J Korean Med Assoc.
2008 Jan;51(1):27-37.
Radiosurgery for Intracranial Disorders
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Dongguk University International Hospital, Korea. soundofmusic@duih.org
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Korea. gknife@plaza.snu.ac.kr, htchung@korea.com
Abstract
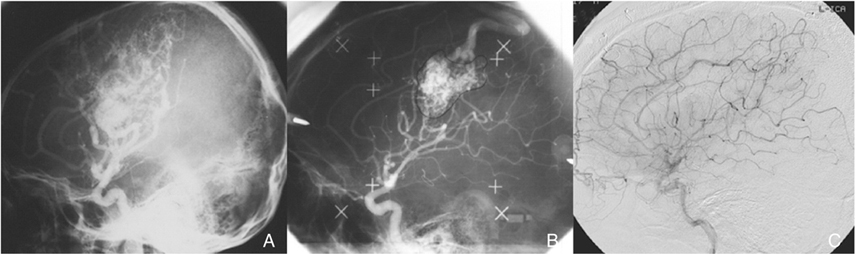
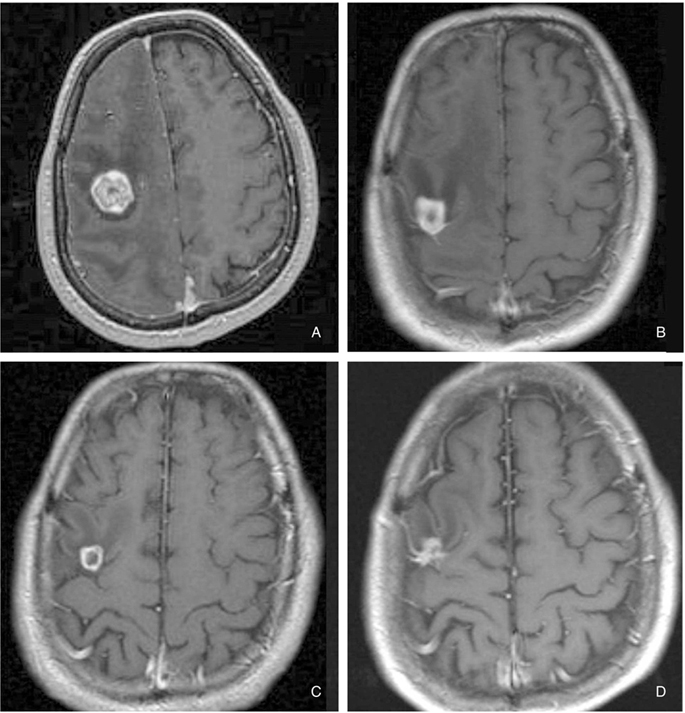
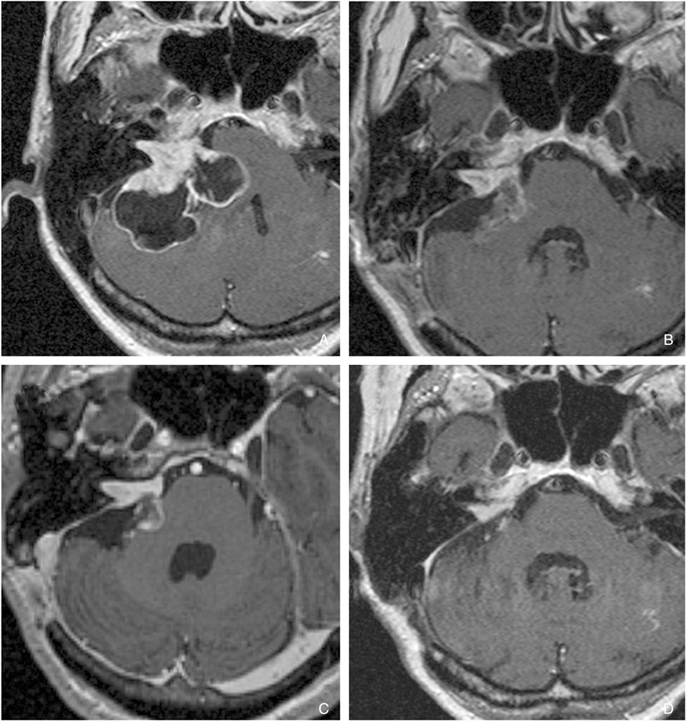
- Stereotactic radiosurgery offers a broad spectrum armamentarium for the safe treatment of various lesions within the central nervous system. Radiosurgery uses stereotactic targeting methods to precisely deliver highly focused, large doses of radiation to small intracranial tumors and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). It is widely used for the treatment of metastatic brain tumors, non-resectable tumors, residual or recurrent benign and malignant tumors as well as for the treatment of AVMs, functional diseases, and pain disorders. Although radiosurgery has the potential to produce complications, the majority of patients experience clinical improvement with less morbidity and mortality than those occur in surgical resection.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hassan ZU, Fahy BG. Anesthetic choices in surgery. Surg Clin North Am. 2005. 85:1075–1089.
Article2. Steiner L, Leksell L, Forster DM, Greitz T, Backlund EO. Stereotactic radiosurgery in intracranial arterio-venous malformations. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1974. 21:S. 195–209.
Article3. Marhofer P, Chan VW. Ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia: current concepts and future trends. Anesth Analg. 2007. 104:1265–1269.
Article4. Szeifert GT, Timperley WR, Forster DM, Kemeny AA. Histopathological changes in cerebral arteriovenous malformations following Gamma Knife radiosurgery. Progress in neurological surgery. 2007. 20:212–219.
Article5. Szeifert GT, Major O, Fazekas I, Nagy Z. Effects of radiation on cerebral vasculature: a review. Neurosurgery. 2001. 48:452–453.
Article6. Maruyama K, Kawahara N, Shin M, Tago M, Kishimoto J, Kurita H, Kawamoto S, Morita A, Kirino T. The risk of hemorrhage after radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. N Engl J Med. 2005. 352:146–153.
Article7. Kemeny AA, Radatz MW, Rowe JG, Walton L, Vaughan P. Gamma Knife treatment for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Progress in neurological surgery. 2007. 20:206–211.
Article8. Karlsson B, Jokura H, Yamamoto M, Soderman M, Lax I. Is repeated radiosurgery an alternative to staged radiosurgery for very large brain arteriovenous malformations? J Neurosurg. 2007. 107:740–744.
Article9. Yang SY, Kim DG, Chung HT, Paek SH, Park JH, Han DH. Radiosurgery for Large Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Acta Neurochir. 2007. (in press).
Article10. Lindquist C. Gamma knife surgery for recurrent solitary metastasis of a cerebral hypernephroma: case report. Neurosurgery. 1989. 25:802–804.
Article11. McDermott MW, Sneed PK. Radiosurgery in metastatic brain cancer. Neurosurgery. 2005. 57:S. S45–S53. discusssion S1-4.
Article12. Kocher M, Maarouf M, Bendel M, Voges J, Muller RP, Sturm V. Linac radiosurgery versus whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases. A survival comparison based on the RTOG recursive partitioning analysis. Strahlenther Onkol. 2004. 180:263–267.
Article13. Kaal EC, Niel CG, Vecht CJ. Therapeutic management of brain metastasis. Lancet neurology. 2005. 4:289–298.
Article14. Yamamoto M. Radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumors. Progress in neurological surgery. 2007. 20:106–128.
Article15. Billing PS, Miller DL, Allen MS, Deschamps C, Trastek VF, Pairolero PC. Surgical treatment of primary lung cancer with synchronous brain metastases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2001. 122:548–553.
Article16. Daniels M, Wright GM. Complete resection of non-small-cell lung cancer and oligo-metastatic brain disease. ANZ J Surg. 2005. 75:963–966.
Article17. Yang SY, Kim DG, Lee SH, Chung HT, Paek SH, Kim JH, Jung HW, Han DH. Pulmonary resection in patients with nonsmall-cell lung cancer treated with gamma knife radiosurgery for synchronous brain metastases. Cancer. 2007. (in press).18. Deen HG, Ebersold MJ, Harner SG, Beatty CW, Marion MS, Wharen RE, Green JD, Quast L. Conservative management of acoustic neuroma: an outcome study. Neurosurgery. 1996. 39:260–264. discussion 4-6.
Article19. Strasnick B, Glasscock ME 3rd, Haynes D, McMenomey SO, Minor LB. The natural history of untreated acoustic neuromas. Laryngoscope. 1994. 104:1115–1119.
Article20. Wiet RJ, Zappia JJ, Hecht CS, O'Connor CA. Conservative management of patients with small acoustic tumors. Laryngoscope. 1995. 105(8 Pt 1):795–800.
Article21. Rosenberg SI. Natural history of acoustic neuromas. Laryngoscope. 2000. 110:497–508.22. Mendenhall WM, Friedman WA, Amdur RJ, Antonelli PJ. Management of acoustic schwannoma. Am J Otolaryngol. 2004. 25:38–47.
Article23. Rutherford SA, King AT. Vestibular schwannoma management: What is the best option? Br J Neurosurg. 2005. 19:309–316.
Article24. Paek SH, Chung HT, Jeong SS, Park CK, Kim CY, Kim JE, Kim DG, Jung HW. Hearing preservation after gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery of vestibular schwannoma. Cancer. 2005. 104:580–590.
Article25. Lunsford LD, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Maitz A, Kondziolka D. Radiosurgery of vestibular schwannomas: summary of experience in 829 cases. J Neurosurg. 2005. 102:S. 195–199.
Article26. Hasegawa T, Kida Y, Kobayashi T, Yoshimoto M, Mori Y, Yoshida J. Long-term outcomes in patients with vestibular schwannomas treated using gamma knife surgery: 10-year follow up. J Neurosurg. 2005. 102:10–16.
Article27. Rowe JG, Radatz MW, Walton L, Hampshire A, Seaman S, Kemeny AA. Gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery for unilateral acoustic neuromas. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003. 74:1536–1542.
Article28. Foote KD, Friedman WA, Buatti JM, Meeks SL, Bova FJ, Kubilis PS. Analysis of risk factors associated with radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. Journal of neurosurgery. 2001. 95:440–449.
Article29. Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Lunsford LD. Results of acoustic neuroma radiosurgery: an analysis of 5 years' experience using current methods. Journal of neurosurgery. 2001. 94:1–6.
Article30. Prasad D, Steiner M, Steiner L. Gamma surgery for vestibular schwannoma. Journal of neurosurgery. 2000. 92:745–759.
Article31. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, McLaughlin MR, Flickinger JC. Long-term outcomes after radiosurgery for acoustic neuromas. The New England journal of medicine. 1998. 339:1426–1433.
Article32. Park CK, Jung HW, Kim JE, Son YJ, Paek SH, Kim DG. Therapeutic strategy for large vestibular schwannomas. J Neurooncol. 2006. 77:167–171.
Article33. Iwai Y, Yamanaka K, Ishiguro T. Surgery combined with radiosurgery of large acoustic neuromas. Surg Neurol. 2003. 59:283–289. discussion 9-91.
Article34. Yang SY, Kim DG, Chung HT, Park SH, Paek SH, Jung HW. Evaluation of tumor response after gamma knife radiosurgery for residual vestibular schwannomas based on MRI morphological features. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007. 2007 Aug 2 [Epub ahead of print].35. Lee JY, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD. Radiosurgery for intracranial meningiomas. Prog Neurol Surg. 2007. 20:142–149.
Article36. Kondziolka D, Levy EI, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD. Long-term outcomes after meningioma radiosurgery: physician and patient perspectives. J Neurosurg. 1999. 91:44–50.
Article37. Hakim R, Alexander E 3rd, Loeffler JS, Shrieve DC, Wen P, Fallon MP, Stieg PE, Black PM. Results of linear accelerator-based radiosurgery for intracranial meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 1998. 42:446–453. discussion 53-54.38. Simpson D. The recurrence of intracranial meningiomas after surgical treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957. 20:22–39.
Article39. Sen C, Hague K. Meningiomas involving the cavernous sinus: histological factors affecting the degree of resection. J Neurosurg. 1997. 87:535–543.
Article40. DeMonte F, Smith HK, al-Mefty O. Outcome of aggressive removal of cavernous sinus meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 1994. 81:245–251.
Article41. Lee JY, Niranjan A, McInerney J, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD. Stereotactic radiosurgery providing long-term tumor control of cavernous sinus meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 2002. 97:65–72.
Article42. Maruyama K, Shin M, Kurita H, Kawahara N, Morita A, Kirino T. Proposed treatment strategy for cavernous sinus meningiomas: a prospective study. Neurosurgery. 2004. 55:1068–1075.
Article43. Park CK, Jung HW, Kim JE, Paek SH, Kim DG. The selection of the optimal therapeutic strategy for petroclival meningiomas. Surg Neurol. 2006. 66:160–165. discussion 5-6.
Article44. Taha JM, Tew JM Jr. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia by percutaneous radiofrequency rhizotomy. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1997. 8:31–39.
Article45. Fields HL. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. New Engl J Med. 1996. 334:1125–1126.
Article46. Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC, Young RF, Vermeulen S, Duma CM, Jacques DB, Rand RW, Regis J, Peragut JC, Manera L, Epstein MH, Lindquist C. Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: a multiinstitutional study using the gamma unit. J Neurosurg. 1996. 84:940–945.
Article47. Young RF, Vermulen S, Posewitz A. Gamma knife radiosurgery for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1998. 70:S. 192–199.
Article48. Rogers CL, Shetter AG, Fiedler JA, Smith KA, Han PP, Speiser BL. Gamma knife radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia: the initial experience of The Barrow Neurological Institute. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000. 47:1013–1019.
Article49. Nicol B, Regine WF, Courtney C, Meigooni A, Sanders M, Young B. Gamma knife radiosurgery using 90 Gy for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2000. 93:S. 152–154.
Article50. Pollock BE, Phuong LK, Foote RL, Stafford SL, Gorman DA. High-dose trigeminal neuralgia radiosurgery associated with increased risk of trigeminal nerve dysfunction. Neurosurgery. 2001. 49:58–62. discussion-4.
Article51. Maesawa S, Salame C, Flickinger JC, Pirris S, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD. Clinical outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery for idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 2001. 94:14–20.
Article52. Petit JH, Herman JM, Nagda S, DiBiase SJ, Chin LS. Radiosurgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: evaluating quality of life and treatment outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. 56:1147–1153.
Article53. Gorgulho AA, De Salles AA. Impact of radiosurgery on the surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Surg Neurol. 2006. 66:350–356.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Introduction to Radiosurgery
- Imaging for therapeutic effect of intracranial arteriovenous malformations with stereotactic radiosurgery: a preliminary report
- Complications after Radiosurgery of the Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation
- Preliminary Report of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for the Movement Disorders
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases