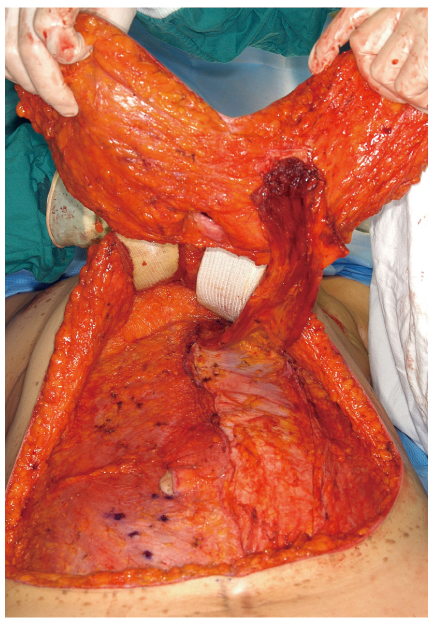
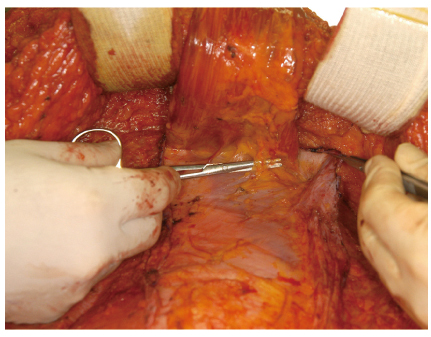
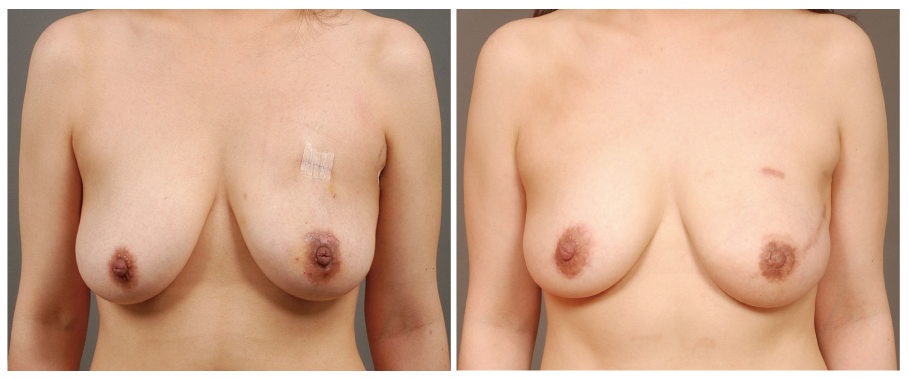
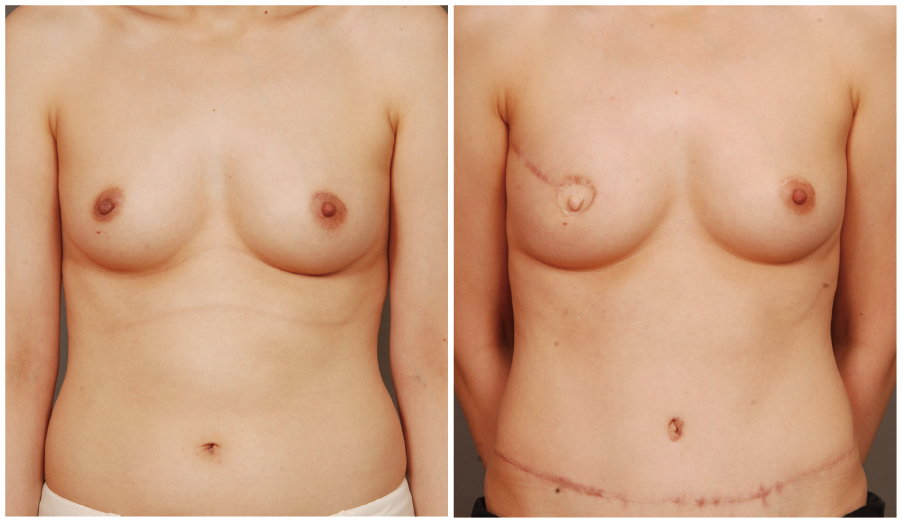
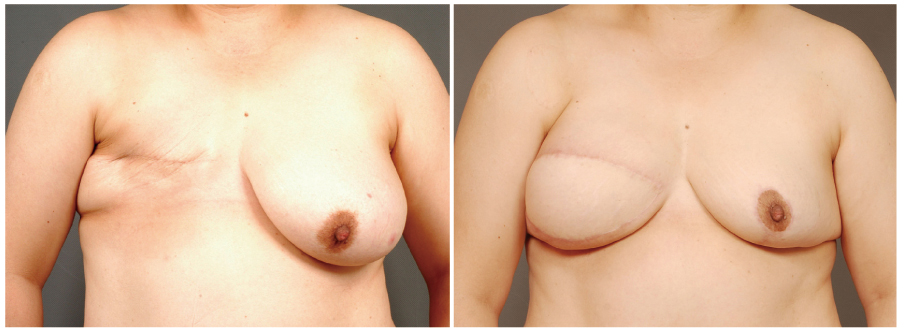
- The demand for the breast reconstruction continues to grow following the acute increase in the incidence of breast cancer in Korea. The pedicled transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous (TRAM) flap is one of the most commonly used methods among the autologous breast reconstruction options. A pedicled TRAM flap consists of the lower abdominal skin, subcutaneous fat tissue, and one of the rectus abdominis muscles. The blood flow to the flap is supplied through the muscle perforators, which should be strictly selected and preserved. This flap can provide sufficient healthy tissue, which can create the most ideal breast shape. Although the free flap has largely replaced the pedicled TRAM flap, the latter has also evolved with increased understanding of anatomy and physiology. Furthermore, if refined techniques are applied, complications can be minimized and comparable outcomes can be achieved. Besides all the advantages of autologous tissue breast reconstruction, the most distinct feature of the pedicled TRAM flap over the free flap is simplicity of flap elevation and elimination of the microsurgical crisis. The pedicled TRAM flap is still a competitive procedure, yielding consistent results with acceptable complication rates for most patients and should be considered as a primary option for breast reconstruction.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahn SH. Korean Breast Cancer Society. Clinical characteristics of breast cancer patients in Korea in 2000. Arch Surg. 2004. 139:27–30.
Article2. Hartrampf CR, Scheflan M, Black PW. Breast reconstruction with a transverse abdominal island flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1982. 69:216–225.
Article3. Shestak KC. Breast reconstruction with a pedicled TRAM flap. Clin Plast Surg. 1998. 25:167–182.
Article4. Jones G. The pedicled TRAM flap in breast reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg. 2007. 34:83–104.
Article5. Kim EK, Eom JS, Ahn SH, Son BH, Lee TJ. Evolution of the pedicled TRAM flap: a prospective study of 500 consecutive cases by a single surgeon in Asian patients. Ann Plast Surg. 2009. 63:378–382.6. Boyd JB, Taylor GI, Corlett R. The vascular territories of the superior epigastric and the deep inferior epigastric systems. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984. 73:1–16.
Article7. Taylor GI, Caddy CM, Watterson PA, Crock JG. The venous territories (venosomes) of the human body: experimental study and clinical implications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1990. 86:185–213.8. Dinner MI, Dowden RV, Scheflan M. Refinements in the use of the transverse abdominal island flap for postmastectomy reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 1983. 11:362–372.
Article9. Spear SL, Ganz JC. Mathes SJ, Hentz VR, editors. Immediate post-mastectomy reconstruction: TRAM flap transposition techniques. Plastic surgery. 2006. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;835–847.10. Ducic I, Spear SL, Cuoco F, Hannan C. Safety and risk factors for breast reconstruction with pedicled transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flaps: a 10-year analysis. Ann Plast Surg. 2005. 55:559–564.
Article11. Kroll SS, Netscher DT. Complications of TRAM flap breast reconstruction in obese patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1989. 84:886–892.
Article12. Spear SL, Ducic I, Cuoco F, Taylor N. Effect of obesity on flap and donor-site complications in pedicled TRAM flap breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007. 119:788–795.
Article13. Clugston PA, Gingrass MK, Azurin D, Fisher J, Maxwell GP. Ipsilateral pedicled TRAM flaps: the safer alternative? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000. 105:77–82.
Article14. Suh HS, Eom JS, Lee TJ. Anatomical location of the tendinous intersections of the rectus abdominis muscle in Korean women. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006. 33:469–473.15. Nahabedian MY, Dooley W, Singh N, Manson PN. Contour abnormalities of the abdomen after breast reconstruction with abdominal flaps: the role of muscle preservation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002. 109:91–101.
Article16. Drever JM, Hodson-Walker N. Closure of the donor defect for breast reconstruction with rectus abdominis myocutaneous flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985. 76:558–565.
Article17. Kroll SS, Marchi M. Comparison of strategies for preventing abdominal-wall weakness after TRAM flap breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992. 89:1045–1051.
Article18. Zienowicz RJ, May JW Jr. Hernia prevention and aesthetic contouring of the abdomen following TRAM flap breast reconstruction by the use of polypropylene mesh. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995. 96:1346–1350.
Article19. Pennington DG, Lam T. Gore-Tex patch repair of the anterior rectus sheath in free rectus abdominis muscle and myocutaneous flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1996. 97:1436–1440.
Article20. Moscona RA, Ramon Y, Toledano H, Barzilay G. Use of synthetic mesh for the entire abdominal wall after TRAM flap transfer. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998. 101:706–710.
Article21. Schusterman MA, Kroll SS, Weldon ME. Immediate breast reconstruction: why the free TRAM over the conventional TRAM flap? Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992. 90:255–261.
Article22. Kroll SS, Gherardini G, Martin JE, Reece GP, Miller MJ, Evans GR, Robb GL, Wang BG. Fat necrosis in free and pedicled TRAM flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998. 102:1502–1507.
Article23. Grotting JC, Urist MM, Maddox WA, Vasconez LO. Conventional TRAM flap versus free microsurgical TRAM flap for immediate breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1989. 83:828–841.
Article24. Kim EK, Lee TJ, Eom JS. Comparison of fat necrosis between zone II and zone III in pedicled transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flaps: a prospective study of 400 consecutive cases. Ann Plast Surg. 2007. 59:256–259.
Article25. Jewell RP, Whitney TM. TRAM fat necrosis in a young surgeon's practice: is it experience, technique, or blood flow? Ann Plast Surg. 1999. 42:424–427.
Article26. Mizgala CL, Hartrampf CR Jr, Bennett GK. Assessment of the abdominal wall after pedicled TRAM flap surgery: 5- to 7-year follow-up of 150 consecutive patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994. 93:988–1002.27. Kroll SS, Schusterman MA, Reece GP, Miller MJ, Robb G, Evans G. Abdominal wall strength, bulging, and hernia after TRAM flap breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995. 96:616–619.
Article28. Suominen S, Asko-Seljavaara S, von Smitten K, Ahovuo J, Sainio P, Alaranta H. Sequelae in the abdominal wall after pedicled or free TRAM flap surgery. Ann Plast Surg. 1996. 36:629–636.
Article29. Kang BS, Eom JS, Lee TJ. Evaluation of abdominal wall function after TRAM breast reconstruction: a prospective study in 375 consecutive cases. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007. 34:435–439.30. Eom JS, Hwang CH, Kim EK, Kim TG, Lee TJ. Secondary contouring of reconstructed breast with fat graft. J Korean Soc Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2009. 15:139–143.31. Slezak S, McGibbon B, Dellon AL. The sensational transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous (TRAM) flap: return of sensibility after TRAM breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 1992. 28:210–217.
Article32. Place MJ, Song T, Hardesty RA, Hendricks DL. Sensory reinnervation of autologous tissue TRAM flaps after breast reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg. 1997. 38:19–22.
Article33. Lee SH, Lee TJ, Eom JS, Son BH, Ahn SH, Lee SD. Incidence and risk factors of pulmonary thromboembolism in pedicled TRAM breast reconstruction. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006. 33:193–197.34. Chung MS, Yoon HS, Son BH, Lee JS, Kim HJ, Park EH, Ahn SH, Lee TJ, Eom JS, Choi HS, Kwak BS. The efficacy of enoxaparin for the prevention of a pulmonary thromboembolism in a skin-sparing mastectomy with immediate recons-truction in breast cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2008. 11:125–132.
Article35. Kim EK, Eom JS, Ahn SH, Son BH, Lee TJ. The efficacy of prophylactic low-molecular-weight heparin to prevent pulmonary thromboembolism in immediate breast reconstruction using the TRAM flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009. 123:9–12.
Article36. Lee TJ, Kirk I, Yoon SY, Chang H. Simultaneous TRAM flap breast reconstruction with contralateral reduction mammoplasty. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. 31:303–308.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Breast reconstruction using the transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous (TRAM) free flap
- Breast Reconstruction Using the Pedicled Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous (Tram) Flap
- Absence of Linea Alba in Breast Reconstruction with Pedicled TRAM Flap: A Case Report
- Various Abdominal Flaps for Breast Reconstruction: Pedicled TRAM, Free TRAM, Muscle-sparing TRAM, DIEP, and SIEA Flaps
- Delivery technique for the pedicled transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap